Rendezvous with a Comet
... Intermediate-periods: period 20 - 200 years Long-periods: period 1-3 million years Orbits steeply inclined to the plane of ecliptic Spend most of their time 10,000 to 100000 AU from Sun About 1 long-period comet is discovered every month It is thought that many of these comets were icy planetesi ...
... Intermediate-periods: period 20 - 200 years Long-periods: period 1-3 million years Orbits steeply inclined to the plane of ecliptic Spend most of their time 10,000 to 100000 AU from Sun About 1 long-period comet is discovered every month It is thought that many of these comets were icy planetesi ...
Study of Planetary Systems and Solar System Objects with JWST
... KBO's compositional make-up and chemical evolution provide clues of the earliest conditions in critical regions of the solar nebula, as well as having relevance to the current distributions of astrobiologically and cosmochemically important materials such as H2O and organic species. Currently, the o ...
... KBO's compositional make-up and chemical evolution provide clues of the earliest conditions in critical regions of the solar nebula, as well as having relevance to the current distributions of astrobiologically and cosmochemically important materials such as H2O and organic species. Currently, the o ...
Sec 28.4 - Highland High School
... to take a closer look at the planetary status of Pluto and other solar system objects. ...
... to take a closer look at the planetary status of Pluto and other solar system objects. ...
27.4 Directed Reading Guide
... 32. Uranus is the ______________________ planet from the sun and the third largest planet in the solar system. 33. Why is Uranus a difficult planet to study? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 34. Uranus has ...
... 32. Uranus is the ______________________ planet from the sun and the third largest planet in the solar system. 33. Why is Uranus a difficult planet to study? _______________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________ 34. Uranus has ...
discovering dwarf planets
... Finding dwarf planets What is a planet? A planet is a body orbiting around the sun with enough mass and therefore gravity to be round. A planet has also ‘cleared its neighbourhood’, orbit by sucking in small bodies or deflecting them away from their orbit. There are eight planets within our Galaxy: ...
... Finding dwarf planets What is a planet? A planet is a body orbiting around the sun with enough mass and therefore gravity to be round. A planet has also ‘cleared its neighbourhood’, orbit by sucking in small bodies or deflecting them away from their orbit. There are eight planets within our Galaxy: ...
Extra Terrestrial Excursions
... Extra Terrestrial Excursions – Special Delivery Imagine that you work for the Solar System’s Delivery Service. You need to determine the time necessary to make certain deliveries and return to Earth. The planets are not lined up in a straight line in their orbits around the Sun. ...
... Extra Terrestrial Excursions – Special Delivery Imagine that you work for the Solar System’s Delivery Service. You need to determine the time necessary to make certain deliveries and return to Earth. The planets are not lined up in a straight line in their orbits around the Sun. ...
Pocket Solar System
... line along the fold marking the orbit and write the name of the planet along that line. This will help keep the writing small enough so the names are less likely to overlap orbits for other planets, especially for the inner planets. An alternative, to speed things up when visitors may not know how t ...
... line along the fold marking the orbit and write the name of the planet along that line. This will help keep the writing small enough so the names are less likely to overlap orbits for other planets, especially for the inner planets. An alternative, to speed things up when visitors may not know how t ...
Activity: Pocket solar system
... line along the fold marking the orbit and write the name of the planet along that line. This will help keep the writing small enough so the names are less likely to overlap orbits for other planets, especially for the inner planets. An alternative, to speed things up when visitors may not know how t ...
... line along the fold marking the orbit and write the name of the planet along that line. This will help keep the writing small enough so the names are less likely to overlap orbits for other planets, especially for the inner planets. An alternative, to speed things up when visitors may not know how t ...
Embedding Comets in the Asteroid Belt - SwRI Boulder
... It is well known that the long-term dynamical stability of asteroids, particularly those in MMRs with the giant planets, is sensitive to the exact orbits of the planets [12, 13]. So, although the above migration simulations place Jupiter and Saturn on roughly their current orbits, we found we needed ...
... It is well known that the long-term dynamical stability of asteroids, particularly those in MMRs with the giant planets, is sensitive to the exact orbits of the planets [12, 13]. So, although the above migration simulations place Jupiter and Saturn on roughly their current orbits, we found we needed ...
space-rocks - WLWV Staff Blogs
... through the solar system. These collisions result in numerous small particles and fragments, called meteoroids. Meteoroids are usually found orbiting the ...
... through the solar system. These collisions result in numerous small particles and fragments, called meteoroids. Meteoroids are usually found orbiting the ...
