Sources of Magnetic Field
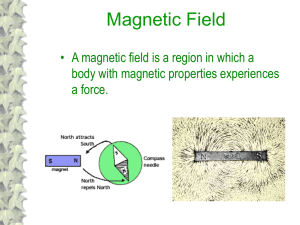
... • A magnetic field is a region in which a body with magnetic properties experiences a force. ...
... • A magnetic field is a region in which a body with magnetic properties experiences a force. ...
The Electric Field
... A field is not just an abstract concept that we use to describe forces. The field is real. The electric field extends throughout space and exerts forces on charged particles. If we place a positive point charge in an electric field, there will be a vector force on that charge in the direction ...
... A field is not just an abstract concept that we use to describe forces. The field is real. The electric field extends throughout space and exerts forces on charged particles. If we place a positive point charge in an electric field, there will be a vector force on that charge in the direction ...
Magnetic field lines
... It is known now that all magnetic phenomena result from forces between electric charges in motion. I. A moving charge or a current sets up or creates a magnetic field. II. The magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge or a current in the field. ...
... It is known now that all magnetic phenomena result from forces between electric charges in motion. I. A moving charge or a current sets up or creates a magnetic field. II. The magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge or a current in the field. ...
Lecture 23 ppt
... distance since N and S fields cancel. • Magnetic poles cannot be isolated. (Big difference with electric charge) e.g. if break bar magnet in two, each half behaves as complete magnet, each with N and S poles. Even when it’s one atom thick! No magnetic monopoles. ...
... distance since N and S fields cancel. • Magnetic poles cannot be isolated. (Big difference with electric charge) e.g. if break bar magnet in two, each half behaves as complete magnet, each with N and S poles. Even when it’s one atom thick! No magnetic monopoles. ...
7-3 The Biot-Savart Law and the Magnetic Vector Potential
... equation ∇ ⋅ ∇xA ( r ) = 0 . Why don’t we include this equation in the above list? ...
... equation ∇ ⋅ ∇xA ( r ) = 0 . Why don’t we include this equation in the above list? ...
Charge
... Coulomb’s Law is an inverse square law similar to the Law of Gravitation It is dissimilar in that electrostatic forces can be attraction or repulsion. Gravity is attraction only. Electrostatic force is strong, gravity is very weak. ...
... Coulomb’s Law is an inverse square law similar to the Law of Gravitation It is dissimilar in that electrostatic forces can be attraction or repulsion. Gravity is attraction only. Electrostatic force is strong, gravity is very weak. ...