Magnetic Effects4 - Cbsephysicstutorials
... chamber and travels undeflected along a straight path with constant speed. What can you say about the initial velocity of the particle? (b) A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction, and comes out o ...
... chamber and travels undeflected along a straight path with constant speed. What can you say about the initial velocity of the particle? (b) A charged particle enters an environment of a strong and non-uniform magnetic field varying from point to point both in magnitude and direction, and comes out o ...
1 hour (Demo) 1.5 hr (Lectu
... unit time, which electrically can be measured by the product of current and voltage. Power = current x voltage Electric power is measured in watts (or kilowatts), where 1 A x 1 V = 1 W. Series circuit – An electric circuit in which electrical devices are connected along a single wire such that the s ...
... unit time, which electrically can be measured by the product of current and voltage. Power = current x voltage Electric power is measured in watts (or kilowatts), where 1 A x 1 V = 1 W. Series circuit – An electric circuit in which electrical devices are connected along a single wire such that the s ...
Document
... are less dense where the field is weaker, the field is not necessarily zero where there are no lines. In fact, there is only one point within the figures below where the field is zero – can you find it? ...
... are less dense where the field is weaker, the field is not necessarily zero where there are no lines. In fact, there is only one point within the figures below where the field is zero – can you find it? ...
Zahn, M. Power Dissipation and Magnetic Forces on MAGLEV Rebars, IEEE Transactions on Magnetics, Vol. 33, No. 2, March 1997, pp. 1021-1036
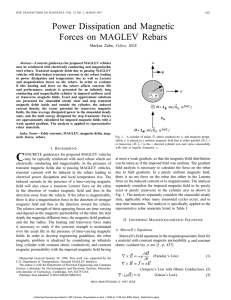
... 2) Magnetization Force: The magnetization force on linear magnetizable material with magnetic permeability that depends on space is ...
... 2) Magnetization Force: The magnetization force on linear magnetizable material with magnetic permeability that depends on space is ...
Powerpoint Slides
... are less dense where the field is weaker, the field is not necessarily zero where there are no lines. In fact, there is only one point within the figures below where the field is zero – can you find it? ...
... are less dense where the field is weaker, the field is not necessarily zero where there are no lines. In fact, there is only one point within the figures below where the field is zero – can you find it? ...
ELECTROSTATICS powerpoint
... Goal: number of electrons (elementary charges) - Need charge in Coulombs first (1e=1.6x10-19 C) - How do we get the charge in Coulombs? - Can find them using coulomb’s law ...
... Goal: number of electrons (elementary charges) - Need charge in Coulombs first (1e=1.6x10-19 C) - How do we get the charge in Coulombs? - Can find them using coulomb’s law ...
CERN and Bubbel Chamber Detective
... There are seven largish electron trails and many smaller ones. If you look closely you can see that they all spiral to the right, so the field must be into the page. If one spiraled the other way it would be positrons 4) The beam particles are negative kaons. Why aren’t their trails curving to the r ...
... There are seven largish electron trails and many smaller ones. If you look closely you can see that they all spiral to the right, so the field must be into the page. If one spiraled the other way it would be positrons 4) The beam particles are negative kaons. Why aren’t their trails curving to the r ...
Sub-femtotesla scalar atomic magnetometer using multipass cells
... where δTc is the standard deviation of repeated measurements of Tc . The two multi-pass cells work as a gradiometer to mea√ sure ∂Bz /∂y with a noise level which is 2 larger than given by Eq. (5). While a scalar magnetometer does not require calibration, we check its response by applying a known sou ...
... where δTc is the standard deviation of repeated measurements of Tc . The two multi-pass cells work as a gradiometer to mea√ sure ∂Bz /∂y with a noise level which is 2 larger than given by Eq. (5). While a scalar magnetometer does not require calibration, we check its response by applying a known sou ...
Observation of magneto-optical second-harmonic - HAL-IOGS
... Surface collective electron oscillations, also known as surface plasmons ~SP!, can be excited in noble metals below the plasma frequency and may give rise to a variety of linear and nonlinear phenomena.1 The coupling of the electric field at optical frequencies with SP in metallic multilayer films r ...
... Surface collective electron oscillations, also known as surface plasmons ~SP!, can be excited in noble metals below the plasma frequency and may give rise to a variety of linear and nonlinear phenomena.1 The coupling of the electric field at optical frequencies with SP in metallic multilayer films r ...
free magnetic energy and flare productivity of active
... To check the statistical correlation between Efree and FIn−day , it is important that the sample is comprised major flaring, moderate flaring, and flare-quiet regions. Therefore, we give priority to NOAA 10930 and 10960, as they are two of the very few active regions which produced major flares. Mor ...
... To check the statistical correlation between Efree and FIn−day , it is important that the sample is comprised major flaring, moderate flaring, and flare-quiet regions. Therefore, we give priority to NOAA 10930 and 10960, as they are two of the very few active regions which produced major flares. Mor ...
Magnetic monopole
A magnetic monopole is a hypothetical elementary particle in particle physics that is an isolated magnet with only one magnetic pole (a north pole without a south pole or vice versa). In more technical terms, a magnetic monopole would have a net ""magnetic charge"". Modern interest in the concept stems from particle theories, notably the grand unified and superstring theories, which predict their existence.Magnetism in bar magnets and electromagnets does not arise from magnetic monopoles. There is no conclusive experimental evidence that magnetic monopoles exist at all in our universe.Some condensed matter systems contain effective (non-isolated) magnetic monopole quasi-particles, or contain phenomena that are mathematically analogous to magnetic monopoles.