Large-Field Inflation - Naturalness and String Theory
... • Why use string theory in cosmology? singularity at the beginning! — need quantum gravity to resolve inflation is UV-sensitive — needs a high-scale theory what are dark energy & dark matter? • if we try to use string theory for cosmology — better build on generic consequences of string theory! ...
... • Why use string theory in cosmology? singularity at the beginning! — need quantum gravity to resolve inflation is UV-sensitive — needs a high-scale theory what are dark energy & dark matter? • if we try to use string theory for cosmology — better build on generic consequences of string theory! ...
A Aberration The apparent change in position of a light
... responsible for the "tunnel vision" effect of traveling at relativistic speeds. Ampere; A (after A.M. Ampere, 1775-1836) The fundamental SI unit of electric current, defined as the current that, when going through two infinitely-long parallel conductors of negligible cross-section and placed 1 m apa ...
... responsible for the "tunnel vision" effect of traveling at relativistic speeds. Ampere; A (after A.M. Ampere, 1775-1836) The fundamental SI unit of electric current, defined as the current that, when going through two infinitely-long parallel conductors of negligible cross-section and placed 1 m apa ...
dipole - Erwin Sitompul
... Both expressions above are not dependent on the path chosen for the line integral, regardless of the source of the E field. ...
... Both expressions above are not dependent on the path chosen for the line integral, regardless of the source of the E field. ...
Coulomb`s Law
... The relationship among electrical forces, charges, and distance. It is like Newton’s law of gravity. But, unlike gravity, electric forces can be attractive or repulsive. Discovered by French Scientist, Charles Coulomb in the 18th Century. ...
... The relationship among electrical forces, charges, and distance. It is like Newton’s law of gravity. But, unlike gravity, electric forces can be attractive or repulsive. Discovered by French Scientist, Charles Coulomb in the 18th Century. ...
Sample Question Paper Class XII Physics (Applicable for March
... contains one value based question of four marks and Section E contains three questions of five marks each. 4. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all the three questions of five marks weightage. You h ...
... contains one value based question of four marks and Section E contains three questions of five marks each. 4. There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all the three questions of five marks weightage. You h ...
Lecture_9
... slightly greater than μ0) or diamagnetic (μ slightly less than μ0). The following is a table of magnetic susceptibility χm, where χm = μ/μ0 – 1. ...
... slightly greater than μ0) or diamagnetic (μ slightly less than μ0). The following is a table of magnetic susceptibility χm, where χm = μ/μ0 – 1. ...
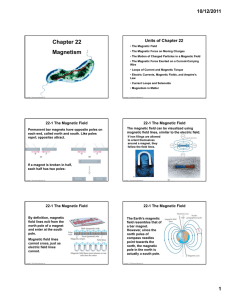
Physics Week 6(Sem. 2) Magnetism Cont’d
... Two parallel conducting wires exert forces on one another, since a current in a conductor creates its own magnetic field. When the current is in the same direction, the two wires attract to one another. This can be confirmed by the right hand rule. If the current in the two wires are going i ...
... Two parallel conducting wires exert forces on one another, since a current in a conductor creates its own magnetic field. When the current is in the same direction, the two wires attract to one another. This can be confirmed by the right hand rule. If the current in the two wires are going i ...
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
... • Spin is an intrinsic property of all atomic particles, much like mass. • Particles can either have their spin vector up (say for example, a counterclockwise rotation) or down (a clockwise rotation.) • Placing the proton in an external magnetic field causes interactions between the angular momentum ...
... • Spin is an intrinsic property of all atomic particles, much like mass. • Particles can either have their spin vector up (say for example, a counterclockwise rotation) or down (a clockwise rotation.) • Placing the proton in an external magnetic field causes interactions between the angular momentum ...