Physics 517/617 Experiment 4A
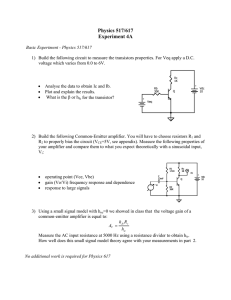
... 2) Build the following Common-Emitter amplifier. You will have to choose resistors R1 and R2 to properly bias the circuit (VCE=5V, see appendix). Measure the following properties of your amplifier and compare them to what you expect theoretically with a sinusoidal input, ...
... 2) Build the following Common-Emitter amplifier. You will have to choose resistors R1 and R2 to properly bias the circuit (VCE=5V, see appendix). Measure the following properties of your amplifier and compare them to what you expect theoretically with a sinusoidal input, ...
Biomedical Instrumentation Tara Alvarez Ph.D.
... • Infinite open loop gain : gain without any feedback; thus the closed loop characteristics of the circuit are determined entirely by the properties of the feedback loop network and are independent of amplifying device • Output impedance = 0 : ideal voltage source • Input impedance = infinity : inpu ...
... • Infinite open loop gain : gain without any feedback; thus the closed loop characteristics of the circuit are determined entirely by the properties of the feedback loop network and are independent of amplifying device • Output impedance = 0 : ideal voltage source • Input impedance = infinity : inpu ...
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS - Power
... lf the voltage at 1 and 2 on the voltage regulatorincreasesduringthe test, this could indicatethat the regulatoris darnagedor defective or the internal fuses have blown. lf the line voltage did not increaseon the generatorwhen the exciter fields were connectedto the 12 vcic,there is an internaiprobl ...
... lf the voltage at 1 and 2 on the voltage regulatorincreasesduringthe test, this could indicatethat the regulatoris darnagedor defective or the internal fuses have blown. lf the line voltage did not increaseon the generatorwhen the exciter fields were connectedto the 12 vcic,there is an internaiprobl ...
STEVAL-ISA067V1
... respectively. Each switching section delivers more than 2.5 A output current. An internal linear regulator provides a fixed 5 V output voltage. Another internal linear regulator provides an adjustable output voltage (default 2.5 V). Both linear regulators can deliver up to 100 mA peak current. ...
... respectively. Each switching section delivers more than 2.5 A output current. An internal linear regulator provides a fixed 5 V output voltage. Another internal linear regulator provides an adjustable output voltage (default 2.5 V). Both linear regulators can deliver up to 100 mA peak current. ...
DN126 - The LT1166: Power Output Stage Automatic Bias System Control IC
... Class AB output stage by incorporating two control loops, the current-control loop and the voltage-control loop. The current-control loop (Figure 2) operates independently of the voltage loop while keeping the product of V1 and V2 constant. The voltage loop maintains the output voltage at the input ...
... Class AB output stage by incorporating two control loops, the current-control loop and the voltage-control loop. The current-control loop (Figure 2) operates independently of the voltage loop while keeping the product of V1 and V2 constant. The voltage loop maintains the output voltage at the input ...
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices
... connections are usually plus and minus 15 volts from a stabilised power supply, and the input and output signals can then be up to ± 12 volts, at low (mA) current. The two basic applications - there are hundreds of others - use negative feedback for stable and predictable performance; see figure 6. ...
... connections are usually plus and minus 15 volts from a stabilised power supply, and the input and output signals can then be up to ± 12 volts, at low (mA) current. The two basic applications - there are hundreds of others - use negative feedback for stable and predictable performance; see figure 6. ...
Physics 517/617 Experiment 1 Instrumentation and Resistor Circuits
... 2) Verify Ohm’s law by measuring and then plotting voltage vs. current for a resistor. Fit your graph(s) to extract the measured resistance. Use a resistor of your choice. Repeat the measurement with a resistor of a much higher value (e.g. 10-100X) than your previous choice. Use a DC power supply fo ...
... 2) Verify Ohm’s law by measuring and then plotting voltage vs. current for a resistor. Fit your graph(s) to extract the measured resistance. Use a resistor of your choice. Repeat the measurement with a resistor of a much higher value (e.g. 10-100X) than your previous choice. Use a DC power supply fo ...
TYPE VOG - Precise
... PRECISE PRECISE VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER TYPE VOG PRECISE Voltage Transformers model type VOG are connected in between phase to earth to provide a proportional low voltage on secondary side. They are design to perform the following functions: 1. Measure/monitor voltage 2. Electrically isolate the instrum ...
... PRECISE PRECISE VOLTAGE TRANSFORMER TYPE VOG PRECISE Voltage Transformers model type VOG are connected in between phase to earth to provide a proportional low voltage on secondary side. They are design to perform the following functions: 1. Measure/monitor voltage 2. Electrically isolate the instrum ...
110V/0W = ∞A! P = VI
... Q = CV for a capacitor; I = dQ/dt; V = L(dI/dt) for an inductor For safety reason, limit the maximum voltage to be less than 12 volts for a beginner (a more relevant limitation is by the maximum power or energy). --------- Even the Ohmic law is not trivial! ------------------------------------------ ...
... Q = CV for a capacitor; I = dQ/dt; V = L(dI/dt) for an inductor For safety reason, limit the maximum voltage to be less than 12 volts for a beginner (a more relevant limitation is by the maximum power or energy). --------- Even the Ohmic law is not trivial! ------------------------------------------ ...
