SOLID-STATE PHYSICS 3, Winter 2008 O. Entin-Wohlman Conductivity and conductance
... is justified, since each trajectory (path) carries a different phase, and on the average the interference is destructive, and the quantum mechanical correction is unimportant. We note that the mere existence of the quantum mechanical additional term in the probability results from the assumption of ...
... is justified, since each trajectory (path) carries a different phase, and on the average the interference is destructive, and the quantum mechanical correction is unimportant. We note that the mere existence of the quantum mechanical additional term in the probability results from the assumption of ...
Course Syllabus
... (The gauges at work sites often use both types of units),(V.1 & V.3) calculate and analyze the forces involved and the electric field orientation of point charges and simple line charges, (V.1 & V.4) realize the application of electric fields in industry, (V.1 & V.4) explain the potential and potent ...
... (The gauges at work sites often use both types of units),(V.1 & V.3) calculate and analyze the forces involved and the electric field orientation of point charges and simple line charges, (V.1 & V.4) realize the application of electric fields in industry, (V.1 & V.4) explain the potential and potent ...
MAGNETIC FIELD ppt
... • A magnetic field is a region in which a body with magnetic properties experiences a force. ...
... • A magnetic field is a region in which a body with magnetic properties experiences a force. ...
Group and phase velocity
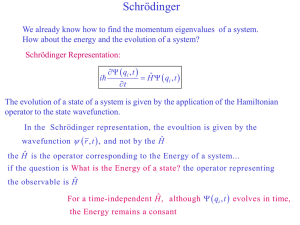
... The evolution of a state of a system is given by the application of the Hamiltonian operator to the state wavefunction. In the Schrodinger representation, the evoultion is given by the wavefunction r , t , and not by the Hˆ ...
... The evolution of a state of a system is given by the application of the Hamiltonian operator to the state wavefunction. In the Schrodinger representation, the evoultion is given by the wavefunction r , t , and not by the Hˆ ...
May 2003
... ~ ∗ = 1). In free space, the dispersion relation is ω = ck and the wave propagates with both phase and group velocity equal to c. Now let the wave propagate through a dilute plasma containing a density N of free mobile electrons of mass m and charge e (along with a background of compensating positiv ...
... ~ ∗ = 1). In free space, the dispersion relation is ω = ck and the wave propagates with both phase and group velocity equal to c. Now let the wave propagate through a dilute plasma containing a density N of free mobile electrons of mass m and charge e (along with a background of compensating positiv ...
Slides - University of Toronto Physics
... on a charged particle. If this is the only force acting on q, it causes the charged particle to accelerate with ...
... on a charged particle. If this is the only force acting on q, it causes the charged particle to accelerate with ...
Electricity and Magnetism
... can be stationary, or they can be moving. When charges move there is a current. Charges exert forces on each other. like charges repel, opposite charge attract The two types of charges are positive and negative (these are just names to show they are different) The force between charges depends on th ...
... can be stationary, or they can be moving. When charges move there is a current. Charges exert forces on each other. like charges repel, opposite charge attract The two types of charges are positive and negative (these are just names to show they are different) The force between charges depends on th ...