Boundless Study Slides
... • electrostatic force The electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles; the amount and direction of attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies. • equilibrium The state of a body at rest or in uniform motion, the resultant of all forces on which is zero. • Faraday shield A ...
... • electrostatic force The electrostatic interaction between electrically charged particles; the amount and direction of attraction or repulsion between two charged bodies. • equilibrium The state of a body at rest or in uniform motion, the resultant of all forces on which is zero. • Faraday shield A ...
Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields
... perpendicular to and directed out of the page with a series of blue dots, which represent the tips of arrows coming toward you (see Fig. 29.6a). In this case, we label the field Bout. If B is directed perpendicularly into the page, we use blue crosses, which represent the feathered tails of arrows f ...
... perpendicular to and directed out of the page with a series of blue dots, which represent the tips of arrows coming toward you (see Fig. 29.6a). In this case, we label the field Bout. If B is directed perpendicularly into the page, we use blue crosses, which represent the feathered tails of arrows f ...
Literatura
... high Reynolds number, such as fish, birds, or insects [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], do not work at the small scale. For example, any attempt to move by imparting momentum to the fluid, as is done in paddling, will be foiled by the large viscous damping. Therefore microorganisms have evolved propulsion strateg ...
... high Reynolds number, such as fish, birds, or insects [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8], do not work at the small scale. For example, any attempt to move by imparting momentum to the fluid, as is done in paddling, will be foiled by the large viscous damping. Therefore microorganisms have evolved propulsion strateg ...
Chapter 16 - dysoncentralne
... hair on a dry day, the comb attracts strands of your hair or small pieces of paper. A simple experiment you might try is to rub an inflated balloon back and forth across your hair. You may find that the balloon is attracted to your hair, as shown in Figure 1(a). On a dry day, a rubbed balloon will s ...
... hair on a dry day, the comb attracts strands of your hair or small pieces of paper. A simple experiment you might try is to rub an inflated balloon back and forth across your hair. You may find that the balloon is attracted to your hair, as shown in Figure 1(a). On a dry day, a rubbed balloon will s ...
Chapter 3: Electric Fields - Farmingdale State College
... Because Ex is negative, the angle φ lies in the second quadrant. The angle that the vector E makes with the positive x-axis is φ + 1800 = 98.80. ...
... Because Ex is negative, the angle φ lies in the second quadrant. The angle that the vector E makes with the positive x-axis is φ + 1800 = 98.80. ...
The hydrodynamics of swimming microorganisms
... the small scale. For example, any attempt to move by imparting momentum to the fluid, as is done in paddling, will be foiled by the large viscous damping. Therefore microorganisms have evolved propulsion strategies that successfully overcome and exploit drag. The aim of this review is to explain the ...
... the small scale. For example, any attempt to move by imparting momentum to the fluid, as is done in paddling, will be foiled by the large viscous damping. Therefore microorganisms have evolved propulsion strategies that successfully overcome and exploit drag. The aim of this review is to explain the ...
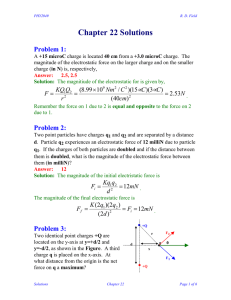
Chapter 22 Solutions
... Problem 8: A neon sign includes a long neon-filled glass tube with electrodes at each end across which an electric field of 20,000 N/C. is placed. This large field accelerates free electrons which collide with and ionize a portion of the neon atoms which emit red light as they recombine. Assuming th ...
... Problem 8: A neon sign includes a long neon-filled glass tube with electrodes at each end across which an electric field of 20,000 N/C. is placed. This large field accelerates free electrons which collide with and ionize a portion of the neon atoms which emit red light as they recombine. Assuming th ...
x - ISMScience.org
... AP Physics courses and exams. However, the tables do not include all equations that might possibly be used. For example, they do not include many equations that can be derived by combining other equations in the tables. Nor do they include equations that are simply special cases of any that are in t ...
... AP Physics courses and exams. However, the tables do not include all equations that might possibly be used. For example, they do not include many equations that can be derived by combining other equations in the tables. Nor do they include equations that are simply special cases of any that are in t ...
physics before and after einstein
... In 1895 he failed his entrance examination to the Federal Institute of Technology (Eidegenössische Technische Hochschule, ETH) in Zürich, because of low marks in French, chemistry and biology (but not in mathematics and physics). He was advised to attend the cantonal school at Aarau for one year, an ...
... In 1895 he failed his entrance examination to the Federal Institute of Technology (Eidegenössische Technische Hochschule, ETH) in Zürich, because of low marks in French, chemistry and biology (but not in mathematics and physics). He was advised to attend the cantonal school at Aarau for one year, an ...
