Magnetic Force
... A proton enters the field heading north at a downward 30° angle with a speed of 5.0 x 106 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the force. ...
... A proton enters the field heading north at a downward 30° angle with a speed of 5.0 x 106 m/s. Find the magnitude and direction of the force. ...
1. A strip of aluminium foil is held between the poles of a strong
... such that the magnetic force on the particle is F. The magnetic force on a particle of mass 2m, charge q and speed 2v travelling in the same direction in the magnetic field is A. ...
... such that the magnetic force on the particle is F. The magnetic force on a particle of mass 2m, charge q and speed 2v travelling in the same direction in the magnetic field is A. ...
SPH 4U REVIEW
... 2.1 x 10-5 J of work are done in moving a point charge, q = 1.3 x 10-6 C, against an electric field. Determine the potential difference between the initial and final positions. ...
... 2.1 x 10-5 J of work are done in moving a point charge, q = 1.3 x 10-6 C, against an electric field. Determine the potential difference between the initial and final positions. ...
Kepler`s elliptic orbits in wave mechanics, and problems with the de
... in which something is carried through for the simple case of the oscillator which is also an urgent requirement for the more complicated cases, where however one encounters great computational difficulties. (It would be nicest if it could be carried through in general, but for the present that is hope ...
... in which something is carried through for the simple case of the oscillator which is also an urgent requirement for the more complicated cases, where however one encounters great computational difficulties. (It would be nicest if it could be carried through in general, but for the present that is hope ...
Electric Field
... • If the direction of an electric field is such that it opposes (acts against) the motion of a charged particle, work must be done to move the particle in that direction. • Potential difference is the work done per unit charge as a charged particle is moved between the points. • V = W/q (volts) ...
... • If the direction of an electric field is such that it opposes (acts against) the motion of a charged particle, work must be done to move the particle in that direction. • Potential difference is the work done per unit charge as a charged particle is moved between the points. • V = W/q (volts) ...
Electric potential
... the field moving a unit positive test charge from point A to point B: VAB = VB - VA = W(AB)/qo the work done can be positive, negative, or zero. only potential (voltage) differences are important - not the absolute potential values; electric potential is defined with respect to some arbitrarily c ...
... the field moving a unit positive test charge from point A to point B: VAB = VB - VA = W(AB)/qo the work done can be positive, negative, or zero. only potential (voltage) differences are important - not the absolute potential values; electric potential is defined with respect to some arbitrarily c ...
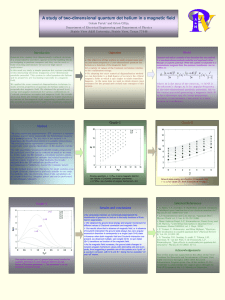
Exact diagonalization analysis of quantum dot helium for
... very accurate estimates for energies and related quantities of a given system. Contrary to other methods, the results obtained from the ED method are unaffected by approximations or limitations, except the computer power. The ED method works very effectively for small systems of up to eight electron ...
... very accurate estimates for energies and related quantities of a given system. Contrary to other methods, the results obtained from the ED method are unaffected by approximations or limitations, except the computer power. The ED method works very effectively for small systems of up to eight electron ...
1
... Find an exact for the electric field E at a point P located at (x,y)=(O,a) from a dipole consisting of a positive charge (+q) and negative charge (-q) at positions (-a,0) and (+a,0) as shown. Vse the symbols ~(Coulomb constant), and unit E-;: t J'-) t t ~ j vectors t and j, as needed. ...
... Find an exact for the electric field E at a point P located at (x,y)=(O,a) from a dipole consisting of a positive charge (+q) and negative charge (-q) at positions (-a,0) and (+a,0) as shown. Vse the symbols ~(Coulomb constant), and unit E-;: t J'-) t t ~ j vectors t and j, as needed. ...
Physics 112 Sample Test 2 NAME __________________________
... In the figure is a U-shaped conducting rail that is oriented vertically and immersed in a horizontal magnetic field (that points into the paper). The rail has no electrical resistance and does not move. A slide bar with mass m, length L, and resistance R can slide vertically without friction while m ...
... In the figure is a U-shaped conducting rail that is oriented vertically and immersed in a horizontal magnetic field (that points into the paper). The rail has no electrical resistance and does not move. A slide bar with mass m, length L, and resistance R can slide vertically without friction while m ...
4 - Ivor Catt`s
... coils of wire around an iron[verification needed] ring, and found that, upon passing a current through one coil, a momentary current was induced in the other coil.[5] This phenomenon is now known as mutual induction. The iron ring-coil apparatus is still on display at the Royal Institution. In subse ...
... coils of wire around an iron[verification needed] ring, and found that, upon passing a current through one coil, a momentary current was induced in the other coil.[5] This phenomenon is now known as mutual induction. The iron ring-coil apparatus is still on display at the Royal Institution. In subse ...
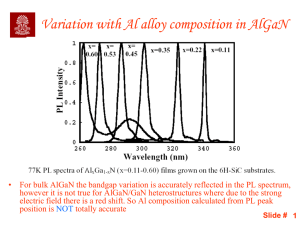
PPT - Hss-1.us
... logic) a particle can't be a wave and a wave can't be a particle. A wave should be the movement of energy through some medium (bunch of particles). But light violates this rule in that it sometimes acts as a particle and sometimes act as wave. • In this section we will look at Electromotive force in ...
... logic) a particle can't be a wave and a wave can't be a particle. A wave should be the movement of energy through some medium (bunch of particles). But light violates this rule in that it sometimes acts as a particle and sometimes act as wave. • In this section we will look at Electromotive force in ...