q 1 - Mr. Cervantes Science Classes
... positive and negative. Rubbing certain electrically neutral objects together (e.g., a glass rod and a silk cloth) tends to cause the electric charges to separate. In the case of the glass and silk, the glass rod loses negative charge and becomes positively charged while the silk cloth gains negative ...
... positive and negative. Rubbing certain electrically neutral objects together (e.g., a glass rod and a silk cloth) tends to cause the electric charges to separate. In the case of the glass and silk, the glass rod loses negative charge and becomes positively charged while the silk cloth gains negative ...
Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime and Horizon
... the fact that the study of quantum fields in curved spacetimes (or in general, non-inertial coordinates) reveals many new phenomena that cannot possibly be foreseen classically, study in this area reveals several pointers as to what a quantum theory of gravity could possibly be like, i.e., what phen ...
... the fact that the study of quantum fields in curved spacetimes (or in general, non-inertial coordinates) reveals many new phenomena that cannot possibly be foreseen classically, study in this area reveals several pointers as to what a quantum theory of gravity could possibly be like, i.e., what phen ...
ppt
... Superposition: for multiple point charges, the forces on each charge from every other charge can be calculated and then added as vectors. The net force on a charge is the vector sum of all the forces acting on it. ...
... Superposition: for multiple point charges, the forces on each charge from every other charge can be calculated and then added as vectors. The net force on a charge is the vector sum of all the forces acting on it. ...
Lecture - Galileo
... •Flux •Electric Flux and Example •Gauss’ Law •Coulombs Law from Gauss’ Law •Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor •Application of Gauss’ Law •Charged wire or rod •Plane of charge ...
... •Flux •Electric Flux and Example •Gauss’ Law •Coulombs Law from Gauss’ Law •Isolated conductor and Electric field outside conductor •Application of Gauss’ Law •Charged wire or rod •Plane of charge ...
Electric Fields and Forces
... law is symbolic of Newton’s Law of Gravitation. The symbol for Electric Field is, “E”. And since it is defined as a force per unit charge he unit is Newtons per Coulomb, N/C. NOTE: the equations above will ONLY help you determine the MAGNITUDE of the field or force. Conceptual understanding will hel ...
... law is symbolic of Newton’s Law of Gravitation. The symbol for Electric Field is, “E”. And since it is defined as a force per unit charge he unit is Newtons per Coulomb, N/C. NOTE: the equations above will ONLY help you determine the MAGNITUDE of the field or force. Conceptual understanding will hel ...
Electric Fields and Forces
... law is symbolic of Newton’s Law of Gravitation. The symbol for Electric Field is, “E”. And since it is defined as a force per unit charge he unit is Newtons per Coulomb, N/C. NOTE: the equations above will ONLY help you determine the MAGNITUDE of the field or force. Conceptual understanding will hel ...
... law is symbolic of Newton’s Law of Gravitation. The symbol for Electric Field is, “E”. And since it is defined as a force per unit charge he unit is Newtons per Coulomb, N/C. NOTE: the equations above will ONLY help you determine the MAGNITUDE of the field or force. Conceptual understanding will hel ...
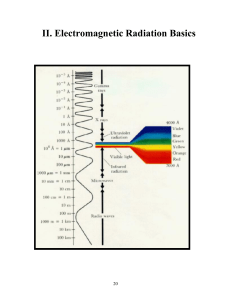
II. Electromagnetic Radiation Basics
... airplanes, reflect off of an ionized trail left behind from a meteor and then finally make it to your radio receiver where they are converted back into sound waves. At first, it seems like visible light and radio waves have nothing to do with each other but they are in fact the same thing. Both are ...
... airplanes, reflect off of an ionized trail left behind from a meteor and then finally make it to your radio receiver where they are converted back into sound waves. At first, it seems like visible light and radio waves have nothing to do with each other but they are in fact the same thing. Both are ...
Physics Chapter 12
... the charges that could be responsible for it. Yet this kind of force is already familiar to you. The force of gravity was explained in terms of a gravitational field of force—when a mass is placed in the gravitational field of another mass, the first mass experiences a force of attraction toward the ...
... the charges that could be responsible for it. Yet this kind of force is already familiar to you. The force of gravity was explained in terms of a gravitational field of force—when a mass is placed in the gravitational field of another mass, the first mass experiences a force of attraction toward the ...
3.4 Faraday`s Law
... Fleming's right hand rule shows the direction of induced current flow when a conductor moves in a magnetic field. The right hand is held with the thumb, first finger and second finger mutually at right angles, as shown in the diagram The Thumb represents the direction of Motion of the conductor. The ...
... Fleming's right hand rule shows the direction of induced current flow when a conductor moves in a magnetic field. The right hand is held with the thumb, first finger and second finger mutually at right angles, as shown in the diagram The Thumb represents the direction of Motion of the conductor. The ...
Electricity & Optics Physics 24100 Lecture 3 – Chapter 22 sec. 1-2
... energy you put into it. – You don’t allow the electric field to move the charges – work is not done by the field. – Instead, work is done on the electric field – the configuration of charges gains potential energy of some form. ...
... energy you put into it. – You don’t allow the electric field to move the charges – work is not done by the field. – Instead, work is done on the electric field – the configuration of charges gains potential energy of some form. ...