11th and 12th Week
... Can be used to calculate the behavior of a complicated arrangement of charges: First calculate the field E it produces, then you’ll know what force it will exert on any “test” charge q that you put somewhere into this field: F = qE (Note: force is proportional to q and points in the SAME direction a ...
... Can be used to calculate the behavior of a complicated arrangement of charges: First calculate the field E it produces, then you’ll know what force it will exert on any “test” charge q that you put somewhere into this field: F = qE (Note: force is proportional to q and points in the SAME direction a ...
16 Part 2
... 1. Field lines indicate the direction of the field; the field is tangent to the line. 2. The magnitude of the field is proportional to the density of the lines. 3. Field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges; the number is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. ...
... 1. Field lines indicate the direction of the field; the field is tangent to the line. 2. The magnitude of the field is proportional to the density of the lines. 3. Field lines start on positive charges and end on negative charges; the number is proportional to the magnitude of the charge. ...
Module 11: The vector nature of electromagnetic radiation
... Under no circumstance does the electric field have a component along the direction of the wave i.e along the x axis. The electric field can be oriented along any direction in the y − z plane. In the cases which we have considered until now, the electric field oscillates up and down a fixed direction ...
... Under no circumstance does the electric field have a component along the direction of the wave i.e along the x axis. The electric field can be oriented along any direction in the y − z plane. In the cases which we have considered until now, the electric field oscillates up and down a fixed direction ...
AS Physics Paper March 2016
... Interplanetary satellites are very complex platforms with dozens of scientific instruments, mechanical devices and radio transmitters and receivers on board. They require considerable power and operate over many years, and those travelling to the outer planets cannot use solar power. They rely inste ...
... Interplanetary satellites are very complex platforms with dozens of scientific instruments, mechanical devices and radio transmitters and receivers on board. They require considerable power and operate over many years, and those travelling to the outer planets cannot use solar power. They rely inste ...
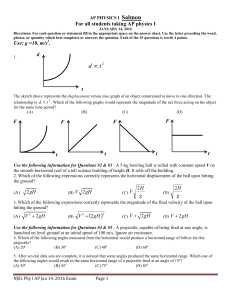
Phy I (AP Phy I) Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
... 7. With what acceleration will this mass slide down the ramp when released? (A) 1.6 m 2 (B) 4.4 m 2 (C) 6 m 2 (D) 10 m 2 s s s s 8. Once the mass reaches the bottom of the ramp and is stationary, what force would have to be applied parallel to the ramp in order for the mass to move up the ramp at a ...
... 7. With what acceleration will this mass slide down the ramp when released? (A) 1.6 m 2 (B) 4.4 m 2 (C) 6 m 2 (D) 10 m 2 s s s s 8. Once the mass reaches the bottom of the ramp and is stationary, what force would have to be applied parallel to the ramp in order for the mass to move up the ramp at a ...
Exam 1
... uniform electric field between two large plates separated by 1m and maintained with an electric potential difference of 30,000 V. The proton travels from lower electric potential to higher on a path perpendicular to the plates. Does the proton reach the far plate, and if not, what is the distance of ...
... uniform electric field between two large plates separated by 1m and maintained with an electric potential difference of 30,000 V. The proton travels from lower electric potential to higher on a path perpendicular to the plates. Does the proton reach the far plate, and if not, what is the distance of ...
File - SloanZone Physics
... Magnetic Fields & Circular Motion 1. A charged particle travels in a circular path in a magnetic field. What changes to the magnetic field and to the velocity of the particle would both cause the radius of its path to decrease? ...
... Magnetic Fields & Circular Motion 1. A charged particle travels in a circular path in a magnetic field. What changes to the magnetic field and to the velocity of the particle would both cause the radius of its path to decrease? ...
Katholieke Hogeschool Limburg
... there is no air and virtually no matter: it is empty. Yet we can still see light from the sun and stars! Apparently light can travel through empty space. But if so, what kind of wave is light? Think of the many forms of wireless communication we use on a daily basis, such as Wi-Fi or the signals of ...
... there is no air and virtually no matter: it is empty. Yet we can still see light from the sun and stars! Apparently light can travel through empty space. But if so, what kind of wave is light? Think of the many forms of wireless communication we use on a daily basis, such as Wi-Fi or the signals of ...
All the 5`s - The Physics Teacher
... The Principle of Conservation of Momentum states that in any collision between two objects, the total momentum before impact equals total momentum after impact, provided no external forces act on the system. (c) Explain why heat does not travel through solids by means of convection. The particles ca ...
... The Principle of Conservation of Momentum states that in any collision between two objects, the total momentum before impact equals total momentum after impact, provided no external forces act on the system. (c) Explain why heat does not travel through solids by means of convection. The particles ca ...
Electricity - TeacherWeb
... Charge spreads out maximally on surface Charge Q inside spherical uncharged shell induces –Q on inside surface of shell • Positive charge Q exists on outside • Electric field just outside a conductor is always perpendicular to the surface ...
... Charge spreads out maximally on surface Charge Q inside spherical uncharged shell induces –Q on inside surface of shell • Positive charge Q exists on outside • Electric field just outside a conductor is always perpendicular to the surface ...