Electrospinning and electrically forced jets. I. Stability theory
... other special parameter limits. The simplicity of the formulas allows straightforward physical interpretation of the two main instability modes; the Rayleigh mode, which is the electrical counterpart of the surface tension driven Rayleigh instability, and a conducting mode, which involves a purely e ...
... other special parameter limits. The simplicity of the formulas allows straightforward physical interpretation of the two main instability modes; the Rayleigh mode, which is the electrical counterpart of the surface tension driven Rayleigh instability, and a conducting mode, which involves a purely e ...
16 Electrostatics WS 08 [v6.0]
... (b) How much work would be required to move a charge of 50 µC from the negative plate to to the positive plate? (Answer: .041 J) € 38. A particle has mass 4.7 x 10−5 kg and charge 3.2 x 10−3 C. The particle accelerates from rest € a speed of 3.5 x 103 m/s. The particle from a positive plate and stri ...
... (b) How much work would be required to move a charge of 50 µC from the negative plate to to the positive plate? (Answer: .041 J) € 38. A particle has mass 4.7 x 10−5 kg and charge 3.2 x 10−3 C. The particle accelerates from rest € a speed of 3.5 x 103 m/s. The particle from a positive plate and stri ...
Review Assessment: q01
... Feedback: By Newton's third law, the Coulomb force of attraction exerted by each particle on the other is of one and the same magnitude. The electron has much less mass than the proton however, so the electron experiences a much greater acceleration. The force directly determines the acceleration so ...
... Feedback: By Newton's third law, the Coulomb force of attraction exerted by each particle on the other is of one and the same magnitude. The electron has much less mass than the proton however, so the electron experiences a much greater acceleration. The force directly determines the acceleration so ...
electrostatic potential and capacitance
... FIGURE 2.1 A test charge q (> 0) is R to P, we apply an external force Fext just enough to moved from the point R to the counter the repulsive electric force FE (i.e, Fext= –FE). point P against the repulsive force on it by the charge Q (> 0) This means there is no net force on or acceleration of pl ...
... FIGURE 2.1 A test charge q (> 0) is R to P, we apply an external force Fext just enough to moved from the point R to the counter the repulsive electric force FE (i.e, Fext= –FE). point P against the repulsive force on it by the charge Q (> 0) This means there is no net force on or acceleration of pl ...
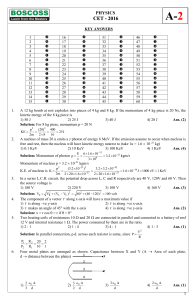
a-2 physics cet
... In a series L.C.R. circuit, the potential drop across L, C and R respectively are 40 V, 120V and 60 V. Then the source voltage is 1) 180 V 2) 220 V 3) 100 V 4) 160 V Ans. (3) Solution: V0 VR2 (VL VC ) 2 602 (40 120) 2 100 volt The component of a vector r along x-axis will have a maximu ...
... In a series L.C.R. circuit, the potential drop across L, C and R respectively are 40 V, 120V and 60 V. Then the source voltage is 1) 180 V 2) 220 V 3) 100 V 4) 160 V Ans. (3) Solution: V0 VR2 (VL VC ) 2 602 (40 120) 2 100 volt The component of a vector r along x-axis will have a maximu ...
Drift velocity and temporal phase fluctuations of sliding charge
... and 87Rb NMR of a Rbo.3Mo03 crystal in the sliding CDW state. The emphasis is on the temporal variation of the CDW phase. Rbo.3Mo03 is representative in most respect of all sliding CDW systems ; its crystal and CDW structure together with the transport properties have been thoroughly investigated [1 ...
... and 87Rb NMR of a Rbo.3Mo03 crystal in the sliding CDW state. The emphasis is on the temporal variation of the CDW phase. Rbo.3Mo03 is representative in most respect of all sliding CDW systems ; its crystal and CDW structure together with the transport properties have been thoroughly investigated [1 ...
Reference - Wayne State Chemistry Department
... be quite sizable, and practical computational methods may require some compromises between efficiency and accuracy. For simulations not involving ionization, TD-HF and TDCIS are the two most promising methods for modeling the electronic response of a molecule involving more than a few atoms. The sui ...
... be quite sizable, and practical computational methods may require some compromises between efficiency and accuracy. For simulations not involving ionization, TD-HF and TDCIS are the two most promising methods for modeling the electronic response of a molecule involving more than a few atoms. The sui ...













![16 Electrostatics WS 08 [v6.0]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017037121_1-cfd8810c1027b8afe3f3fc4cd06262cb-300x300.png)