kb-chokes.pdf
... supply is better regulated, ie the difference in rail voltage from idle to full tilt boogie is smaller. for this reason they are preferred in amps that draw variations in current with wide variations of output power, like class B amps. the problem with big ass cap approach is that the high current p ...
... supply is better regulated, ie the difference in rail voltage from idle to full tilt boogie is smaller. for this reason they are preferred in amps that draw variations in current with wide variations of output power, like class B amps. the problem with big ass cap approach is that the high current p ...
CT33-
... Answer: zero!! It's a trick question! Transformers only work with AC voltages. The DC voltage V from the battery produces a DC current in the primary coil, but produces no voltage of any kind in the secondary coil. Transformers work because of Faraday's Law: the changing flux produced by the AC curr ...
... Answer: zero!! It's a trick question! Transformers only work with AC voltages. The DC voltage V from the battery produces a DC current in the primary coil, but produces no voltage of any kind in the secondary coil. Transformers work because of Faraday's Law: the changing flux produced by the AC curr ...
An LCLC resonant topology based filament power supply for
... minimum possible. A full bridge topology with fixed frequency operation is used in this inverter. The diagonal switches are driven together alternately to place an AC voltage across the resonant tank. Power is only transferred to the output section during the ON times of the switches. When the switc ...
... minimum possible. A full bridge topology with fixed frequency operation is used in this inverter. The diagonal switches are driven together alternately to place an AC voltage across the resonant tank. Power is only transferred to the output section during the ON times of the switches. When the switc ...
Lab 2 – Stepper Motor
... Therefore, we need to lower the voltage that is supplied to the motor. We can do this with a voltage regulator. A voltage regulator is a circuit that can take a variable, unregulated input voltage (such as from a battery or your AC-DC wall adapter) and output a stable, constant voltage that doesn’t ...
... Therefore, we need to lower the voltage that is supplied to the motor. We can do this with a voltage regulator. A voltage regulator is a circuit that can take a variable, unregulated input voltage (such as from a battery or your AC-DC wall adapter) and output a stable, constant voltage that doesn’t ...
Name: Record Responses in med blue bold font Module 8 Lesson 2
... removing the battery, or the lightbulb, or one of the wires, current will not flow. 4. Batteries To keep an electric current continually flowing in the electric circuit a _______ ________needs to be maintained in the circuit. A ______ can provide the voltage difference that is needed to keep current ...
... removing the battery, or the lightbulb, or one of the wires, current will not flow. 4. Batteries To keep an electric current continually flowing in the electric circuit a _______ ________needs to be maintained in the circuit. A ______ can provide the voltage difference that is needed to keep current ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... 14-bit, 1 MSPS, 2-channel, simultaneous sampling SAR ADCs. These devices have a total of four analog multiplexed inputs (two per channel), which operate in single-ended mode. The analog input range on the AD7366/AD7367 is programmable and can support ±10 V, ±5 V, and 0 V to 10 V using the internal 2 ...
... 14-bit, 1 MSPS, 2-channel, simultaneous sampling SAR ADCs. These devices have a total of four analog multiplexed inputs (two per channel), which operate in single-ended mode. The analog input range on the AD7366/AD7367 is programmable and can support ±10 V, ±5 V, and 0 V to 10 V using the internal 2 ...
LR9641 DESCRIPTION FEATURES
... also employs a proprietary control scheme that switches the device into a power save mode during light load, thereby extending the range of high efficiency operation. An OVP function protects the IC itself and its downstream system against input voltage surges. With this OVP function, the IC can sta ...
... also employs a proprietary control scheme that switches the device into a power save mode during light load, thereby extending the range of high efficiency operation. An OVP function protects the IC itself and its downstream system against input voltage surges. With this OVP function, the IC can sta ...
Non-RF Applications for the Surface Mount Schottky Diode Pairs
... and consumer applications. Traditionally, many of these diodes are used for mixing and power monitoring in RF applications such as mobile and cordless phones, satellite television receivers, and RFID (radio frequency identification) systems. However, an increasing number of these diodes are also bei ...
... and consumer applications. Traditionally, many of these diodes are used for mixing and power monitoring in RF applications such as mobile and cordless phones, satellite television receivers, and RFID (radio frequency identification) systems. However, an increasing number of these diodes are also bei ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... Figure 1 shows the AD5781 configured in a gain-of-two mode such that a single reference source can be used to generate a symmetrical bipolar output voltage range. This mode of operation uses an external op amp (A2), as well as on-chip resistors (see AD5781 data sheet) to provide the gain of two. The ...