8 Data Conversion Methods I
... encoding logic is then used to convert this bar-chart type of comparator output code into a conventional binary code. Table 8.1 below shows the ranges occupied by the input signal, the corresponding comparator output states and the associated final output binary codes. This type of converter is very ...
... encoding logic is then used to convert this bar-chart type of comparator output code into a conventional binary code. Table 8.1 below shows the ranges occupied by the input signal, the corresponding comparator output states and the associated final output binary codes. This type of converter is very ...
IS31PW3500
... Copyright © 2011 Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. All rights reserved. ISSI reserves the right to make changes to this specification and its products at any time without notice. ISSI assumes no liability arising out of the application or use of any information, products or services described herei ...
... Copyright © 2011 Integrated Silicon Solution, Inc. All rights reserved. ISSI reserves the right to make changes to this specification and its products at any time without notice. ISSI assumes no liability arising out of the application or use of any information, products or services described herei ...
Shocking Stuff - Kotara High School
... Use the circuit drawn in Qu. 4. The reading on the ammeter was 5.0 amps. Determine the effect on the ammeter reading if a second identical globe was added in series with the first. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Use the circuit drawn in Qu. 4. The reading on the ammeter was 5.0 amps. Determine the effect on the ammeter reading if a second identical globe was added in series with the first. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ...
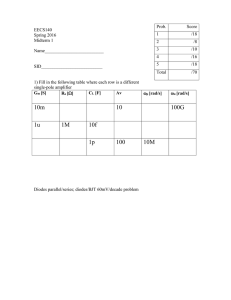
16spMid1b
... Av, intrinsic Av, resistive load 4) You have biased the amplifier below with a particular input overdrive voltage Vov. Both devices are in saturation, and the quadratic model is appropriate. The low frequency gain is -1000. Cgs1=1pF, Cgd1=0.1pF. ...
... Av, intrinsic Av, resistive load 4) You have biased the amplifier below with a particular input overdrive voltage Vov. Both devices are in saturation, and the quadratic model is appropriate. The low frequency gain is -1000. Cgs1=1pF, Cgd1=0.1pF. ...
In Problems 1 and 2, find the Thévenin and Norton equivalent
... In phase is a condition where the phase angle of the voltage is equal to the phase angle of the current. Note that this does not mean that the phase angle will be equal to 0o. This will never occur because the current iR must have the same phase as vR because the current is flowing through a resisto ...
... In phase is a condition where the phase angle of the voltage is equal to the phase angle of the current. Note that this does not mean that the phase angle will be equal to 0o. This will never occur because the current iR must have the same phase as vR because the current is flowing through a resisto ...
Lecture_1
... Ideal Volt Meters have infinite resistance. (i.e. they do not draw current.) Real Volt Meters have a non-zero finite resistance and draw some current. Ideal Ammeters have zero internal resistance. (i.e. when placed in a circuit, they have no voltage drop.) Real Ammeters have a non-zero resistance an ...
... Ideal Volt Meters have infinite resistance. (i.e. they do not draw current.) Real Volt Meters have a non-zero finite resistance and draw some current. Ideal Ammeters have zero internal resistance. (i.e. when placed in a circuit, they have no voltage drop.) Real Ammeters have a non-zero resistance an ...
Solutions - RF and microwave circuits
... 5. This is a problem calling for the usage of the maximum power transfer theorem. To maximize the power transferred across the load, we need to choose its value such that it is equal to that of the Thévenin resistance as seen by RL . To find it, we can simply zero out the current source and find Re ...
... 5. This is a problem calling for the usage of the maximum power transfer theorem. To maximize the power transferred across the load, we need to choose its value such that it is equal to that of the Thévenin resistance as seen by RL . To find it, we can simply zero out the current source and find Re ...
DM7404 Hex Inverting Gates
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N14A ...
... 14-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-001, 0.300" Wide Package Number N14A ...
FETishizator V3.0
... Theory tells, if you connect a cap to the inverting input (here: transistor base) of a current amplifying part, the complete circuit acts like an inductance. Big bargain in this small and sophisticated circuit! I also enclosed the copper layout in real life size (1:1), from which you can easily make ...
... Theory tells, if you connect a cap to the inverting input (here: transistor base) of a current amplifying part, the complete circuit acts like an inductance. Big bargain in this small and sophisticated circuit! I also enclosed the copper layout in real life size (1:1), from which you can easily make ...
Schmitt trigger
In electronics a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input signal to a digital output signal. The circuit is named a ""trigger"" because the output retains its value until the input changes sufficiently to trigger a change. In the non-inverting configuration, when the input is higher than a chosen threshold, the output is high. When the input is below a different (lower) chosen threshold the output is low, and when the input is between the two levels the output retains its value. This dual threshold action is called hysteresis and implies that the Schmitt trigger possesses memory and can act as a bistable multivibrator (latch or flip-flop). There is a close relation between the two kinds of circuits: a Schmitt trigger can be converted into a latch and a latch can be converted into a Schmitt trigger.Schmitt trigger devices are typically used in signal conditioning applications to remove noise from signals used in digital circuits, particularly mechanical contact bounce. They are also used in closed loop negative feedback configurations to implement relaxation oscillators, used in function generators and switching power supplies.