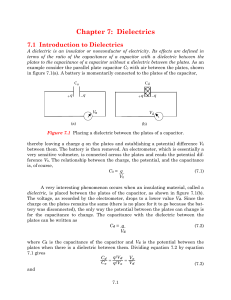
The Interaction of Radio-Frequency Fields With
... V(r) and vector potential A(r, t) in terms of creation and annihilation operators and using these fields in the Hamiltonian, which is then used in the Schrödinger equation to obtain the wavefunction (see, for example, [3]). The static electromagnetic field is sometimes modeled by virtual photons tha ...
... V(r) and vector potential A(r, t) in terms of creation and annihilation operators and using these fields in the Hamiltonian, which is then used in the Schrödinger equation to obtain the wavefunction (see, for example, [3]). The static electromagnetic field is sometimes modeled by virtual photons tha ...
Storing and processing optical information with ultraslow light in Bose-Einstein... Zachary Dutton and Lene Vestergaard Hau
... off and the atomic wave functions evolve due to kinetic energy, the external trapping potential, and atom-atom interactions. (We label all these external dynamics to distinguish them from couplings between the internal levels provided by the light fields.) To successfully regenerate the probe pulse ...
... off and the atomic wave functions evolve due to kinetic energy, the external trapping potential, and atom-atom interactions. (We label all these external dynamics to distinguish them from couplings between the internal levels provided by the light fields.) To successfully regenerate the probe pulse ...
Structure and dynamics of electrorheological fluids
... Reversible chaining is also observed in direct optical imaging. The distinctive scattering lobes are superficially the twodimensional counterpart to the spinodal ring observed in three-dimensional systems and thus compel a comparison to this model. In fact, if the laser beam is directed along the fi ...
... Reversible chaining is also observed in direct optical imaging. The distinctive scattering lobes are superficially the twodimensional counterpart to the spinodal ring observed in three-dimensional systems and thus compel a comparison to this model. In fact, if the laser beam is directed along the fi ...
Electromagnetic oscillations of the Earth`s upper atmosphere (review)
... In the present paper, we will not investigate the influence of the medium’s ground state motion on the oscillations, but we will consider the equilibrium state when pressure P̄ and density ρ̄ depend only on the z-coordinate and are connected to each other by the static equilibrium equation ∂ P̄ /∂z ...
... In the present paper, we will not investigate the influence of the medium’s ground state motion on the oscillations, but we will consider the equilibrium state when pressure P̄ and density ρ̄ depend only on the z-coordinate and are connected to each other by the static equilibrium equation ∂ P̄ /∂z ...
Coil Design and Related Studies for the Fusion-Fission
... The world’s demand for energy is increasing and the increase is likely to continue for many years to come. The main resource for energy production today is fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas. Since these resources are limited and prices are rising, other energy sources ought to replace them. The ...
... The world’s demand for energy is increasing and the increase is likely to continue for many years to come. The main resource for energy production today is fossil fuels such as coal, oil and gas. Since these resources are limited and prices are rising, other energy sources ought to replace them. The ...
Precipitate drifting and coarsening caused ... of
... along the matrix/precipitate interface should be lower than that along the grain boundary. Furthermore, since the precipitates on a grain boundary are discontinuous, additional mechanismmust be invoked to block diffusion betweenthe precipitates. In the bamboo-like lines, arrays of precipitates may s ...
... along the matrix/precipitate interface should be lower than that along the grain boundary. Furthermore, since the precipitates on a grain boundary are discontinuous, additional mechanismmust be invoked to block diffusion betweenthe precipitates. In the bamboo-like lines, arrays of precipitates may s ...
Review Assessment: q01
... directed at another positively charged particle. There is a repulsive force but force directly determines acceleration, not velocity. The force just makes it so that the velocity in this case is decreasing. To say that a positively charged particle can never be approaching another positively charged ...
... directed at another positively charged particle. There is a repulsive force but force directly determines acceleration, not velocity. The force just makes it so that the velocity in this case is decreasing. To say that a positively charged particle can never be approaching another positively charged ...
