Colloidal suspensions driven by external fields
... In conclusion, we have briefly described three different examples of slow dynamics in colloidal suspensions driven by an external field: i) phase separation kinetics under an external driving field, ii) crystal nucleation under shear, and iii) chain formation in an external magnetic field. They all ...
... In conclusion, we have briefly described three different examples of slow dynamics in colloidal suspensions driven by an external field: i) phase separation kinetics under an external driving field, ii) crystal nucleation under shear, and iii) chain formation in an external magnetic field. They all ...
Electronic Shells of Dirac Fermions in Graphene Quantum Rings in
... In Fig. 2 a single particle spectrum of one-benzene-ring thick structure consisting of N = 96 carbon atoms is shown as a function of level index. Such a structure has 5 atoms on one of exterior edges and 3 atoms on one of the interior edges. 50% of atoms lie on the edges. Instead of a continuous Dir ...
... In Fig. 2 a single particle spectrum of one-benzene-ring thick structure consisting of N = 96 carbon atoms is shown as a function of level index. Such a structure has 5 atoms on one of exterior edges and 3 atoms on one of the interior edges. 50% of atoms lie on the edges. Instead of a continuous Dir ...
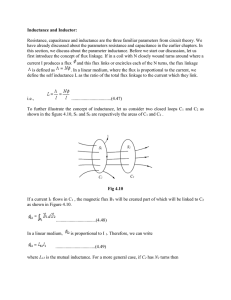
Inductance and Inductor
... coils and it is stored as magnetic energy. Let us consider a scenario where we consider a coil in which the current is increased from 0 to a value I. As mentioned earlier, the self inductance of a coil in general can be written as ...
... coils and it is stored as magnetic energy. Let us consider a scenario where we consider a coil in which the current is increased from 0 to a value I. As mentioned earlier, the self inductance of a coil in general can be written as ...
When a positive charge moves in the direction of the electric field, A
... D. not enough information given to decide ...
... D. not enough information given to decide ...
Electrostatic potential
... to be the same equation to me. I see that electric field is derived using the force between the charges while the electric potential is derived using the electrical energy between the charges, however I do not understand what you mean when you say that electric field is the ?gradient? of the electri ...
... to be the same equation to me. I see that electric field is derived using the force between the charges while the electric potential is derived using the electrical energy between the charges, however I do not understand what you mean when you say that electric field is the ?gradient? of the electri ...
Electrostatics
... blueberry was the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would just be a marble. An electron is also very dense. ...
... blueberry was the size of a football stadium, the nucleus would just be a marble. An electron is also very dense. ...
Quantum Correlations with Spacelike Separated Beam Splitters in
... It is not sufficient to precisely equalize the path lengths, we also have to ensure that the coherence length of the photons is smaller than the permitted discrepancy. This is the case because, with the interference filter placed after the photon pair source, the photons coherence length is about 0. ...
... It is not sufficient to precisely equalize the path lengths, we also have to ensure that the coherence length of the photons is smaller than the permitted discrepancy. This is the case because, with the interference filter placed after the photon pair source, the photons coherence length is about 0. ...
The intrinsic “spin” and orbital motion of electrons gives rise to the
... Putting iron in the center of a solenoid can create a strong electromagnet with fields 100x - 1000x the applied fields (also, can turn fields on and off). ...
... Putting iron in the center of a solenoid can create a strong electromagnet with fields 100x - 1000x the applied fields (also, can turn fields on and off). ...
XII-1 - OP Jindal School, Raigarh
... An infinite number of charges, each equal to 4µC, are placed along x-axis at x= 1m, 2m, 4m, 8m, and so on. Find the total force on a charge of 1C placed at the origin. Three particles, each of mass 1g and carrying a charge q, are suspended from a common point by insulated mass less strings, each 1m ...
... An infinite number of charges, each equal to 4µC, are placed along x-axis at x= 1m, 2m, 4m, 8m, and so on. Find the total force on a charge of 1C placed at the origin. Three particles, each of mass 1g and carrying a charge q, are suspended from a common point by insulated mass less strings, each 1m ...