Antennas & Propagation
... Outside the Antenna the electromagnetic field can propagate on its own without the source J, since both fields are coupled through the formulas! Lecture II, 1. Oct. 2001 ...
... Outside the Antenna the electromagnetic field can propagate on its own without the source J, since both fields are coupled through the formulas! Lecture II, 1. Oct. 2001 ...
15_chapter 5
... 5.3 Field Induced Viscosity Enhancement in Magnetite Nanofluids Figure 5.7 shows the variation of ...
... 5.3 Field Induced Viscosity Enhancement in Magnetite Nanofluids Figure 5.7 shows the variation of ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... (a) A curent from A to B is increasing in magnetude. What is the direction of induced current, if any in the loop shown in Fig. (b) If inslead of current it is an electron, what will happen ? Answer : (a) When current in the wire AB increases, the flux linked with the loop (which is out of the page) ...
... (a) A curent from A to B is increasing in magnetude. What is the direction of induced current, if any in the loop shown in Fig. (b) If inslead of current it is an electron, what will happen ? Answer : (a) When current in the wire AB increases, the flux linked with the loop (which is out of the page) ...
Magnetism and Matter
... Introduction : As early as 600BC, Greeks knew that pieces of naturally occurring iron ore magnetite had the property of attracting small pieces of iron. The word magnetism originates from the place magnesia in Greece. This property of attraction is called magnetism. The iron ore showing this propert ...
... Introduction : As early as 600BC, Greeks knew that pieces of naturally occurring iron ore magnetite had the property of attracting small pieces of iron. The word magnetism originates from the place magnesia in Greece. This property of attraction is called magnetism. The iron ore showing this propert ...
Objective Questions
... 3. Is it possible to orient a current loop in a uniform magnetic field such that the loop does not tend to rotate? Explain. 4. Explain why it is not possible to determine the charge and the mass of a charged particle separately by measuring accelerations produced by electric and magnetic forces on t ...
... 3. Is it possible to orient a current loop in a uniform magnetic field such that the loop does not tend to rotate? Explain. 4. Explain why it is not possible to determine the charge and the mass of a charged particle separately by measuring accelerations produced by electric and magnetic forces on t ...
Chapter 29
... 5. How can a current loop be used to determine the presence of a magnetic field in a given region of space? 6. Charged particles from outer space, called cosmic rays, strike the Earth more frequently near the poles than near the equator. Why? 7. Can a constant magnetic field set into motion an elect ...
... 5. How can a current loop be used to determine the presence of a magnetic field in a given region of space? 6. Charged particles from outer space, called cosmic rays, strike the Earth more frequently near the poles than near the equator. Why? 7. Can a constant magnetic field set into motion an elect ...
Lecture Notes 12: Lienard-Wiechert Retarded Potentials for Moving Point Charge, Retarded Electric and Magnetic Fields Associated with Moving Point Charge
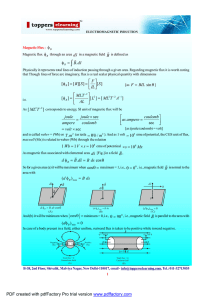
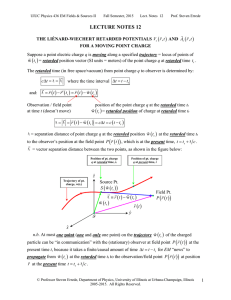
... In general, if the train’s velocity vector v makes an angle θ with the observer’s line of sight r̂ (n.b. assuming that the train is far enough away from the observer that the solid angle subtended by the train is such that rays of light emitted from both ends of train are parallel) the extra dista ...
... In general, if the train’s velocity vector v makes an angle θ with the observer’s line of sight r̂ (n.b. assuming that the train is far enough away from the observer that the solid angle subtended by the train is such that rays of light emitted from both ends of train are parallel) the extra dista ...
Moissis, A.A., and M. Zahn. Boundary Value Problems in Electrofluidized and Magnetically Stabilized Beds, Chemical Engineering Communications 67, 181-204, 1988
... magnetic or electric field collinear with the direction of the gas flow is applied to a bed of highly magnetizable or polarizable particles [2-10]. Unlike magnetic systems which only have magnetization forces, electric field systems can also have free charge forces described by Coulomb's law. Such s ...
... magnetic or electric field collinear with the direction of the gas flow is applied to a bed of highly magnetizable or polarizable particles [2-10]. Unlike magnetic systems which only have magnetization forces, electric field systems can also have free charge forces described by Coulomb's law. Such s ...
Notes on (algebra based) Physics
... 3. Discussion: Observe that this velocity is greater than the velocity calculated for the case θ = 0◦ , after Eq. (1.9). When exerted at an angle the force contribution is less in the direction of motion. But, the normal force decreases in this case and leads to reduction in the friction too. This s ...
... 3. Discussion: Observe that this velocity is greater than the velocity calculated for the case θ = 0◦ , after Eq. (1.9). When exerted at an angle the force contribution is less in the direction of motion. But, the normal force decreases in this case and leads to reduction in the friction too. This s ...
Chapter 19
... •The SI unit of charge, the Coulomb (C), can be defned in terms of the Ampere. –If a conductor carries a steady current of 1 A, then the quantty of charge that fows through any cross secton in 1 second is 1 C. ...
... •The SI unit of charge, the Coulomb (C), can be defned in terms of the Ampere. –If a conductor carries a steady current of 1 A, then the quantty of charge that fows through any cross secton in 1 second is 1 C. ...