Magnetism - Bartol Research Institute
... • What is the magnetic moment of
the ground state? (M=B(L+2S))
• What is the average squared moment
?
• Show that = <1|M|G>
where |1> is the first excited state.
...
... • What is the magnetic moment
why do magnetic forces depend on who
... now that electrons in atoms jumping between energy levels produce spectral lines, so any affect on the way they move shows up in a shift of the lines. Today we regard the spinning electrons inside atoms as existing as quantum mechanical standing waves. Despite this, the electrons still act like tiny ...
... now that electrons in atoms jumping between energy levels produce spectral lines, so any affect on the way they move shows up in a shift of the lines. Today we regard the spinning electrons inside atoms as existing as quantum mechanical standing waves. Despite this, the electrons still act like tiny ...
the influence of the mechanical fatigue on the energy loss
... Thus the inductance of a coil of N turns can be determined from the magnetic circuit. Note that the inductance of a coil is directly proportional to the permeability of the medium inside the core of the coil. By using a ferromagnetic material such as iron as the core, the inductance can be increased ...
... Thus the inductance of a coil of N turns can be determined from the magnetic circuit. Note that the inductance of a coil is directly proportional to the permeability of the medium inside the core of the coil. By using a ferromagnetic material such as iron as the core, the inductance can be increased ...
Chapter 31
... the contacts to the rotating loop are made using a split ring called a commutator Use the active figure to vary the speed of rotation and observe the effect on the emf generated ...
... the contacts to the rotating loop are made using a split ring called a commutator Use the active figure to vary the speed of rotation and observe the effect on the emf generated ...
... You may use your one sheet of notes and formulas, but you must not collaborate with any other person. Do all four problems, showing your method and working clearly (a correct answer alone is not necessarily sufficient). Be sure to include correct SI units in your answers where appropriate. The numbe ...
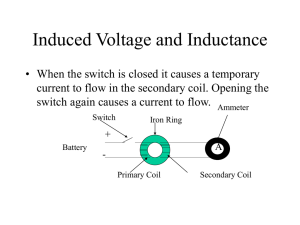
Induced Voltage and Inductance
... were able to flow, it oppose the change that causes it. • In the above diagram as the bar moves to the right the flux is increased into the page. To offset this the induced current must flow counterclockwise.If the bar is moved to the left current would flow clockwise. Induced current tends to maint ...
... were able to flow, it oppose the change that causes it. • In the above diagram as the bar moves to the right the flux is increased into the page. To offset this the induced current must flow counterclockwise.If the bar is moved to the left current would flow clockwise. Induced current tends to maint ...
The Atom`s Family
... Key Concepts A good way to increase the strength of the magnetic field is to coil the wire into a loop Then all the field lines point in the same direction in the center of the loop ...
... Key Concepts A good way to increase the strength of the magnetic field is to coil the wire into a loop Then all the field lines point in the same direction in the center of the loop ...
Physics 231 Course Review, Part 1
... 3. Electric Field Lines The local direction of the Field Lines is the direction of the electric field at that point The “density” of electric field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field at that point The direction of the electric field line give the direction of the force on ...
... 3. Electric Field Lines The local direction of the Field Lines is the direction of the electric field at that point The “density” of electric field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the electric field at that point The direction of the electric field line give the direction of the force on ...
AP® Physics C: Electricity and Magnetism 2006 Free
... A loop of wire of width w and height h contains a switch and a battery and is connected to a spring of force constant k, as shown above. The loop carries a current I in a clockwise direction, and its bottom is in a constant, uniform magnetic field directed into the plane of the page. (a) On the diag ...
... A loop of wire of width w and height h contains a switch and a battery and is connected to a spring of force constant k, as shown above. The loop carries a current I in a clockwise direction, and its bottom is in a constant, uniform magnetic field directed into the plane of the page. (a) On the diag ...
AP Physics 2 – Magnetostatics MC 1 – Answer Key Solution Answer
... wire. Using RHRflat for this wire we get down as a force. The force on the top wire BC is irrelevant because the top and bottom wires have the same current but the B field is smaller for the top wire so the bottom wire will dominate the force direction no matter what. Therefore, the direction is dow ...
... wire. Using RHRflat for this wire we get down as a force. The force on the top wire BC is irrelevant because the top and bottom wires have the same current but the B field is smaller for the top wire so the bottom wire will dominate the force direction no matter what. Therefore, the direction is dow ...
Unit Test #1- Electricity and Magnetism Time: 1 hour Total: 25
... a) Conductor whenever the magnetic field in the region of the conductor changes b) Conductor whenever the magnetic field in the region of the conductor stays the same c) Circuit whenever the electric current in the region of the circuit changes d) Circuit whenever the electric current in the region ...
... a) Conductor whenever the magnetic field in the region of the conductor changes b) Conductor whenever the magnetic field in the region of the conductor stays the same c) Circuit whenever the electric current in the region of the circuit changes d) Circuit whenever the electric current in the region ...
Electromagnet

An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. Electromagnets usually consist of a large number of closely spaced turns of wire that create the magnetic field. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.The main advantage of an electromagnet over a permanent magnet is that the magnetic field can be quickly changed by controlling the amount of electric current in the winding. However, unlike a permanent magnet that needs no power, an electromagnet requires a continuous supply of current to maintain the magnetic field.Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment. Electromagnets are also employed in industry for picking up and moving heavy iron objects such as scrap iron and steel.