Magnetism
... South end of the magnet. The field is strongest at the poles. Notice the lines are closer together there. ...
... South end of the magnet. The field is strongest at the poles. Notice the lines are closer together there. ...
1-Electromagnetic Forces - MrD-Home
... Current carrying wire… • A static distribution of charges produces an electric field • Charges in motion (an electrical current) produce a magnetic field ...
... Current carrying wire… • A static distribution of charges produces an electric field • Charges in motion (an electrical current) produce a magnetic field ...
Chapter 14: Magnetism Brent Royuk Phys-110
... There is a “braking effect” caused by a generator that is a voltage that resists the changing current, and it’s called Back EMF. When motors are spun by electricity, they generate a back EMF ...
... There is a “braking effect” caused by a generator that is a voltage that resists the changing current, and it’s called Back EMF. When motors are spun by electricity, they generate a back EMF ...
Solution Derivations for Capa #8
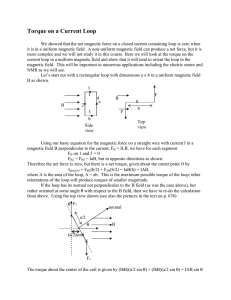
... The direction is given by curling your fingers in the direction of I. It is important for the next problem. 4) Calculate the magnitude of the torque about the z-axis on the loop. Torque is given by τ = µ × B = |µ| |B| sin φ Imagine looking at the problem from the top. In this case, B is pointing dow ...
... The direction is given by curling your fingers in the direction of I. It is important for the next problem. 4) Calculate the magnitude of the torque about the z-axis on the loop. Torque is given by τ = µ × B = |µ| |B| sin φ Imagine looking at the problem from the top. In this case, B is pointing dow ...
Physical Science Chapter 17 Practice Test #2
... a. repel each other. c. cancel out each other’s magnetic fields. b. attract each other. d. point toward the north pole. 4. The magnetism of a piece of magnetized iron can be weakened by a. heating and hammering the iron. c. bending the iron. b. touching unmagnetized iron. d. None of the above 5. The ...
... a. repel each other. c. cancel out each other’s magnetic fields. b. attract each other. d. point toward the north pole. 4. The magnetism of a piece of magnetized iron can be weakened by a. heating and hammering the iron. c. bending the iron. b. touching unmagnetized iron. d. None of the above 5. The ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.