... Figure 1 shows the AD5781 configured in a gain-of-two mode such that a single reference source can be used to generate a symmetrical bipolar output voltage range. This mode of operation uses an external op amp (A2), as well as on-chip resistors (see AD5781 data sheet) to provide the gain of two. The ...
Lab: Current and Voltage in a circuit
... 1. Set your multimeter to read DC Voltage (the symbol V with the straight line and dotted line over the top). Make sure your red lead is in the appropriate port of the multimeter—it should be in the port labeled with the V, which means you may need to change this from where it was when you measured ...
... 1. Set your multimeter to read DC Voltage (the symbol V with the straight line and dotted line over the top). Make sure your red lead is in the appropriate port of the multimeter—it should be in the port labeled with the V, which means you may need to change this from where it was when you measured ...
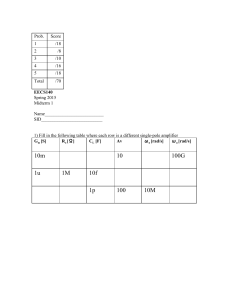
10m 10 100G 1u 1M 10f 1p 100 10M
... 4) You have biased the amplifier below with a particular input overdrive voltage Vov. Both devices are in saturation, and the quadratic model is appropriate. The low frequency gain is 1000. Cgs1=1pF, Cgd1=0.1pF. ...
... 4) You have biased the amplifier below with a particular input overdrive voltage Vov. Both devices are in saturation, and the quadratic model is appropriate. The low frequency gain is 1000. Cgs1=1pF, Cgd1=0.1pF. ...
Sample Paper - 2008 Subject – Physics CLASS – XII Time: Three
... doubled, state with reasons, how the following will change. a) Electric field between the plates b) Capacitance of the capacitor and c) Energy stored in the capacitor. 20. The input resistance of a silicon transistor is 665 Ω. Its base current is changed by 15 μ A which results in a change of collec ...
... doubled, state with reasons, how the following will change. a) Electric field between the plates b) Capacitance of the capacitor and c) Energy stored in the capacitor. 20. The input resistance of a silicon transistor is 665 Ω. Its base current is changed by 15 μ A which results in a change of collec ...
Definitions for Thévenin`s Theorem
... Thévenin's theorem is a popular theorem, used often for analysis of electronic circuits. Using this theorem, a model of the circuit can be developed based on its output characteristic. It was discovered in 1883 by French telegraph engineer León Charles Thévenin's. ...
... Thévenin's theorem is a popular theorem, used often for analysis of electronic circuits. Using this theorem, a model of the circuit can be developed based on its output characteristic. It was discovered in 1883 by French telegraph engineer León Charles Thévenin's. ...
2N3055 MJ2955
... UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS ...
... UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS ...
UB0/ATR - Microener
... The set current corresponds to input Amps (CT’s secondary) in the version for connection to CTs. In the version for input from Core Balance CT, the set current corresponds to primary side Amps. (1) Standard for connection to CT (2) Standard for connection to Core Balance transformer ratio 100/1A ...
... The set current corresponds to input Amps (CT’s secondary) in the version for connection to CTs. In the version for input from Core Balance CT, the set current corresponds to primary side Amps. (1) Standard for connection to CT (2) Standard for connection to Core Balance transformer ratio 100/1A ...
Impedance
... is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current (AC) circuit ...
... is the measure of the opposition that a circuit presents to the passage of a current when a voltage is applied. In quantitative terms, it is the complex ratio of the voltage to the current in an alternating current (AC) circuit ...
Schmitt trigger
In electronics a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input signal to a digital output signal. The circuit is named a ""trigger"" because the output retains its value until the input changes sufficiently to trigger a change. In the non-inverting configuration, when the input is higher than a chosen threshold, the output is high. When the input is below a different (lower) chosen threshold the output is low, and when the input is between the two levels the output retains its value. This dual threshold action is called hysteresis and implies that the Schmitt trigger possesses memory and can act as a bistable multivibrator (latch or flip-flop). There is a close relation between the two kinds of circuits: a Schmitt trigger can be converted into a latch and a latch can be converted into a Schmitt trigger.Schmitt trigger devices are typically used in signal conditioning applications to remove noise from signals used in digital circuits, particularly mechanical contact bounce. They are also used in closed loop negative feedback configurations to implement relaxation oscillators, used in function generators and switching power supplies.