Chapter 27:
... What is coming up for magnetic fields 1. A MOVING charge (or charges) produce a magnetic field in the space around it. 2. The magnetic field exerts a force on any other MOVING charge or current that is present in the field. ...
... What is coming up for magnetic fields 1. A MOVING charge (or charges) produce a magnetic field in the space around it. 2. The magnetic field exerts a force on any other MOVING charge or current that is present in the field. ...
7TH CLASSES PHYSICS DAILY PLAN
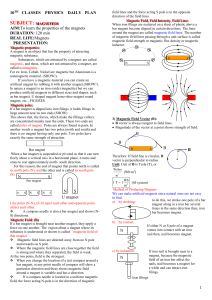
... becomes a magnet. Because, sudden motions of the domains in the iron bar are aligned in the direction in the earth’s magnetic field PPrroodduucciinngg EElleeccttrroo m maaggnneett By using electric current we will produce some effect of a magnet. When electric current passes through a conducting wir ...
... becomes a magnet. Because, sudden motions of the domains in the iron bar are aligned in the direction in the earth’s magnetic field PPrroodduucciinngg EElleeccttrroo m maaggnneett By using electric current we will produce some effect of a magnet. When electric current passes through a conducting wir ...
SUPERCONDUCTING MATERIALS
... reason the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches a speed that can sustain levitation. Propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forwards. The propulsion coils that exert a f ...
... reason the train must have wheels or some other form of landing gear to support the train until it reaches a speed that can sustain levitation. Propulsion coils on the guideway are used to exert a force on the magnets in the train and make the train move forwards. The propulsion coils that exert a f ...
202b399
... A conducting bar moves on conducting rails as shown. There is a uniform magnetic with magnitude .4 tesla directed into the page. The bar is pushed to the right at a constant speed of 25 m/s. The resistance (which completes the loop) is 2 . a) What is the EMF? b) What is the size and direction (cloc ...
... A conducting bar moves on conducting rails as shown. There is a uniform magnetic with magnitude .4 tesla directed into the page. The bar is pushed to the right at a constant speed of 25 m/s. The resistance (which completes the loop) is 2 . a) What is the EMF? b) What is the size and direction (cloc ...
Power Point
... – The electric force acts along the direction of the electric field – The magnetic force acts perpendicular to the magnetic field ...
... – The electric force acts along the direction of the electric field – The magnetic force acts perpendicular to the magnetic field ...
Ch33 - Siena College
... passes through an area bounded by a closed curve, the line integral of the magnetic field around the curve is given by Ampère’s law: ...
... passes through an area bounded by a closed curve, the line integral of the magnetic field around the curve is given by Ampère’s law: ...
p3 unit2 sco
... a conductor, and the time(t) taken, calculate the third quantity - given two of the voltage, the charge and energy developed by the source, calculate the third quantity • apply Ohm’s Law to series, parallel, and combination circuits - explain the energy transfer of charge around a circuit - list and ...
... a conductor, and the time(t) taken, calculate the third quantity - given two of the voltage, the charge and energy developed by the source, calculate the third quantity • apply Ohm’s Law to series, parallel, and combination circuits - explain the energy transfer of charge around a circuit - list and ...
Exam 4 Solutions
... 20. A 12 V battery is connected through a switch at time t=0 to a 1 F capacitor. There is a series resistor of 5 Ω in the circuit. At what time, in units of seconds (to two significant figures), is the voltage across the capacitor 6 V? a. 3.5 b. 1.5 c. 2.0 d. 2.5 e. 3.0 Solution: From chap. 27, eq. ...
... 20. A 12 V battery is connected through a switch at time t=0 to a 1 F capacitor. There is a series resistor of 5 Ω in the circuit. At what time, in units of seconds (to two significant figures), is the voltage across the capacitor 6 V? a. 3.5 b. 1.5 c. 2.0 d. 2.5 e. 3.0 Solution: From chap. 27, eq. ...
magnetic field - Derry Area School District
... • The resulting beam of ions introduced into the mass spectrometer has a distribution of speeds. Ions with a particular velocity are selected by means of a velocity selector, made up of charged plates and a magnetic field that allow particles traveling at only that velocity to go undeflected. • The ...
... • The resulting beam of ions introduced into the mass spectrometer has a distribution of speeds. Ions with a particular velocity are selected by means of a velocity selector, made up of charged plates and a magnetic field that allow particles traveling at only that velocity to go undeflected. • The ...
Title of PAPER - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... paper will be higher than that required. However, current research is still in the early stages and so hyperthermia via 1.9nm diameter nanoparticles cannot be neglected [1, 2, 6, 10, 11]).The velocity difference is calculated as the velocity of blood flow in the aorta (~1ms-1 [12]) the desired parti ...
... paper will be higher than that required. However, current research is still in the early stages and so hyperthermia via 1.9nm diameter nanoparticles cannot be neglected [1, 2, 6, 10, 11]).The velocity difference is calculated as the velocity of blood flow in the aorta (~1ms-1 [12]) the desired parti ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.