student worksheet
... Analysis 1. What is the relative amount of matter (in the bodies of the planets and sun) compared to the amount of space in the solar system? ...
... Analysis 1. What is the relative amount of matter (in the bodies of the planets and sun) compared to the amount of space in the solar system? ...
Chapter 20 Notes: Solar System The Solar System Sun’s Interior
... Only seen during a total solar eclipse extends millions of kilometers into space as solar wind ...
... Only seen during a total solar eclipse extends millions of kilometers into space as solar wind ...
SNC 1D The Sun
... Sun has enough hydrogen fuel (for fusion) for 10 billion years Our Sun has 5 billion more years left ...
... Sun has enough hydrogen fuel (for fusion) for 10 billion years Our Sun has 5 billion more years left ...
Helioseismology and the Helium Abundance
... • Determination of the gravitational quadrupole moment J2 ...
... • Determination of the gravitational quadrupole moment J2 ...
Sun`s rap song
... They appear due to cooler gases making darker dots. Another magnetic disturbance is known as a solar flare. It’s a brief and bright eruption, that is not rare. 21. The heat flow in a magnetic field can be reduced, And from cooler gas prominences are produced. Due to less pressure inside and hotter g ...
... They appear due to cooler gases making darker dots. Another magnetic disturbance is known as a solar flare. It’s a brief and bright eruption, that is not rare. 21. The heat flow in a magnetic field can be reduced, And from cooler gas prominences are produced. Due to less pressure inside and hotter g ...
Sun`s rap song
... They appear due to cooler gases making darker dots. Another magnetic disturbance is known as a solar flare. It’s a brief and bright eruption, that is not rare. 21. The heat flow in a magnetic field can be reduced, And from cooler gas prominences are produced. Due to less pressure inside and hotter g ...
... They appear due to cooler gases making darker dots. Another magnetic disturbance is known as a solar flare. It’s a brief and bright eruption, that is not rare. 21. The heat flow in a magnetic field can be reduced, And from cooler gas prominences are produced. Due to less pressure inside and hotter g ...
solar eclipse
... Friday 20th March 2015 Solar and Lunar Eclipses WALT: To explain how eclipses happen To describe the different types of solar eclipse To look at ancient explanations of eclipses ...
... Friday 20th March 2015 Solar and Lunar Eclipses WALT: To explain how eclipses happen To describe the different types of solar eclipse To look at ancient explanations of eclipses ...
Solar system - Science 504
... Solar system and galaxy Lots of planets in the galaxy . Only 8 planets in our solar system . Both have planets . Galaxy is much bigger than the solar system . The galaxy has ...
... Solar system and galaxy Lots of planets in the galaxy . Only 8 planets in our solar system . Both have planets . Galaxy is much bigger than the solar system . The galaxy has ...
Jupiter • The largest planet in the solar system
... planets do. Has the same ingredients as a star, but it did not grow massive enough to ignite. The fifth planet from the sun. The composition is similar to that of the sun — mostly hydrogen and helium. Took most of the mass left over after the formation of the sun, ending up with more than tw ...
... planets do. Has the same ingredients as a star, but it did not grow massive enough to ignite. The fifth planet from the sun. The composition is similar to that of the sun — mostly hydrogen and helium. Took most of the mass left over after the formation of the sun, ending up with more than tw ...
Chapter 25.1: Exploring the Solar System and 25.5 The Origin of the
... Balls of dust collided an explanation for and grew larger & the Current motions larger and eventually of the Sun, Planets, these asteroid-like and most Moons. bodies combined to form planets! ...
... Balls of dust collided an explanation for and grew larger & the Current motions larger and eventually of the Sun, Planets, these asteroid-like and most Moons. bodies combined to form planets! ...
Ch. 23: “Touring Our Solar System”
... A meteoroid is a small, solid particle that travels through space. A meteor is the luminous phenomenon observed when a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere and burns up, popularly called a shooting star. A meteorite is any portion of a meteoroid that reaches Earth’s surface. ...
... A meteoroid is a small, solid particle that travels through space. A meteor is the luminous phenomenon observed when a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere and burns up, popularly called a shooting star. A meteorite is any portion of a meteoroid that reaches Earth’s surface. ...
27Oct_2014
... • Sunspots are highly localized cool regions in the photosphere of the Sun – Discovered by Galileo – Can be many times larger than the Earth! – They contain intense magnetic fields, as evidenced by the Zeeman effect ...
... • Sunspots are highly localized cool regions in the photosphere of the Sun – Discovered by Galileo – Can be many times larger than the Earth! – They contain intense magnetic fields, as evidenced by the Zeeman effect ...
Chapter 14 Vocabulary: The Solar System
... Comet: A loose collection of ice, dust, & small rocky particles, typically with a long, narrow orbit (p 573) Nucleus: The solid inner core of a comet (p 573) Asteroid: Rocky objects revolving around the sun that are too small & numerous to be considered planets (p 574) Meteoroid: A chunk of rock or ...
... Comet: A loose collection of ice, dust, & small rocky particles, typically with a long, narrow orbit (p 573) Nucleus: The solid inner core of a comet (p 573) Asteroid: Rocky objects revolving around the sun that are too small & numerous to be considered planets (p 574) Meteoroid: A chunk of rock or ...
Celestial Objects notes
... through the atmosphere strikes Earth’s surface. Asteroids are small rocks revolving in an orbital path around the Sun. Although they are too small to be called planets, they can still crash into space ships or Earth and do significant damage. Most asteroids lie in a vast area between the orbits of M ...
