7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
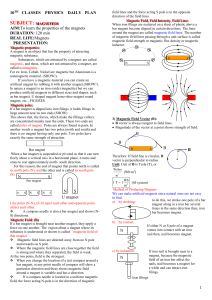
... omes to rest approximately north- south direction. For this reason, the end of magnet that points north is called its north pole (N), and the other end is called its south pole (S). ...
... omes to rest approximately north- south direction. For this reason, the end of magnet that points north is called its north pole (N), and the other end is called its south pole (S). ...
2 - Helios Home Page
... Charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere and the electric field it produces at points outside the sphere is like the field of a point particle with charge equal to the net charge on the sphere. That is, the magnitude of the field is given by E = q/4πε0r2, where q is the magnitu ...
... Charge is distributed uniformly over the surface of the sphere and the electric field it produces at points outside the sphere is like the field of a point particle with charge equal to the net charge on the sphere. That is, the magnitude of the field is given by E = q/4πε0r2, where q is the magnitu ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
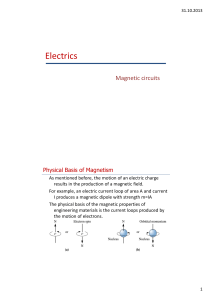
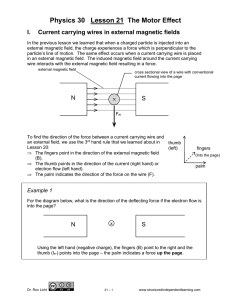
... After Oersted’s discovery, Andre-Marie Ampere performed extensive experiments and did an insightful mathematical analysis of the magnetic field induced around a current carrying wire. In addition, he studied the forces between current carrying wires. The induced magnetic fields around the wires inte ...
... After Oersted’s discovery, Andre-Marie Ampere performed extensive experiments and did an insightful mathematical analysis of the magnetic field induced around a current carrying wire. In addition, he studied the forces between current carrying wires. The induced magnetic fields around the wires inte ...
Plum pudding
... Solution: There are two forces acting on each electron: The one due to the other electron and the one due to the charge inside the sphere of radius “x”. Notice that the charge outside this radius doesn’t contribute any net force. So: - The force due to the other electron is repulsive and given by: ...
... Solution: There are two forces acting on each electron: The one due to the other electron and the one due to the charge inside the sphere of radius “x”. Notice that the charge outside this radius doesn’t contribute any net force. So: - The force due to the other electron is repulsive and given by: ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.