Faraday`s Law of Induction
... The line integral of the electric field around a closed loop is equal to the negative of the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the area enclosed by the loop. This line integral is equal to the generated voltage or emf in the loop, so Faraday's law is the basis for electric generators. It a ...
... The line integral of the electric field around a closed loop is equal to the negative of the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the area enclosed by the loop. This line integral is equal to the generated voltage or emf in the loop, so Faraday's law is the basis for electric generators. It a ...
L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]
... Magnetic forces • Magnetic fields exert sidewise forces on charges • A charge is turned around by the magnetic force • There is NO magnetic force if the charge is ...
... Magnetic forces • Magnetic fields exert sidewise forces on charges • A charge is turned around by the magnetic force • There is NO magnetic force if the charge is ...
File - SloanZone Physics
... 6. Charged particles having momentum p1, pass perpendicularly through a magnetic field and their circular path has a radius of r. What would the radius be for particles with the same charge having momentum p22p1 ...
... 6. Charged particles having momentum p1, pass perpendicularly through a magnetic field and their circular path has a radius of r. What would the radius be for particles with the same charge having momentum p22p1 ...
Physics 213 — Problem Set 8 —Solutions Spring 1998
... and J(r) = 0 for r > R, where r is the distance from a point of interest to the central axis running along the length of the wire. (a) Find the resulting magnetic field inside (r ≤ R) and outside (r > R) the wire. (b) Plot the magnitude of the magnetic field as a function of r. (c) Find the location ...
... and J(r) = 0 for r > R, where r is the distance from a point of interest to the central axis running along the length of the wire. (a) Find the resulting magnetic field inside (r ≤ R) and outside (r > R) the wire. (b) Plot the magnitude of the magnetic field as a function of r. (c) Find the location ...
magnetic field - Rosehill
... If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter how small the pieces of the magnet become, each piece ...
... If you take a bar magnet and break it into two pieces, each piece will again have a North pole and a South pole. If you take one of those pieces and break it into two, each of the smaller pieces will have a North pole and a South pole. No matter how small the pieces of the magnet become, each piece ...
Magnetism 17.1 Properties of Magnets 17.2 Electromagnets 17.3
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
2 - Physics at Oregon State University
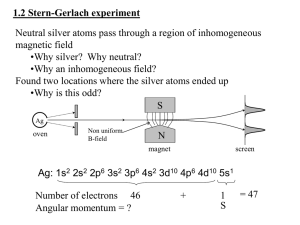
... •How can a neutral atom interact with a magnetic field? •Let’s derive it classically from intro-course principles •What does a simple magnetic dipole look like? •What does the energy look like? •What will the force be and why does the B need to be inhomogeneous? •How do we relate this to angular mom ...
... •How can a neutral atom interact with a magnetic field? •Let’s derive it classically from intro-course principles •What does a simple magnetic dipole look like? •What does the energy look like? •What will the force be and why does the B need to be inhomogeneous? •How do we relate this to angular mom ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.




![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008057814_1-60bd3a273eeadb9e6de7a28a98376c5d-300x300.png)