Lecture 23 - UConn Physics
... • If Ampere’s Law were correct, the right hand side of Faraday’s Law should be equal to zero -- since no magnetic current. • Therefore(?), maybe there is a problem with Ampere’s Law. • In fact, Maxwell proposes a modification of Ampere’s Law by adding another term (the “displacement” current) to the ...
... • If Ampere’s Law were correct, the right hand side of Faraday’s Law should be equal to zero -- since no magnetic current. • Therefore(?), maybe there is a problem with Ampere’s Law. • In fact, Maxwell proposes a modification of Ampere’s Law by adding another term (the “displacement” current) to the ...
1. Short Answer 2
... Free current I flows uniformly through the inner conductor in the +ẑ direction and back along the outer cylinder in the -ẑ direction, as shown below. The space between the two cylinders contains a linear insulating material with permeability µ. The inner and outer conductors have no magnetic susce ...
... Free current I flows uniformly through the inner conductor in the +ẑ direction and back along the outer cylinder in the -ẑ direction, as shown below. The space between the two cylinders contains a linear insulating material with permeability µ. The inner and outer conductors have no magnetic susce ...
p3 unit2 sco
... - list and name the type of energy transformation from various sources of electrical energy, including voltaic cells, piezoelectric, thermoelectric, photoelectric and generators - analyze the relationship between voltage rises and voltage drops across linear resistors and sources - define electrical ...
... - list and name the type of energy transformation from various sources of electrical energy, including voltaic cells, piezoelectric, thermoelectric, photoelectric and generators - analyze the relationship between voltage rises and voltage drops across linear resistors and sources - define electrical ...
PHY2112 - College of DuPage
... 10. Calculate the magnetic field caused by a moving charge 11. Calculate the force on a moving charge due to a magnetic field 12. Calculate the magnetic forces and torques on both looped and straight current carrying wires. 13. Calculate the currents caused by both mutual-inductance and self-inducta ...
... 10. Calculate the magnetic field caused by a moving charge 11. Calculate the force on a moving charge due to a magnetic field 12. Calculate the magnetic forces and torques on both looped and straight current carrying wires. 13. Calculate the currents caused by both mutual-inductance and self-inducta ...
01ST_Q
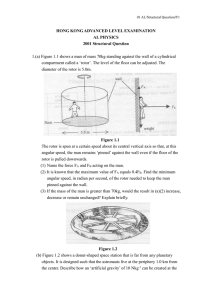
... (2) Drops gradually from P to Q and becomes steady along QC. (c) (1) What is the maximum torque acting on the coil due to the current when it is rotating at constant speed? (2) For the motor running at constant speed, calculate (I) the back e.m.f. developed across the coil; (II) its efficiency in co ...
... (2) Drops gradually from P to Q and becomes steady along QC. (c) (1) What is the maximum torque acting on the coil due to the current when it is rotating at constant speed? (2) For the motor running at constant speed, calculate (I) the back e.m.f. developed across the coil; (II) its efficiency in co ...
PHYS_2326_022409
... Charges in Motion – Electric Current Electric Current – a method to deliver energy Very convenient way to transport energy no moving parts (only microscopic charges) Electric currents is in the midst of electronic circuits and living organisms alike ...
... Charges in Motion – Electric Current Electric Current – a method to deliver energy Very convenient way to transport energy no moving parts (only microscopic charges) Electric currents is in the midst of electronic circuits and living organisms alike ...
Document
... flows in one direction and a common example is a battery: AC stands for “Alternating Current” – the current changes direction 50 times every second (frequency = 50Hz). In the UK mains electricity is 230V AC, not DC, as AC is easier to generate and transmit over long distances. ...
... flows in one direction and a common example is a battery: AC stands for “Alternating Current” – the current changes direction 50 times every second (frequency = 50Hz). In the UK mains electricity is 230V AC, not DC, as AC is easier to generate and transmit over long distances. ...
Slide 1
... • The potential energy difference is due to a physical separation (a distance) between the two points • This potential difference provides a force which can move charges from place to place. • This is sometimes called an electromotive force (emf) ...
... • The potential energy difference is due to a physical separation (a distance) between the two points • This potential difference provides a force which can move charges from place to place. • This is sometimes called an electromotive force (emf) ...
Ch. 20 Magnetic Induction
... change from 0 to its maximum value of I = /R immediately. Faraday’s Law prevent this. As the current increases from zero, a magnetic field is produced and the flux through the loop increases. The increasing flux induces an emf that opposes the change in magnetic flux. ...
... change from 0 to its maximum value of I = /R immediately. Faraday’s Law prevent this. As the current increases from zero, a magnetic field is produced and the flux through the loop increases. The increasing flux induces an emf that opposes the change in magnetic flux. ...