Worked Examples - Mit - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... A circular loop of wire of radius a is placed in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. The magnetic field varies with time according to B ( t ) = B0 + bt , where a and b are constants. (a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop at t = ...
... A circular loop of wire of radius a is placed in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the loop perpendicular to the direction of the field. The magnetic field varies with time according to B ( t ) = B0 + bt , where a and b are constants. (a) Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop at t = ...
B 1 - Purdue Physics
... Bapplied = Magnetic field applied by the red wire. Blue wire feels a force up. x ...
... Bapplied = Magnetic field applied by the red wire. Blue wire feels a force up. x ...
Document
... Intensity of field at a point – Force on unit positive charge placed at that point. ...
... Intensity of field at a point – Force on unit positive charge placed at that point. ...
Van Vleck Magnetism and High Magnetic Fields:
... ions. Such anisotropy, which is not observed in ordinary NMR, emphasizes further the intermediate character of ‘‘enhanced’’ NMR. Because of these features, Van Vleck paramagnets can be used for cooling nuclear spin systems and for studying the effects of nuclear magnetic ordering at higher temperatu ...
... ions. Such anisotropy, which is not observed in ordinary NMR, emphasizes further the intermediate character of ‘‘enhanced’’ NMR. Because of these features, Van Vleck paramagnets can be used for cooling nuclear spin systems and for studying the effects of nuclear magnetic ordering at higher temperatu ...
AP-C Electric Force and Electric Field
... Electric field strength is measured in N/C, which are equivalent to V/m. ...
... Electric field strength is measured in N/C, which are equivalent to V/m. ...
chap 21 magnetism
... Force on moving charge in magnetic Field • The magnetic force exerted on a positive charge is in the opposite direction of the force exerted on a negative charge moving in the same direction • The magnitude of the magnetic force exerted on the moving particle is proportional to sin where is the ...
... Force on moving charge in magnetic Field • The magnetic force exerted on a positive charge is in the opposite direction of the force exerted on a negative charge moving in the same direction • The magnitude of the magnetic force exerted on the moving particle is proportional to sin where is the ...
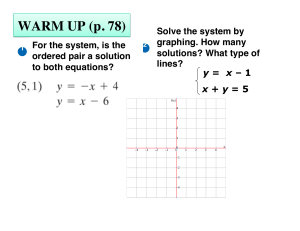
6.2ab solve systems by substitution
... 9.0 Solve a system of two linear equations in two variables and interpret the answer graphically. ...
... 9.0 Solve a system of two linear equations in two variables and interpret the answer graphically. ...
6.3 - ThisIsPhysics
... distance of one metre in a vacuum that results in a force of exactly 2 x 10-7 N per metre of length of each wire. ...
... distance of one metre in a vacuum that results in a force of exactly 2 x 10-7 N per metre of length of each wire. ...
Electric Potential - K
... An electron enters a uniform electric field of 145N/C pointed toward the right. The point of entry is 1.5m to the right of a given mark, and the point where the electron leaves the field is 4.6m to the right of that mark. (a) Determine the change in the electric potential energy of the electron (Ans ...
... An electron enters a uniform electric field of 145N/C pointed toward the right. The point of entry is 1.5m to the right of a given mark, and the point where the electron leaves the field is 4.6m to the right of that mark. (a) Determine the change in the electric potential energy of the electron (Ans ...