... through the atmosphere strikes Earth’s surface. Asteroids are small rocks revolving in an orbital path around the Sun. Although they are too small to be called planets, they can still crash into space ships or Earth and do significant damage. Most asteroids lie in a vast area between the orbits of M ...
Chapter 14 The Solar System
... 2. ____ giants: The name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. 3. ____ cloud: A spherical region of comets that surrounds the solar system. 4. ____ planets: The name often given to the four inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. 5. ____ zone: The ...
... 2. ____ giants: The name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. 3. ____ cloud: A spherical region of comets that surrounds the solar system. 4. ____ planets: The name often given to the four inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. 5. ____ zone: The ...
Chapter 14 The Solar System
... 2. ____ giants: The name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. 3. ____ cloud: A spherical region of comets that surrounds the solar system. 4. ____ planets: The name often given to the four inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. 5. ____ zone: The ...
... 2. ____ giants: The name often given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. 3. ____ cloud: A spherical region of comets that surrounds the solar system. 4. ____ planets: The name often given to the four inner planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. 5. ____ zone: The ...
Chapter 14
... 1. Comet- a loose collection of ice, dust, and small rocky particles, typically with a long, narrow orbit. 2. Coma- clouds of gas and dust from a fuzzy outer layer. 3. Nucleus- the solid inner core of a comet. 4. Kuiper belt- is a doughnut-shaped region that extends from beyond Neptune’s orbit to ab ...
... 1. Comet- a loose collection of ice, dust, and small rocky particles, typically with a long, narrow orbit. 2. Coma- clouds of gas and dust from a fuzzy outer layer. 3. Nucleus- the solid inner core of a comet. 4. Kuiper belt- is a doughnut-shaped region that extends from beyond Neptune’s orbit to ab ...
Chapter 11
... particles enter the Earth’s atmosphere at the poles where they collide with the gas in the atmosphere to create Auroras (Northern/Southern lights) page 394. ...
... particles enter the Earth’s atmosphere at the poles where they collide with the gas in the atmosphere to create Auroras (Northern/Southern lights) page 394. ...
Section 18.3 - CPO Science
... extending millions of kilometers beyond the sun. Sunspots are areas of gas that are cooler than the gases around them. ...
... extending millions of kilometers beyond the sun. Sunspots are areas of gas that are cooler than the gases around them. ...
Overview of our Solar System 1112 notes
... • The first thing formed in our solar system • The largest and only star in our solar system • Provides almost all of the energy used in the solar system • Earth only gets 0.000000001% of the sun’s total energy ...
... • The first thing formed in our solar system • The largest and only star in our solar system • Provides almost all of the energy used in the solar system • Earth only gets 0.000000001% of the sun’s total energy ...
File
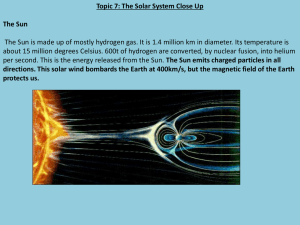
... The Sun is made up of mostly hydrogen gas. It is 1.4 million km in diameter. Its temperature is about 15 million degrees Celsius. 600t of hydrogen are converted, by nuclear fusion, into helium per second. This is the energy released from the Sun. The Sun emits charged particles in all directions. Th ...
... The Sun is made up of mostly hydrogen gas. It is 1.4 million km in diameter. Its temperature is about 15 million degrees Celsius. 600t of hydrogen are converted, by nuclear fusion, into helium per second. This is the energy released from the Sun. The Sun emits charged particles in all directions. Th ...
Introduction Cosmology Cosmetics Cosmetology ..Greek words
... particles, e.g., electrons) Large scale => gravity Small scale => laws of quantum mechanics What is “scientific”? ...
... particles, e.g., electrons) Large scale => gravity Small scale => laws of quantum mechanics What is “scientific”? ...
Lecture 12
... Helioseismology uses sound waves bouncing within the Sun to study flows and structures deep inside. How are they detected and measured? A. By listening very carefully, since 55-minute periods hard to hear otherwise B. By observing Doppler shifts of spectral line emitted by solar surface moving up an ...
... Helioseismology uses sound waves bouncing within the Sun to study flows and structures deep inside. How are they detected and measured? A. By listening very carefully, since 55-minute periods hard to hear otherwise B. By observing Doppler shifts of spectral line emitted by solar surface moving up an ...
Heliosphere

The heliosphere is the bubble-like region of space dominated by the Sun, which extends far beyond the orbit of Pluto. Plasma ""blown"" out from the Sun, known as the solar wind, creates and maintains this bubble against the outside pressure of the interstellar medium, the hydrogen and helium gas that permeates the Milky Way Galaxy. The solar wind flows outward from the Sun until encountering the termination shock, where motion slows abruptly. The Voyager spacecraft have actively explored the outer reaches of the heliosphere, passing through the shock and entering the heliosheath, a transitional region which is in turn bounded by the outermost edge of the heliosphere, called the heliopause. The overall shape of the heliosphere is controlled by the interstellar medium, through which it is traveling, as well as the Sun, and does not appear to be perfectly spherical. The limited data available and unexplored nature of these structures have resulted in many theories.On September 12, 2013, NASA announced that Voyager 1 had exited the heliosphere on August 25, 2012, when it measured a sudden increase in plasma density of about forty times. Because the heliopause marks one boundary between the Sun's solar wind and the rest of the galaxy, a spacecraft such as Voyager 1 which has departed the heliosphere can be said to have reached interstellar space.