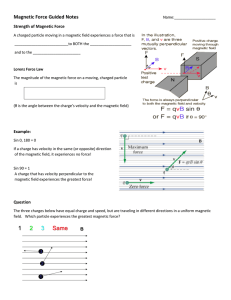
Another recent exam sample #2
... 15. A current loop is oriented in three different positions relative to a uniform magnetic field. In position 1 the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the field lines. In position 2 and 3 the plane of the loop is parallel to the field as shown. The torque on the loop is maximum in a. Only positio ...
... 15. A current loop is oriented in three different positions relative to a uniform magnetic field. In position 1 the plane of the loop is perpendicular to the field lines. In position 2 and 3 the plane of the loop is parallel to the field as shown. The torque on the loop is maximum in a. Only positio ...
Grades 9-12 Physics
... how to calculate the electric field due to a point charge and recognize that static electric fields have as their source some arrangement of electric charges. the force on a moving particle (with charge q) in a magnetic field is qvB sin(a) where a is the angle between v and B (v and B are the magnit ...
... how to calculate the electric field due to a point charge and recognize that static electric fields have as their source some arrangement of electric charges. the force on a moving particle (with charge q) in a magnetic field is qvB sin(a) where a is the angle between v and B (v and B are the magnit ...
PPT - LSU Physics & Astronomy
... Initially unpolarized light of intensity I0 is sent into a system of three polarizers as shown. What fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polariz ...
... Initially unpolarized light of intensity I0 is sent into a system of three polarizers as shown. What fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? • Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polariz ...
PracticeQuiz F&E
... label it F1. (1 pt) b) Draw a vector representing the Force on q2 by q1 and label it F2. (1 pt) c) Find the magnitude of F1. (Don’t forget units!) (3 pts) ...
... label it F1. (1 pt) b) Draw a vector representing the Force on q2 by q1 and label it F2. (1 pt) c) Find the magnitude of F1. (Don’t forget units!) (3 pts) ...
Electric Field
... • A Van de Graaff dome of radius 0.20 meters is charged to 3.00 x 10-4 C. What is the strength and direction of the electric field at the following distances from the center? – 5.0 cm – 20.0 cm – 1.0 meter ...
... • A Van de Graaff dome of radius 0.20 meters is charged to 3.00 x 10-4 C. What is the strength and direction of the electric field at the following distances from the center? – 5.0 cm – 20.0 cm – 1.0 meter ...
Chapter 22
... Space around charge filled with lines of force or electric field lines Direction of E-field lines or direction of the tangent to a curved field line gives the direction of E at that point. Number of E-field lines per unit area , measured in a planeto the lines, is proportional to the magnitud ...
... Space around charge filled with lines of force or electric field lines Direction of E-field lines or direction of the tangent to a curved field line gives the direction of E at that point. Number of E-field lines per unit area , measured in a planeto the lines, is proportional to the magnitud ...
04-01ElectricField
... a mass of 0.12 kg experiences a downward force of 7.80 N. What is the gravitational field on the surface of this planet? g = F/m, m = 1.12 kg, E = 7.80 N down g = (7.80 N down)/(0.12 kg) = 65 N/kg down ...
... a mass of 0.12 kg experiences a downward force of 7.80 N. What is the gravitational field on the surface of this planet? g = F/m, m = 1.12 kg, E = 7.80 N down g = (7.80 N down)/(0.12 kg) = 65 N/kg down ...
Q1. In Figure 1, three positively charged particles form a right angle
... A proton of kinetic energy 4.8 × 106 eV travels head-on toward a lead nucleus (with 82 protons). Assuming that the proton does not penetrate the nucleus and that the only force between the proton and the nucleus is Coulomb force, calculate the smallest separation between the proton and the nucleus w ...
... A proton of kinetic energy 4.8 × 106 eV travels head-on toward a lead nucleus (with 82 protons). Assuming that the proton does not penetrate the nucleus and that the only force between the proton and the nucleus is Coulomb force, calculate the smallest separation between the proton and the nucleus w ...
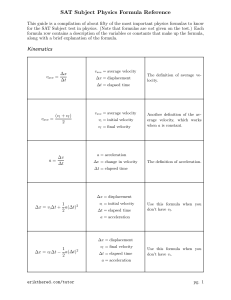
SAT Subject Physics Formula Reference
... number specific to the capacitor (like R for resistors), q is the charge on one side of the capacitor, and V is the voltage across the capacitor. ...
... number specific to the capacitor (like R for resistors), q is the charge on one side of the capacitor, and V is the voltage across the capacitor. ...
Electromagnetic Waves
... A varying magnetic field induces an emf and hence an electric field (Faraday’s Law) Electric field is also produced by changing magnetic field Question: is there a symmetry between electric and magnetic fields, i.e. can magnetic field be produced by changing electric field??? Maxwell: YES!!! ...
... A varying magnetic field induces an emf and hence an electric field (Faraday’s Law) Electric field is also produced by changing magnetic field Question: is there a symmetry between electric and magnetic fields, i.e. can magnetic field be produced by changing electric field??? Maxwell: YES!!! ...
Electric Fields - Xavier High School
... Electric Fields The electric field is a vector quantity that relates the force exerted on a test charge to the size of the test charge. Huh? ...
... Electric Fields The electric field is a vector quantity that relates the force exerted on a test charge to the size of the test charge. Huh? ...