(DOC, Unknown) - Natural Philosophy Alliance
... day world will have an open field to investigate the true nature of everything which finally would lead to the fact that there is a Universal Creator. Maxwell proposed that light propagates as electromagnetic radiation or electromagnetic wave with a fixed velocity by solving his field equations of e ...
... day world will have an open field to investigate the true nature of everything which finally would lead to the fact that there is a Universal Creator. Maxwell proposed that light propagates as electromagnetic radiation or electromagnetic wave with a fixed velocity by solving his field equations of e ...
document
... The two TDCs are coupled via parallel cables to an FPGAbased motherboard, which transfers the relevant TDC data to a computer workstation via a TCP/IP link. The motherboard and computer workstation contain components sensitive to strong magnetic fields and temperatures and must be kept at room tempe ...
... The two TDCs are coupled via parallel cables to an FPGAbased motherboard, which transfers the relevant TDC data to a computer workstation via a TCP/IP link. The motherboard and computer workstation contain components sensitive to strong magnetic fields and temperatures and must be kept at room tempe ...
Study of charged soot aggregates formed by benzene pyrolysis.
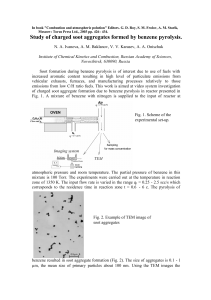
... An imaging system was used for soot observations. To this aim, a small portion of aerosol was injected to an optical cell. Light of a He-Ne laser beam scattered by soot particles at an angle of 90° passed through a flat window to a microscope objective and then to a CCD camera connected to a TV syst ...
... An imaging system was used for soot observations. To this aim, a small portion of aerosol was injected to an optical cell. Light of a He-Ne laser beam scattered by soot particles at an angle of 90° passed through a flat window to a microscope objective and then to a CCD camera connected to a TV syst ...
Slide 1
... Q18 If two charges are both doubled in magnitude without changing the distance between them, will the force that one charge exerts on the other also be doubled? The force varies as q1q2/r2 so the force will increase by a factor of 4 ...
... Q18 If two charges are both doubled in magnitude without changing the distance between them, will the force that one charge exerts on the other also be doubled? The force varies as q1q2/r2 so the force will increase by a factor of 4 ...
ppt - UZH-Particle Physics at CERN
... There are models predicting non-linear electric filed in heavily irradiated silicon: the main idea that the thermally generated electrons and holes, while drift towards the electrodes, are trapped by the trapping centers (induced by the irradiation damage) in the silicon bulk and form non-uniform sp ...
... There are models predicting non-linear electric filed in heavily irradiated silicon: the main idea that the thermally generated electrons and holes, while drift towards the electrodes, are trapped by the trapping centers (induced by the irradiation damage) in the silicon bulk and form non-uniform sp ...
Chapter 13 Maxwell’s Equations and Electromagnetic Waves
... One might then wonder whether or not the converse could be true, namely, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. If so, then the right-hand side of Eq. (13.1.1) will have to be modified to reflect such “symmetry” between E and B . To see how magnetic fields can be created by a time-vary ...
... One might then wonder whether or not the converse could be true, namely, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. If so, then the right-hand side of Eq. (13.1.1) will have to be modified to reflect such “symmetry” between E and B . To see how magnetic fields can be created by a time-vary ...
CHAPTER 23 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL • Potential difference and
... conducting plates separated by 10.0 cm have uniform surface charge densities +σ and −σ. The difference in potential between the plates is 500V. (a) Which plate has the higher potential? (b) What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates? (c) An electron is released from rest next to ...
... conducting plates separated by 10.0 cm have uniform surface charge densities +σ and −σ. The difference in potential between the plates is 500V. (a) Which plate has the higher potential? (b) What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates? (c) An electron is released from rest next to ...
AH Electromagnetism Problems 2015
... In an oscilloscope an electron enters the electric field between two horizontal metal plates. The electron enters the electric field at a point midway between the plates in a direction parallel to the plates. The speed of the electron as it enters the electric field is 6.0 x 106 m s−1. The electric ...
... In an oscilloscope an electron enters the electric field between two horizontal metal plates. The electron enters the electric field at a point midway between the plates in a direction parallel to the plates. The speed of the electron as it enters the electric field is 6.0 x 106 m s−1. The electric ...
Nuclear Gravitation Field Theory
... represents the mass of a neutron; and “ψ(r,θ,φ,t)” represents the wave function of the particle of interest as a function of position in three-dimensional space (in spherical coordinates) and time. The Schrodinger Wave Equation above is the “Classical Quantum Mechanics” equation. With the Nuclear Gr ...
... represents the mass of a neutron; and “ψ(r,θ,φ,t)” represents the wave function of the particle of interest as a function of position in three-dimensional space (in spherical coordinates) and time. The Schrodinger Wave Equation above is the “Classical Quantum Mechanics” equation. With the Nuclear Gr ...