4. Electric Fields in Matter
... On may calculate D in the same way as E in the vacuum if the different boundary conditions for E and D do not play role. In this case, one simply replaces o This is the case if: a) When the space is filled with a homogenous dielectric. b) When the symmetry of the problem makes ...
... On may calculate D in the same way as E in the vacuum if the different boundary conditions for E and D do not play role. In this case, one simply replaces o This is the case if: a) When the space is filled with a homogenous dielectric. b) When the symmetry of the problem makes ...
Electric Fields
... FE = electrostatic force, Newtons (N) k = electric or Coulomb’s constant = 9 x 109 Nm2/C2 q1 = charge of the first object, C q2 = charge of the second object, C d = distance between the two charges (center to center), m ...
... FE = electrostatic force, Newtons (N) k = electric or Coulomb’s constant = 9 x 109 Nm2/C2 q1 = charge of the first object, C q2 = charge of the second object, C d = distance between the two charges (center to center), m ...
Word
... field is perpendicular to the current that produced it. It turns out that not only do currents produce a magnetic field, but a changing magnetic field produces a current. This effect is called electromagnetic induction, because the changing magnetic field induces an electric field which can cause a ...
... field is perpendicular to the current that produced it. It turns out that not only do currents produce a magnetic field, but a changing magnetic field produces a current. This effect is called electromagnetic induction, because the changing magnetic field induces an electric field which can cause a ...
... You may use your one sheet of notes and formulas, but you must not collaborate with any other person. Do all four problems, showing your method and working clearly (a correct answer alone is not necessarily sufficient). Be sure to include correct SI units in your answers where appropriate. The numbe ...
the electric field - IHS Physics Mr. Arnold
... Electric field diagrams show a sample of the vectors, but there is an electric field vector at every point whether one is shown or not. The arrow indicates the direction and strength of the field at the point to which it is attached – at the point where the tail of the vector is placed. The length o ...
... Electric field diagrams show a sample of the vectors, but there is an electric field vector at every point whether one is shown or not. The arrow indicates the direction and strength of the field at the point to which it is attached – at the point where the tail of the vector is placed. The length o ...
Chapter 19 Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... the opposition to the movement of charges flowing through a material Resistance of the material depends on its atomic structure ( close together vs. spread out) ...
... the opposition to the movement of charges flowing through a material Resistance of the material depends on its atomic structure ( close together vs. spread out) ...
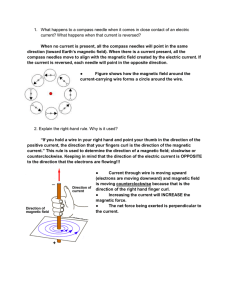
When no current is present, all the compass
... 3. Why is a solenoid used to create a stronger magnetic field? What does it resemble? To increase the magnetic force from the presence of a current, without increasing the current (because that is often dangerous), you can wrap a wire into a coil. This is called a solenoid and it is MUCH safer. By ...
... 3. Why is a solenoid used to create a stronger magnetic field? What does it resemble? To increase the magnetic force from the presence of a current, without increasing the current (because that is often dangerous), you can wrap a wire into a coil. This is called a solenoid and it is MUCH safer. By ...