Phy753syl-ziad
... Review: Electric field and potential, multipole potentials and fields, electric field in material media; Magnetic field, Biot Savart’s law and Ampere’s law, magnetic field in material media, vector potential, Green’s theorem. Boundary value problems in electrostatics and magnetostatics: Laplace’s an ...
... Review: Electric field and potential, multipole potentials and fields, electric field in material media; Magnetic field, Biot Savart’s law and Ampere’s law, magnetic field in material media, vector potential, Green’s theorem. Boundary value problems in electrostatics and magnetostatics: Laplace’s an ...
Lecture 9 Source of Magnetic field
... The magnetic flux FB is FB B dA The unit of magnetic flux is T.m2 = Wb Wb is a weber ...
... The magnetic flux FB is FB B dA The unit of magnetic flux is T.m2 = Wb Wb is a weber ...
Physical Science Chapter 15 Exam
... Matching: Match the description to the correct term. 12. unlike poles attract, like poles repel 13. Device for protecting buildings and other structures from lightning strikes. 14. Device that produces a strong magnetic field when electricity passes through it 15. Object capable of attracting object ...
... Matching: Match the description to the correct term. 12. unlike poles attract, like poles repel 13. Device for protecting buildings and other structures from lightning strikes. 14. Device that produces a strong magnetic field when electricity passes through it 15. Object capable of attracting object ...
PHYS_2326_040909
... current in the direction of rotation. Think of the electron as a ball with charge distributed over its surface. When the ball spins, that charge is set in motion around the electron's spin axis, resulting in a magnetic field specific to the electron. The electron is like a magnetic dipole, a miniatu ...
... current in the direction of rotation. Think of the electron as a ball with charge distributed over its surface. When the ball spins, that charge is set in motion around the electron's spin axis, resulting in a magnetic field specific to the electron. The electron is like a magnetic dipole, a miniatu ...
Mathematics and waves
... The Maxwell equations have also been the starting point for the development of relativity theory by Albert Einstein because they predict the existence of a fixed speed of light, independent of the speed of the ...
... The Maxwell equations have also been the starting point for the development of relativity theory by Albert Einstein because they predict the existence of a fixed speed of light, independent of the speed of the ...
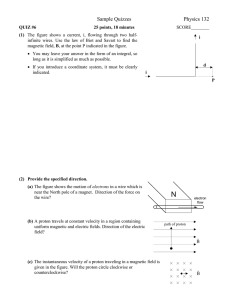
Sample Quizzes Physics 132
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
Current electricity
... 13:- Capacitance does not increases or decreases by increasing or decreasing the charge effect was first observed by EDWIN HALL. So it is called Hall effect. on the plates because with increase or decrease in charge voltage also increase or decrease. 29:- When current is in x- direction & Magnetic f ...
... 13:- Capacitance does not increases or decreases by increasing or decreasing the charge effect was first observed by EDWIN HALL. So it is called Hall effect. on the plates because with increase or decrease in charge voltage also increase or decrease. 29:- When current is in x- direction & Magnetic f ...
Class #34 Slides
... visible light range from 400 nm (violet) to about 780 nm (red). What is the range of frequencies of visible light? (1 nm = 10-9 m) ...
... visible light range from 400 nm (violet) to about 780 nm (red). What is the range of frequencies of visible light? (1 nm = 10-9 m) ...
cyclotron
... experiences a force in the electric field which is set up between the 2 chambers. It accelerates and enters into the chamber which is at low potential (-ve). Inside the chamber electric field is 0 but the magnetic field changes the direction of the particle into semi-circular path. By the time it co ...
... experiences a force in the electric field which is set up between the 2 chambers. It accelerates and enters into the chamber which is at low potential (-ve). Inside the chamber electric field is 0 but the magnetic field changes the direction of the particle into semi-circular path. By the time it co ...
Stationary charge
... A positive electric charge of negligible weight is released from rest between the poles of horseshoe magnet. What should be the direction of the acceleration of the charge caused by the magnetic field? Answer You don’t say if the magnet is in a gravitational field or not. However since the force on ...
... A positive electric charge of negligible weight is released from rest between the poles of horseshoe magnet. What should be the direction of the acceleration of the charge caused by the magnetic field? Answer You don’t say if the magnet is in a gravitational field or not. However since the force on ...
Week 8 Homework 1 Serway 20.1 Physics 1B
... An emf is caused by a change in flux, which can be produced by a change in magnetic field strength, magnetic field direction, or area perpendicular to the magnetic field. Since the magnetic field in this problem is constant (not changing in magnitude or direction), an emf can only be produced by cha ...
... An emf is caused by a change in flux, which can be produced by a change in magnetic field strength, magnetic field direction, or area perpendicular to the magnetic field. Since the magnetic field in this problem is constant (not changing in magnitude or direction), an emf can only be produced by cha ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.