Electricity and Magnetism - U
... west. Water flowing through a hose could be said to involve the transport of an immense amount of charge – about 3 · 1023 electrons per gram of water! But since an equal number of protons move along with the electrons (every water molecule contains ten of each), the electric current is zero. On the ...
... west. Water flowing through a hose could be said to involve the transport of an immense amount of charge – about 3 · 1023 electrons per gram of water! But since an equal number of protons move along with the electrons (every water molecule contains ten of each), the electric current is zero. On the ...
Silicon quantum electronics
... cess that causes loss of information, called decoherence. In other words, the computation has to be finished well within the typical time scale on which decoherence takes place, i.e. the coherence time. Decoherence can be prevented if the qubit is isolated from the outside world. But this is in cont ...
... cess that causes loss of information, called decoherence. In other words, the computation has to be finished well within the typical time scale on which decoherence takes place, i.e. the coherence time. Decoherence can be prevented if the qubit is isolated from the outside world. But this is in cont ...
Electric Current Circuits in Astrophysics
... density everywhere, the parallel electric field vanishes. This is the situation on the ‘closed’ field lines which are located near the star. On the open field lines the speed of the charges is assumed to be the speed of light since the wind is expected to be relativistic from the beginning (4). Thin ...
... density everywhere, the parallel electric field vanishes. This is the situation on the ‘closed’ field lines which are located near the star. On the open field lines the speed of the charges is assumed to be the speed of light since the wind is expected to be relativistic from the beginning (4). Thin ...
Chapter 16 - dysoncentralne
... When you rub a balloon across your hair, how do the balloon and your hair become electrically charged? To answer this question, you’ll need to know a little about the atoms that make up the matter around you. Every atom contains even smaller particles. Positively charged particles, called protons, a ...
... When you rub a balloon across your hair, how do the balloon and your hair become electrically charged? To answer this question, you’ll need to know a little about the atoms that make up the matter around you. Every atom contains even smaller particles. Positively charged particles, called protons, a ...
Field (physics)
In physics, a field is a physical quantity that has a value for each point in space and time. For example, on a weather map, the surface wind velocity is described by assigning a vector to each point on a map. Each vector represents the speed and direction of the movement of air at that point. As another example, an electric field can be thought of as a ""condition in space"" emanating from an electric charge and extending throughout the whole of space. When a test electric charge is placed in this electric field, the particle accelerates due to a force. Physicists have found the notion of a field to be of such practical utility for the analysis of forces that they have come to think of a force as due to a field.In the modern framework of the quantum theory of fields, even without referring to a test particle, a field occupies space, contains energy, and its presence eliminates a true vacuum. This lead physicists to consider electromagnetic fields to be a physical entity, making the field concept a supporting paradigm of the edifice of modern physics. ""The fact that the electromagnetic field can possess momentum and energy makes it very real... a particle makes a field, and a field acts on another particle, and the field has such familiar properties as energy content and momentum, just as particles can have"". In practice, the strength of most fields has been found to diminish with distance to the point of being undetectable. For instance the strength of many relevant classical fields, such as the gravitational field in Newton's theory of gravity or the electrostatic field in classical electromagnetism, is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source (i.e. they follow the Gauss's law). One consequence is that the Earth's gravitational field quickly becomes undetectable on cosmic scales.A field can be classified as a scalar field, a vector field, a spinor field or a tensor field according to whether the represented physical quantity is a scalar, a vector, a spinor or a tensor, respectively. A field has a unique tensorial character in every point where it is defined: i.e. a field cannot be a scalar field somewhere and a vector field somewhere else. For example, the Newtonian gravitational field is a vector field: specifying its value at a point in spacetime requires three numbers, the components of the gravitational field vector at that point. Moreover, within each category (scalar, vector, tensor), a field can be either a classical field or a quantum field, depending on whether it is characterized by numbers or quantum operators respectively. In fact in this theory an equivalent representation of field is a field particle, namely a boson.