Powerpoint - BU Imaging Science
... • Most moons (especially the larger ones) orbit in near-circular orbits in the same plane as the equator of their parent planet • Most moons rotate so that their equator is in the plane of their orbit • Most moons rotate in the same “sense” as their orbit around the parent planet • Everything is rot ...
... • Most moons (especially the larger ones) orbit in near-circular orbits in the same plane as the equator of their parent planet • Most moons rotate so that their equator is in the plane of their orbit • Most moons rotate in the same “sense” as their orbit around the parent planet • Everything is rot ...
Our Planetary System (Chapter 7)
... • Most moons (especially the larger ones) orbit in near-circular orbits in the same plane as the equator of their parent planet • Most moons rotate so that their equator is in the plane of their orbit • Most moons rotate in the same “sense” as their orbit around the parent planet • Everything is rot ...
... • Most moons (especially the larger ones) orbit in near-circular orbits in the same plane as the equator of their parent planet • Most moons rotate so that their equator is in the plane of their orbit • Most moons rotate in the same “sense” as their orbit around the parent planet • Everything is rot ...
Some SOLAR SYSTEM notes
... 7.What is the asteroid belt? The asteroid belt is a zone between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is said that the asteroids in the asteroid belt never formed a planet because the gravity of nearby Jupiter kept pulling them apart. Today, millions of asteroids probably inhabit the asteroid belt, wi ...
... 7.What is the asteroid belt? The asteroid belt is a zone between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. It is said that the asteroids in the asteroid belt never formed a planet because the gravity of nearby Jupiter kept pulling them apart. Today, millions of asteroids probably inhabit the asteroid belt, wi ...
Lecture 1 - Sizes and distances, scientific notation
... Scale model of solar system • To fit the solar system into the classroom, we scaled the radius of the orbit of Neptune to be about 18 meters (59 feet) • Sun is the size of a match head • Jupiter is smaller than a grain of salt • Earth has the diameter of a strand of hair ...
... Scale model of solar system • To fit the solar system into the classroom, we scaled the radius of the orbit of Neptune to be about 18 meters (59 feet) • Sun is the size of a match head • Jupiter is smaller than a grain of salt • Earth has the diameter of a strand of hair ...
Solar System 3
... • These objects, which include the first observed and named, Pluto, also have eccentric orbits in comparison to the inner eight planets. • Although Pluto was discovered in 1930, no other objects of comparable size and greater distance were detected until the 1990s and later. • Pluto has a very eccen ...
... • These objects, which include the first observed and named, Pluto, also have eccentric orbits in comparison to the inner eight planets. • Although Pluto was discovered in 1930, no other objects of comparable size and greater distance were detected until the 1990s and later. • Pluto has a very eccen ...
Our Solar System
... Asteroids, meteoroids and comets are small pieces of rock left over as debris from the formation of the solar system. A comet can be a beautiful sight and is unlike any other object in the sky. A few of the brightest comets are visible with the naked eye as extended fuzzy patches. Seeing most, howe ...
... Asteroids, meteoroids and comets are small pieces of rock left over as debris from the formation of the solar system. A comet can be a beautiful sight and is unlike any other object in the sky. A few of the brightest comets are visible with the naked eye as extended fuzzy patches. Seeing most, howe ...
What is the solar system?
... Classify List the inner planets in order from smallest to largest. ______________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Critic ...
... Classify List the inner planets in order from smallest to largest. ______________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ Critic ...
Section 4
... • In recent years, scientists have discovered hundreds of objects in our solar system beyond Neptune’s orbit. These objects are called trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) and exist in the Kuiper Belt. • Kuiper Belt a region of the solar system that is just beyond the orbit of Neptune and that contains dw ...
... • In recent years, scientists have discovered hundreds of objects in our solar system beyond Neptune’s orbit. These objects are called trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) and exist in the Kuiper Belt. • Kuiper Belt a region of the solar system that is just beyond the orbit of Neptune and that contains dw ...
How to Use This Presentation
... • In recent years, scientists have discovered hundreds of objects in our solar system beyond Neptune’s orbit. These objects are called trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) and exist in the Kuiper Belt. • Kuiper Belt a region of the solar system that is just beyond the orbit of Neptune and that contains dw ...
... • In recent years, scientists have discovered hundreds of objects in our solar system beyond Neptune’s orbit. These objects are called trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) and exist in the Kuiper Belt. • Kuiper Belt a region of the solar system that is just beyond the orbit of Neptune and that contains dw ...
