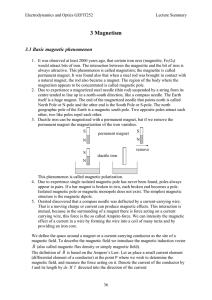
The Magnetic Field
... arise from currents in its molten iron core. – The magnetic poles are offset slightly from the geographic poles of the Earth’s rotation axis. – The geographic north pole is actually a south magnetic pole. ...
... arise from currents in its molten iron core. – The magnetic poles are offset slightly from the geographic poles of the Earth’s rotation axis. – The geographic north pole is actually a south magnetic pole. ...
Coulomb`s Law
... • The charge (q) of a particle is NOT a vector quantity. • Therefore, when described as “POSITIVE” or “NEGATIVE” that tells whether it is a proton or electron, but is NOT part of the magnitude of the charge. • DO NOT PUT THE NEGATIVES ...
... • The charge (q) of a particle is NOT a vector quantity. • Therefore, when described as “POSITIVE” or “NEGATIVE” that tells whether it is a proton or electron, but is NOT part of the magnitude of the charge. • DO NOT PUT THE NEGATIVES ...
P (0,d) y x a −a x+dx
... As part of your calculation, you should find the unit vector which points in the direction from the charge element towards point P . ...
... As part of your calculation, you should find the unit vector which points in the direction from the charge element towards point P . ...
Chapter 30
... one electron is canceled by that of another electron orbiting in the same direction ...
... one electron is canceled by that of another electron orbiting in the same direction ...
Physics 2102 Spring 2002 Lecture 2
... • Electric charge - Electric force on other electric charges - Electric field, and electric potential • Moving electric charges : current ...
... • Electric charge - Electric force on other electric charges - Electric field, and electric potential • Moving electric charges : current ...
国家杰出青年科学基金 申请书
... Relativistic s-w model + the configuration mixing within one major shell for the mirror pairs, 150-15N, 170-17F, 39K-39Ca and 41Ca-41S, removes most of the discrepancies for isovector moments while leaving the isoscalar moments unaltered, i.e. also in agreement with experiment when vertex correcti ...
... Relativistic s-w model + the configuration mixing within one major shell for the mirror pairs, 150-15N, 170-17F, 39K-39Ca and 41Ca-41S, removes most of the discrepancies for isovector moments while leaving the isoscalar moments unaltered, i.e. also in agreement with experiment when vertex correcti ...
Homework No. 04 (2014 Fall) PHYS 320: Electricity and Magnetism I
... (c) Rewrite your results for the case when the solid slab is a perfect conductor? (Assume the same charge per unit area σ. Note that the charge is now only on the surface.) (d) Rewrite your results for the case of a uniformly charged hollow slab of infinite extent and thickness 2R with charge per un ...
... (c) Rewrite your results for the case when the solid slab is a perfect conductor? (Assume the same charge per unit area σ. Note that the charge is now only on the surface.) (d) Rewrite your results for the case of a uniformly charged hollow slab of infinite extent and thickness 2R with charge per un ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... The fine structure cannot be explained with the Coulomb interaction between the nucleus and the electrons. It results from a magnetic interaction between the orbital magnetic moment and the intrinsic moments of the electron, the spinorbital coupling. Depending on whether the two moments are parallel ...
... The fine structure cannot be explained with the Coulomb interaction between the nucleus and the electrons. It results from a magnetic interaction between the orbital magnetic moment and the intrinsic moments of the electron, the spinorbital coupling. Depending on whether the two moments are parallel ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.





![L 29 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Laws of Magnetism The electric](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001482032_1-b69d1eb7a0f8c001e0e2a09bf26d62d2-300x300.png)