Electrostatic Test 4) What is the force of repulsion between two
... makes a 20 degree angle with the left side of the vertical. The electric field has a strength of 700 N/C and is directed to the right. The mass of the ball is 6.1 g. What are the magnitude and sign of the charge on the ball? 8) An electron is projected out along the +x axis with an initial speed of ...
... makes a 20 degree angle with the left side of the vertical. The electric field has a strength of 700 N/C and is directed to the right. The mass of the ball is 6.1 g. What are the magnitude and sign of the charge on the ball? 8) An electron is projected out along the +x axis with an initial speed of ...
Deriving the Fresnel Equations 5.2.2 Fresnel Equations
... First we write down the continuity of the tangential or here parallel component of E (and always same thing for H in principle). Since E has only components in y-directions we have for those components E in + Eref = Etr While this looks a bit like the energy or intensity conservation equation from b ...
... First we write down the continuity of the tangential or here parallel component of E (and always same thing for H in principle). Since E has only components in y-directions we have for those components E in + Eref = Etr While this looks a bit like the energy or intensity conservation equation from b ...
Homework#1, Problem 1 - Louisiana State University
... At each point on the surface of the cube shown in Fig. 24-26, the electric field is in the z direction. The length of each edge of the cube is 2.3 m. On the top surface of the cube E = -38 k N/C, and on the bottom face of the cube E = +11 k N/C. Determine the net charge contained within the cube. [- ...
... At each point on the surface of the cube shown in Fig. 24-26, the electric field is in the z direction. The length of each edge of the cube is 2.3 m. On the top surface of the cube E = -38 k N/C, and on the bottom face of the cube E = +11 k N/C. Determine the net charge contained within the cube. [- ...
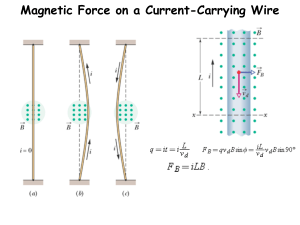
Physics 2145 Spring 2016 Test 3 (4 pages)
... ___1.(5)___ Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The net force on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field is zero. B) The magnetic field of a solenoid is constant inside the solenoid. C) The net force on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field depends on the angle between the loop ax ...
... ___1.(5)___ Which of the following statements is FALSE? A) The net force on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field is zero. B) The magnetic field of a solenoid is constant inside the solenoid. C) The net force on a current loop in a uniform magnetic field depends on the angle between the loop ax ...