Plasma Process 4 kin..
... an electric field that depends on the local densities of the charge carrier. Because of this, we will begin to look at the velocity distribution function f (r, v, t ) = f x, y, z, vx , vy , vz , t . The number of particles that are inside a volume of dxdydzdvx dvy dvz is simply ...
... an electric field that depends on the local densities of the charge carrier. Because of this, we will begin to look at the velocity distribution function f (r, v, t ) = f x, y, z, vx , vy , vz , t . The number of particles that are inside a volume of dxdydzdvx dvy dvz is simply ...
Magnets and Magnetic Fields
... F = BIL . A current flowing through a loop of wire between two magnet poles experiences a force that causes rotation (See and understand demo). When the motor turns 180°, a commutator (switch) changes the direction of the current so that the force is now changed 180°, and rotation continues. ...
... F = BIL . A current flowing through a loop of wire between two magnet poles experiences a force that causes rotation (See and understand demo). When the motor turns 180°, a commutator (switch) changes the direction of the current so that the force is now changed 180°, and rotation continues. ...
electric potential
... This work is equal to the increase in potential energy of the charge. It is also the NEGATIVE of the work done BY THE FIELD in moving the charge from the same points. ...
... This work is equal to the increase in potential energy of the charge. It is also the NEGATIVE of the work done BY THE FIELD in moving the charge from the same points. ...
ppt-Ch-23
... The electric field just outside the surface of a conductor is easy to determine using Gauss’ law. Consider a section of the surface that is small enough to neglect any curvature and thus the section is considered flat. A tiny cylindrical Gaussian surface is embedded in the section as in Fig. 23-10: ...
... The electric field just outside the surface of a conductor is easy to determine using Gauss’ law. Consider a section of the surface that is small enough to neglect any curvature and thus the section is considered flat. A tiny cylindrical Gaussian surface is embedded in the section as in Fig. 23-10: ...
Appendix A. The Normal Geomagnetic Field in Hutchinson, Kansas ( ) Model: IGRF2000
... Magnetic declination is sometimes referred to as the magnetic variation or the magnetic compass correction. It is the angle formed between true north and the projection of the magnetic field vector on the horizontal plane. By convention, declination is measured positive east and negative west (i.e. ...
... Magnetic declination is sometimes referred to as the magnetic variation or the magnetic compass correction. It is the angle formed between true north and the projection of the magnetic field vector on the horizontal plane. By convention, declination is measured positive east and negative west (i.e. ...
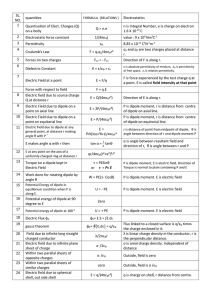
SL. NO. quantities FORMULA (RELATIONS ) Electrostatics 1
... n is Integral Number, e is charge on electron 1.6 X 10-19 C ...
... n is Integral Number, e is charge on electron 1.6 X 10-19 C ...
... (note that A 0 because by the continuity equation for a stationary situation 'J 0 .) From the definition of the vector potential, and using Stokes theorem we find that the magnetic flux through an area S is given by the contour integral around the loop closing that area ...
... (note that A 0 because by the continuity equation for a stationary situation 'J 0 .) From the definition of the vector potential, and using Stokes theorem we find that the magnetic flux through an area S is given by the contour integral around the loop closing that area ...
∫ ) r '
... Exercise: A current loop, carrying a current I, is made of a wire of the shape of square with side a. Find the magnetic field on the axis perpendicular to the current loop, and passing through its ...
... Exercise: A current loop, carrying a current I, is made of a wire of the shape of square with side a. Find the magnetic field on the axis perpendicular to the current loop, and passing through its ...
Chapter 18 – Electric Potential and Capacitance
... ranges from 1.5 volts to 12 volts – as charges move from one terminal to another, the energy can be used for work, like water falling over a water mill is used to do work • Household electrical outlet is 120 volts ...
... ranges from 1.5 volts to 12 volts – as charges move from one terminal to another, the energy can be used for work, like water falling over a water mill is used to do work • Household electrical outlet is 120 volts ...