THE FRIGID REALM
... rotation axis. No explanation for this. Uranus lacks an internal heat source, unlike the other three outer planets. The interior pressures are too low for metallic hydrogen to form, so hydrogen remains molecular down to the rocky core. A slushy layer of water ice and dissolved ammonia may form the “ ...
... rotation axis. No explanation for this. Uranus lacks an internal heat source, unlike the other three outer planets. The interior pressures are too low for metallic hydrogen to form, so hydrogen remains molecular down to the rocky core. A slushy layer of water ice and dissolved ammonia may form the “ ...
plutinos
... rotational periods of two different bodies with simple whole number ratios. Tidal or gravitational lock is an extreme case of orbital resonance; the Earth’s moon’s orbital period exactly matches its own rotational period (roughly one month) — the ratio in this case is 1:1. The cause of resonance is ...
... rotational periods of two different bodies with simple whole number ratios. Tidal or gravitational lock is an extreme case of orbital resonance; the Earth’s moon’s orbital period exactly matches its own rotational period (roughly one month) — the ratio in this case is 1:1. The cause of resonance is ...
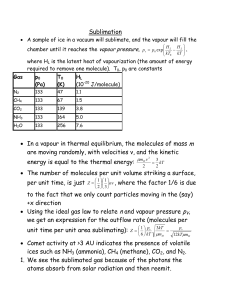
Sublimation • In a vapour in thermal equilibrium, the molecules of
... atoms absorb from solar radiation and then reemit. ...
... atoms absorb from solar radiation and then reemit. ...
Page 598 - ClassZone
... a diameter of about 1200 kilometers. Given their similarity in mass, some scientists consider Pluto and Charon to be a double planet, rather than a planet-moon system. Pluto is so far away from Earth—an average of 39.5 AUs from the sun— that it was not discovered until 1930. Its surface temperature ...
... a diameter of about 1200 kilometers. Given their similarity in mass, some scientists consider Pluto and Charon to be a double planet, rather than a planet-moon system. Pluto is so far away from Earth—an average of 39.5 AUs from the sun— that it was not discovered until 1930. Its surface temperature ...
2/1/2012- Outer Planets Notes
... • Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. • It is four times larger than Earth with 27 moons. • The atmosphere of Uranus contains hydrogen, helium, and about two percent methane. • The methane gives the planet its blue-green color. • Uranus’s axis of rotation is tilted, so that it is nearly paral ...
... • Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. • It is four times larger than Earth with 27 moons. • The atmosphere of Uranus contains hydrogen, helium, and about two percent methane. • The methane gives the planet its blue-green color. • Uranus’s axis of rotation is tilted, so that it is nearly paral ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Clicker Question: In the leading theory of solar system formation, the planets: A: were ejected from the Sun following a close encounter with another star. B: formed from the same flattened, swirling gas cloud that formed the sun. C: were formed before the Sun. D: were captured by the Sun as it tra ...
... Clicker Question: In the leading theory of solar system formation, the planets: A: were ejected from the Sun following a close encounter with another star. B: formed from the same flattened, swirling gas cloud that formed the sun. C: were formed before the Sun. D: were captured by the Sun as it tra ...
Scattered disc

The scattered disc (or scattered disk) is a distant region of the Solar System that is sparsely populated by icy minor planets, a subset of the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects. The scattered-disc objects (SDOs) have orbital eccentricities ranging as high as 0.8, inclinations as high as 40°, and perihelia greater than 30 astronomical units (4.5×109 km; 2.8×109 mi). These extreme orbits are thought to be the result of gravitational ""scattering"" by the gas giants, and the objects continue to be subject to perturbation by the planet Neptune.Although the closest scattered-disc objects approach the Sun at about 30–35 AU, their orbits can extend well beyond 100 AU. This makes scattered objects among the most distant and coldest objects in the Solar System. The innermost portion of the scattered disc overlaps with a torus-shaped region of orbiting objects traditionally called the Kuiper belt, but its outer limits reach much farther away from the Sun and farther above and below the ecliptic than the Kuiper belt proper.Because of its unstable nature, astronomers now consider the scattered disc to be the place of origin for most periodic comets in the Solar System, with the centaurs, a population of icy bodies between Jupiter and Neptune, being the intermediate stage in an object's migration from the disc to the inner Solar System. Eventually, perturbations from the giant planets send such objects towards the Sun, transforming them into periodic comets. Many Oort cloud objects are also thought to have originated in the scattered disc. Detached objects are not sharply distinct from scattered disc objects, and some such as Sedna have sometimes been considered to be included in this group.