Electromagnetism Quiz Review
... between the poles of a magnet. In which of the following positions would induce the greatest current in the loop? ...
... between the poles of a magnet. In which of the following positions would induce the greatest current in the loop? ...
Ampere`s Law
... by a wire and a 3-ohm resistor. A uniform magnetic field is in the z direction; its magnitude decreases steadily from .08 tesla to 0 in a time of 4 ...
... by a wire and a 3-ohm resistor. A uniform magnetic field is in the z direction; its magnitude decreases steadily from .08 tesla to 0 in a time of 4 ...
Physics Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70
... m-3. Find the drift velocity of electrons if a potential gradient of 1 Vm-1 is applied across X. Q. 18. What type of materials are used for making a. Permanent magnets b. Transformer cores. Give two line reasons for each Q. 19. In the circuit, what is the reading of the voltmeter? What resistance sh ...
... m-3. Find the drift velocity of electrons if a potential gradient of 1 Vm-1 is applied across X. Q. 18. What type of materials are used for making a. Permanent magnets b. Transformer cores. Give two line reasons for each Q. 19. In the circuit, what is the reading of the voltmeter? What resistance sh ...
P21 Homework Set #5
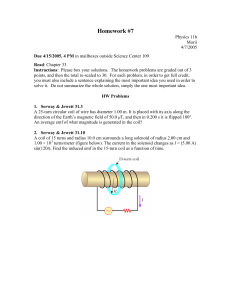
... Note that for the magnetic field of the loop, R is the radius of the loop, whereas, for the magnetic field of the wire, r is the distance from the straight section of the wire. In this situation, r is the distance from the point where the wire begins to bend into a loop. By using the right-hand rule ...
... Note that for the magnetic field of the loop, R is the radius of the loop, whereas, for the magnetic field of the wire, r is the distance from the straight section of the wire. In this situation, r is the distance from the point where the wire begins to bend into a loop. By using the right-hand rule ...
Global Lithospheric Apparent Susceptibility Distribution Converted
... the most fast quantitative interpretation tool for global studies. We just call this method AS85 hereinafter for short. Although Gubbins et al. (2011) provided a formula to directly calculate the apparent magnetic vector distribution, the AS85 method introduced constraints of magnetized direction an ...
... the most fast quantitative interpretation tool for global studies. We just call this method AS85 hereinafter for short. Although Gubbins et al. (2011) provided a formula to directly calculate the apparent magnetic vector distribution, the AS85 method introduced constraints of magnetized direction an ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.