Magnets Induction 2017
... 2. Gently shake the shavings around to see how the shavings respond to the magnet. 3. Try different shaped magnets but especially use a bar magnet. 4. Draw what you see when using the bar magnet. List ways Magnetic fields are like electric fields. ...
... 2. Gently shake the shavings around to see how the shavings respond to the magnet. 3. Try different shaped magnets but especially use a bar magnet. 4. Draw what you see when using the bar magnet. List ways Magnetic fields are like electric fields. ...
Chapter 31
... the plane of the coil is turned on. If the field changes linearly from 0 to 0.50 T in 0.80 s, (a) what is the magnitude of the induced emf in the coil while the field is changing? (b) If the ends of the coil are connected to a circuit and the total resistance is 2.0 , what is the current in the coi ...
... the plane of the coil is turned on. If the field changes linearly from 0 to 0.50 T in 0.80 s, (a) what is the magnitude of the induced emf in the coil while the field is changing? (b) If the ends of the coil are connected to a circuit and the total resistance is 2.0 , what is the current in the coi ...
Physics 30 - Structured Independent Learning
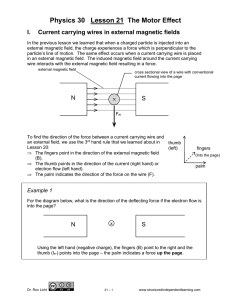
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
... B Using the left hand (negative charge), the fingers (B) point to the left and the thumb (e- flow) points down the page – the palm indicates a force which is out of the ...
Permanent magnets - KCPE-KCSE
... describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials understand the term ‘magnetic field line’ understand that magnetism is induced in some materials when they are placed in a magnetic field describe experiments to investigate the magnetic field pattern for a permanent bar magnet and that ...
... describe the properties of magnetically hard and soft materials understand the term ‘magnetic field line’ understand that magnetism is induced in some materials when they are placed in a magnetic field describe experiments to investigate the magnetic field pattern for a permanent bar magnet and that ...
When a coil of wire and a bar magnet are moved in relation to each
... Ex. 2 - An external agent supplies a 0.086-N force that keeps the rod moving at a constant speed of 5.0 m/s. Determine the work done in 60.0 s by the external agent. ...
... Ex. 2 - An external agent supplies a 0.086-N force that keeps the rod moving at a constant speed of 5.0 m/s. Determine the work done in 60.0 s by the external agent. ...
Goal: To understand Electro-magnetic fields
... • We have learned what magnetic fields are and why they are very important. • We have learned that the magnitude of the force is qvB and is perpendicular to either v or B. • We learned how to use the Right Hand Rule to find the direction of the force, velocity, or magnetic field. • In a constant B f ...
... • We have learned what magnetic fields are and why they are very important. • We have learned that the magnitude of the force is qvB and is perpendicular to either v or B. • We learned how to use the Right Hand Rule to find the direction of the force, velocity, or magnetic field. • In a constant B f ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.




![L 28 Electricity and Magnetism [6] Basic facts of Magnetism Induced](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001466251_1-8da9639fe3ec02e7200c360f9d7985ff-300x300.png)