Worksheet_18 - Iowa State University
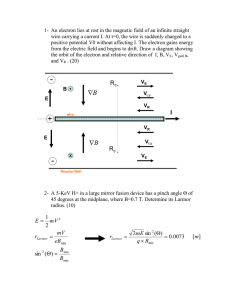
... turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 0.050 T, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b) What is the magnetic flux through a cube drawn around the electron? ...
... turned on. The strength of the magnetic field is 0.050 T, and it is directed into the paper. (a) Describe the path of the electron after the field has been turned on (assuming only magnetic effects). (b) What is the magnetic flux through a cube drawn around the electron? ...
Midterm Exam No. 01 (Spring 2014)
... axis determined by the cross product of direction of radius vector and direction of current. (a) If you double the radius of the solenoid, how much does the magnetic field inside the solenoid change? (b) The force on a charge particle due to a magnetic field is given by F = qv × B. What is the force ...
... axis determined by the cross product of direction of radius vector and direction of current. (a) If you double the radius of the solenoid, how much does the magnetic field inside the solenoid change? (b) The force on a charge particle due to a magnetic field is given by F = qv × B. What is the force ...
TCAP Review 2013 – Page 9 – Electromagnetism
... Draw the figure of the Earth’s magnetic poles on p. 429. ...
... Draw the figure of the Earth’s magnetic poles on p. 429. ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.



![NAME: Quiz #5: Phys142 1. [4pts] Find the resulting current through](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006404813_1-90fcf53f79a7b619eafe061618bfacc1-300x300.png)