Voltage Control of Metal-insulator Transition and Non-volatile Ferroelastic
... among them and eliminate the domain inhomogeneity, leading to large changes in the electronic properties4,9,15–17. Making use of these effects in device applications requires the ability to switch between the distinct electronic states with a control voltage in a stable and reversible manner14,18. D ...
... among them and eliminate the domain inhomogeneity, leading to large changes in the electronic properties4,9,15–17. Making use of these effects in device applications requires the ability to switch between the distinct electronic states with a control voltage in a stable and reversible manner14,18. D ...
The Magnetic Field of the Earth
... “poles”: quadrupoles, octopoles, and so on. The equivalence with gravitational potential theory will follow from the fact that both the gravitational and the magnetic potential are solutions to Laplace’s equation. ...
... “poles”: quadrupoles, octopoles, and so on. The equivalence with gravitational potential theory will follow from the fact that both the gravitational and the magnetic potential are solutions to Laplace’s equation. ...
a long loop coil system for insertion device magnet measurement
... ∫Bx dz and ∫By dz, of each block surface can be measured by the “dynamic scan” method to reduce the time consumption and the whole insertion device will be measured by the “static scan” method. This system is am automatic measurement and data acquisition system which was developed on the LabView app ...
... ∫Bx dz and ∫By dz, of each block surface can be measured by the “dynamic scan” method to reduce the time consumption and the whole insertion device will be measured by the “static scan” method. This system is am automatic measurement and data acquisition system which was developed on the LabView app ...
Electromagnetism and Circular Motion in a Cyclotron
... strip of cloth in which a stone or lead weight was placed. The stone was then swung around until going at very high velocity, and finally released to hit a target. This is almost exactly like a cyclotron! 1) Get a stone: If you are using a sling you need not just any stone, but one of the right shap ...
... strip of cloth in which a stone or lead weight was placed. The stone was then swung around until going at very high velocity, and finally released to hit a target. This is almost exactly like a cyclotron! 1) Get a stone: If you are using a sling you need not just any stone, but one of the right shap ...
Vector Review - UCSB C.L.A.S.
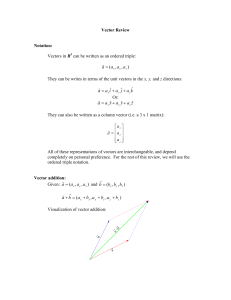
... → The position vector r ( x, y, z ) is a vector from the origin to an arbitrary point in R3. → The magnitude of the position vector is the distance from the origin to (x,y,z). ...
... → The position vector r ( x, y, z ) is a vector from the origin to an arbitrary point in R3. → The magnitude of the position vector is the distance from the origin to (x,y,z). ...
Pulsed high magnetic field sensor using polymethyl
... In order to measure the Verdet constant and the temperature dependence of V L, the sensing element was subjected to an applied magnetic field (∼2.4 kG) generated by a single layer solenoid (46.2 mm in diameter, 485 mm in length, 572 turns) and a capacitor of 8 µF charged to 4.50 kV. The electric cur ...
... In order to measure the Verdet constant and the temperature dependence of V L, the sensing element was subjected to an applied magnetic field (∼2.4 kG) generated by a single layer solenoid (46.2 mm in diameter, 485 mm in length, 572 turns) and a capacitor of 8 µF charged to 4.50 kV. The electric cur ...
Topics in Early Universe Cosmology
... • Chapter 2 is based on [20] which was written in collaboration with Robert Brandenberger. I performed most of the analytical computations and wrote a large fraction of the body of the text. I derived analytically the energy densities, the equation of state parameters, the equations of motions and s ...
... • Chapter 2 is based on [20] which was written in collaboration with Robert Brandenberger. I performed most of the analytical computations and wrote a large fraction of the body of the text. I derived analytically the energy densities, the equation of state parameters, the equations of motions and s ...
Electric Fields and Solvation in Microscopic Liquids
... references [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] along with many others. This chapter will be organized as to provide a conceptual understanding of dielectrics in Section I of this chapter, basics about continuum dielectrics and polarization in Section II of this chapter including the concepts of bound and free charge ...
... references [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] along with many others. This chapter will be organized as to provide a conceptual understanding of dielectrics in Section I of this chapter, basics about continuum dielectrics and polarization in Section II of this chapter including the concepts of bound and free charge ...
Electric forces_ fields_ voltage and capacitance review
... ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material through which charge can ...
... ELECTRIC FORCES AND ELECTRIC FIELDS Electric charge is the fundamental quantity that underlies all electrical phenomena. There are two types of charges, positive and negative, and like charges repel each other, and unlike charges attract each other. A conductor is a material through which charge can ...
a revised electromagnetic theory with fundamental applications
... quantum mechanics does not provide fully adequate descriptions of physical reality. These difficulties are not removed by and are not directly associated with quantum mechanics. Instead electromagnetic field theory is a far from completed area of research, and QED will also become subject to the typ ...
... quantum mechanics does not provide fully adequate descriptions of physical reality. These difficulties are not removed by and are not directly associated with quantum mechanics. Instead electromagnetic field theory is a far from completed area of research, and QED will also become subject to the typ ...
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity that has a value for each point in space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface wind velocity is described by assigning a vector to each point on a map. Each vector represents the speed and direction of the movement of air at that point. As another example, an electric field can be thought of as a ""condition in space"" emanating from an electric charge and extending throughout the whole of space. When a test electric charge is placed in this electric field, the particle accelerates due to a force. Physicists have found the notion of a field to be of such practical utility for the analysis of forces that they have come to think of a force as due to a field.In the modern framework of the quantum theory of fields, even without referring to a test particle, a field occupies space, contains energy, and its presence eliminates a true vacuum. This lead physicists to consider electromagnetic fields to be a physical entity, making the field concept a supporting paradigm of the edifice of modern physics. ""The fact that the electromagnetic field can possess momentum and energy makes it very real... a particle makes a field, and a field acts on another particle, and the field has such familiar properties as energy content and momentum, just as particles can have"". In practice, the strength of most fields has been found to diminish with distance to the point of being undetectable. For instance the strength of many relevant classical fields, such as the gravitational field in Newton's theory of gravity or the electrostatic field in classical electromagnetism, is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source (i.e. they follow the Gauss's law). One consequence is that the Earth's gravitational field quickly becomes undetectable on cosmic scales.A field can be classified as a scalar field, a vector field, a spinor field or a tensor field according to whether the represented physical quantity is a scalar, a vector, a spinor or a tensor, respectively. A field has a unique tensorial character in every point where it is defined: i.e. a field cannot be a scalar field somewhere and a vector field somewhere else. For example, the Newtonian gravitational field is a vector field: specifying its value at a point in spacetime requires three numbers, the components of the gravitational field vector at that point. Moreover, within each category (scalar, vector, tensor), a field can be either a classical field or a quantum field, depending on whether it is characterized by numbers or quantum operators respectively. In fact in this theory an equivalent representation of field is a field particle, namely a boson.