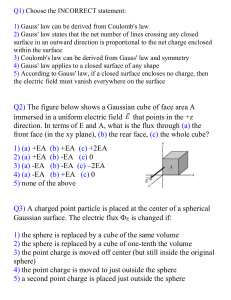
Gauss` Law
... metal shell that has a net charge of -100e. What is the charge on (a) the shell's inner surface and (b) its outer surface? 1) (a) –50e (b) –100e 2) (a) +50e (b) +150e 3) (a) +50e (b) –100e 4) (a) 0e (b) –150e 5) none of the above Q27) A solid, conducting sphere of radius a carries an excess charge o ...
... metal shell that has a net charge of -100e. What is the charge on (a) the shell's inner surface and (b) its outer surface? 1) (a) –50e (b) –100e 2) (a) +50e (b) +150e 3) (a) +50e (b) –100e 4) (a) 0e (b) –150e 5) none of the above Q27) A solid, conducting sphere of radius a carries an excess charge o ...
Electricity, Energy and Magnetism
... over miniscule distances. It is what keeps quarks (the basic particles of neutrons and protons) bonded together. the electroweak force which controls a radioactive process in which a neutron breaks down into a proton and a fast moving electron (beta particle) the electromagnetic force which is what ...
... over miniscule distances. It is what keeps quarks (the basic particles of neutrons and protons) bonded together. the electroweak force which controls a radioactive process in which a neutron breaks down into a proton and a fast moving electron (beta particle) the electromagnetic force which is what ...
1 Electrostatics Lecture No : 14 Tittle : Faraday`s Law of Induction
... Figure shows a conducting loop connected to a sensitive ammeter. Because there is no battery or other source of emf included, there is no current in the circuit. However, if we move a bar magnet toward the loop, a current suddenly appears in the circuit. The current disappears when the magnet stops ...
... Figure shows a conducting loop connected to a sensitive ammeter. Because there is no battery or other source of emf included, there is no current in the circuit. However, if we move a bar magnet toward the loop, a current suddenly appears in the circuit. The current disappears when the magnet stops ...
No Slide Title
... Check It Out! Example 2B Solve 3x + 15 – 9 = 2(x + 2). 3x + 15 – 9 = 2(x + 2) Distribute 2 to the expression in parentheses. 3x + 15 – 9 = 2(x) + 2(2) ...
... Check It Out! Example 2B Solve 3x + 15 – 9 = 2(x + 2). 3x + 15 – 9 = 2(x + 2) Distribute 2 to the expression in parentheses. 3x + 15 – 9 = 2(x) + 2(2) ...
Magnetism and Electrostatics
... Section 1. 1.1. Charged particles create electric fields that can push on other charged particles with an electric r r force Felectric = qE . These electric fields are represented by drawing electric field lines that show the direction of the electric force. Magnetic fields are more complex because ...
... Section 1. 1.1. Charged particles create electric fields that can push on other charged particles with an electric r r force Felectric = qE . These electric fields are represented by drawing electric field lines that show the direction of the electric force. Magnetic fields are more complex because ...