connection between wave functions in the dirac and
... A. J. Silenko1 Institute of Nuclear Problems, Belarusian State University, Minsk, Belarus When the FoldyÄWouthuysen (FW) transformation is exact and the particle energy is positive, upper spinors in the Dirac and FW representations differ only by a constant factor and lower spinors in the FW represe ...
... A. J. Silenko1 Institute of Nuclear Problems, Belarusian State University, Minsk, Belarus When the FoldyÄWouthuysen (FW) transformation is exact and the particle energy is positive, upper spinors in the Dirac and FW representations differ only by a constant factor and lower spinors in the FW represe ...
Lecture 12
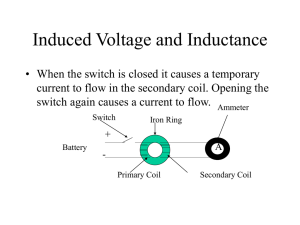
... The circuit shown in the figure consists of a wire loop connected to a sensitive ammeter (known as a "galvanometer"). If we approach the loop with a permanent magnet we see a current being registered by the galvanometer. The results can be summarized as follows: 1. A current appears only if there is ...
... The circuit shown in the figure consists of a wire loop connected to a sensitive ammeter (known as a "galvanometer"). If we approach the loop with a permanent magnet we see a current being registered by the galvanometer. The results can be summarized as follows: 1. A current appears only if there is ...
Lecture 4
... •The integral is the sum of the tangential (to the path) component of the electric field along a path from A to B. •The question now is: Does this integral depend upon the exact path chosen to move from A to B? •If it does, we have a lousy definition. • Hopefully, it doesn’t. • It doesn’t. But, don’ ...
... •The integral is the sum of the tangential (to the path) component of the electric field along a path from A to B. •The question now is: Does this integral depend upon the exact path chosen to move from A to B? •If it does, we have a lousy definition. • Hopefully, it doesn’t. • It doesn’t. But, don’ ...
Lecture 1210
... The circuit shown in the figure consists of a wire loop connected to a sensitive ammeter (known as a "galvanometer"). If we approach the loop with a permanent magnet we see a current being registered by the galvanometer. The results can be summarized as follows: 1. A current appears only if there is ...
... The circuit shown in the figure consists of a wire loop connected to a sensitive ammeter (known as a "galvanometer"). If we approach the loop with a permanent magnet we see a current being registered by the galvanometer. The results can be summarized as follows: 1. A current appears only if there is ...
Exam 3
... A) 0.16 V B) 0.13 V C) 91 mV D) 68 mV E) 29 mV Ans: C 23. You place a coil that has 200 turns and a cross-sectional area of 0.050 m2 so that its plane is normal to a field of 3.0 T. If the field is uniformly decreased to zero in 5.0 s, what emf is induced in the coil? A) 0.15 kV B) 0.12 kV C) 6.0 V ...
... A) 0.16 V B) 0.13 V C) 91 mV D) 68 mV E) 29 mV Ans: C 23. You place a coil that has 200 turns and a cross-sectional area of 0.050 m2 so that its plane is normal to a field of 3.0 T. If the field is uniformly decreased to zero in 5.0 s, what emf is induced in the coil? A) 0.15 kV B) 0.12 kV C) 6.0 V ...
ELECTROSTATICS I Electric charges and Coulomb’s law (Important formulae and Concepts)
... 15. Explain the underlying principle of working of a parallel plate capacitor. If two similar plates, each of area A having surface charge densities + and - are separated by a distance d in air, write expression for (i) the electric field at points between the two plates. (ii) The potential diffe ...
... 15. Explain the underlying principle of working of a parallel plate capacitor. If two similar plates, each of area A having surface charge densities + and - are separated by a distance d in air, write expression for (i) the electric field at points between the two plates. (ii) The potential diffe ...
36 Magnetism
... Magnetic poles behave similarly to electric charges in some ways, but there is a very important difference. • Electric charges can be isolated, but magnetic poles cannot. • A north magnetic pole never exists without the presence of a south pole, and vice versa. • The north and south poles of a magne ...
... Magnetic poles behave similarly to electric charges in some ways, but there is a very important difference. • Electric charges can be isolated, but magnetic poles cannot. • A north magnetic pole never exists without the presence of a south pole, and vice versa. • The north and south poles of a magne ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.