Lecture 23 - Purdue Physics
... Polarization of EM Radiation • For any EM wave, the electric field is perpendicular to the direction of propagation • There are many possible directions of the electric field in an EM wave • Knowing the direction of the electric field in an EM wave is important for determining how the wave interact ...
... Polarization of EM Radiation • For any EM wave, the electric field is perpendicular to the direction of propagation • There are many possible directions of the electric field in an EM wave • Knowing the direction of the electric field in an EM wave is important for determining how the wave interact ...
FROM ANTI-GRAVITY TO ZERO-POINT ENERGY
... distance r to the point of measurement. Knowing this, and using Vallee's value of the vacuum energy density, it is possible to calculate the associated gravitational field under a condition of charge approximately that found in CCT (q = 10" C) when ...
... distance r to the point of measurement. Knowing this, and using Vallee's value of the vacuum energy density, it is possible to calculate the associated gravitational field under a condition of charge approximately that found in CCT (q = 10" C) when ...
1st Term Exam
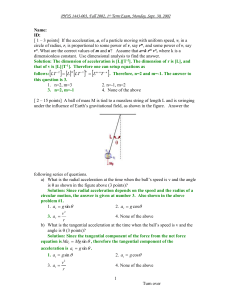
... Solution: Since this is a projectile motion, and there is no air resistance, the only force involved in this motion is gravitational force. The answer is 1. 1. Gravitational force only 2. Gravitational, Tangential, and Radial forces 3. Radial, Frictional, and Tangential forces 4. None of the above d ...
... Solution: Since this is a projectile motion, and there is no air resistance, the only force involved in this motion is gravitational force. The answer is 1. 1. Gravitational force only 2. Gravitational, Tangential, and Radial forces 3. Radial, Frictional, and Tangential forces 4. None of the above d ...
PYP001-122-Final Exam Solution [Choice A is the correct
... A) Thermal energy that is transferred from one substance to another is called heat. B) The temperature of the melting point is the same as the temperature of vaporization point for a substance. C) All changes of state involve a change in color. D) The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called ...
... A) Thermal energy that is transferred from one substance to another is called heat. B) The temperature of the melting point is the same as the temperature of vaporization point for a substance. C) All changes of state involve a change in color. D) The change of state from a gas to a liquid is called ...
Electric Charge
... 11. A capacitor that is connected to a 45 V source contains 90 μC of charge. What is the capacitor’s capacitance? ...
... 11. A capacitor that is connected to a 45 V source contains 90 μC of charge. What is the capacitor’s capacitance? ...
types_of_questions
... balls are at the same horizontal level at the beginning of the experiment. The same quantity of heat is supplied to both balls. The change of temperature of both balls is same. (All kinds of heat losses are negligible) (see fig.) ...
... balls are at the same horizontal level at the beginning of the experiment. The same quantity of heat is supplied to both balls. The change of temperature of both balls is same. (All kinds of heat losses are negligible) (see fig.) ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 6
... difference between the two ends of the line changes each time a vortex crosses the line. Then use the Josephson relation to get the voltage drop across the line. Divide by the length to get the electric field. You should get the same result as at the beginning of the problem. What is the direction o ...
... difference between the two ends of the line changes each time a vortex crosses the line. Then use the Josephson relation to get the voltage drop across the line. Divide by the length to get the electric field. You should get the same result as at the beginning of the problem. What is the direction o ...
Physics 880.06: Problem Set 6
... difference between the two ends of the line changes each time a vortex crosses the line. Then use the Josephson relation to get the voltage drop across the line. Divide by the length to get the electric field. You should get the same result as at the beginning of the problem. What is the direction o ...
... difference between the two ends of the line changes each time a vortex crosses the line. Then use the Josephson relation to get the voltage drop across the line. Divide by the length to get the electric field. You should get the same result as at the beginning of the problem. What is the direction o ...
Chapter 18 – Potential and Capacitance
... ENERGY is required to bring the particle back to rest (if it has mass). The sum of these two is ZERO. ...
... ENERGY is required to bring the particle back to rest (if it has mass). The sum of these two is ZERO. ...
Information in Radio Waves
... It is important to define the transverse wave as a wave in which the field vectors are oriented perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation. You can also introduce wavelength and frequency here. ...
... It is important to define the transverse wave as a wave in which the field vectors are oriented perpendicular to the direction of energy propagation. You can also introduce wavelength and frequency here. ...
Observation of Locally Negative Velocity of the Electromagnetic
... many plane waves. So, is this effect due to superposition (interference)? Not entirely. One can easily obtain an explicit propagating solution looking almost exactly like the last (far-field) term of (2) for the source-driven threedimensional scalar wave equation. Nevertheless, a similar effect was, ...
... many plane waves. So, is this effect due to superposition (interference)? Not entirely. One can easily obtain an explicit propagating solution looking almost exactly like the last (far-field) term of (2) for the source-driven threedimensional scalar wave equation. Nevertheless, a similar effect was, ...
Generating Gravity and time. (Mahona Mercury engine and Mahona
... From figure 5 in A), we see a stationary electron in a wire. If this electron moves to the other end of the wire at speeds much less than C for us on Earth, the particle obeys the laws of Newtonian Physics. In B), we see our electron now moves through the wire with a speed of c, so as discussed earl ...
... From figure 5 in A), we see a stationary electron in a wire. If this electron moves to the other end of the wire at speeds much less than C for us on Earth, the particle obeys the laws of Newtonian Physics. In B), we see our electron now moves through the wire with a speed of c, so as discussed earl ...