January 2011
... a) What is the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field inside the cylinder? (Ignore end effects, and other sources of the B field). b) Next, directed towards the above current-carrying cylinder and parallel to its axis is a parallel monochromatic beam of energetic charged particles. Show that ...
... a) What is the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field inside the cylinder? (Ignore end effects, and other sources of the B field). b) Next, directed towards the above current-carrying cylinder and parallel to its axis is a parallel monochromatic beam of energetic charged particles. Show that ...
Theoretical Studies of Magnetic Monopole
... existence of a particular symmetry between electricity and magnetism, analogues to the dual symmetry we have seen in the classical modification of the Maxwell theory. He argued the necessity of such a symmetry that without it the important experimental ratio ~c/e2 , fine structure constant, would re ...
... existence of a particular symmetry between electricity and magnetism, analogues to the dual symmetry we have seen in the classical modification of the Maxwell theory. He argued the necessity of such a symmetry that without it the important experimental ratio ~c/e2 , fine structure constant, would re ...
lesson
... 2. Place nails and paperclips on the table in piles and evenly spread out the coiled nails and wire. 3. Keep the batteries and jumpers on your side of the table. SAFETY! ● Be careful with smaller gauge wire; it will have a tendency to get warm. Lesson’s Big Idea ● An electromagnet is a spool of wire ...
... 2. Place nails and paperclips on the table in piles and evenly spread out the coiled nails and wire. 3. Keep the batteries and jumpers on your side of the table. SAFETY! ● Be careful with smaller gauge wire; it will have a tendency to get warm. Lesson’s Big Idea ● An electromagnet is a spool of wire ...
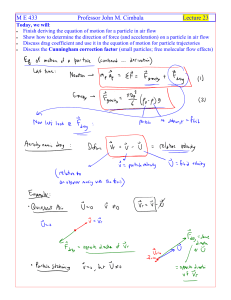
Lecture 23
... at velocity v as sketched to the right. At the location of the particle, and at a given instant in time, the air velocity is U as also sketched. ...
... at velocity v as sketched to the right. At the location of the particle, and at a given instant in time, the air velocity is U as also sketched. ...
Electrochemistry and Electrical Circuits and Their Elements
... force is generated and the direction of E is toward the negative charge. Likewise, if the other charge is positive, a repulsive force is generated and the direction of E is away from the positive charge. Electric field E is expressed in units of newtons per coulomb. If E is known, it is possible to ...
... force is generated and the direction of E is toward the negative charge. Likewise, if the other charge is positive, a repulsive force is generated and the direction of E is away from the positive charge. Electric field E is expressed in units of newtons per coulomb. If E is known, it is possible to ...
The Transactional Interpretation of Quantum Mechanics http://www
... (Though all of them were blind), That each by observation, Might satisfy his mind. . The First approached the Elephant, And happening to fall, Against his broad and sturdy side, At once began to bawl: “God bless me! but the Elephant, Is very like a wall!” The Second, feeling of the tusk, Cried, “Ho! ...
... (Though all of them were blind), That each by observation, Might satisfy his mind. . The First approached the Elephant, And happening to fall, Against his broad and sturdy side, At once began to bawl: “God bless me! but the Elephant, Is very like a wall!” The Second, feeling of the tusk, Cried, “Ho! ...
Lesson 11 – Faraday`s Law of Induction
... screen, so as to oppose change in the external field. Note that in this case, the induced field is in the same direction as the external field. To produce an induced magnetic field into the screen, the current must be clockwise. The minus sign in Faraday's law expresses this tendency to oppose chan ...
... screen, so as to oppose change in the external field. Note that in this case, the induced field is in the same direction as the external field. To produce an induced magnetic field into the screen, the current must be clockwise. The minus sign in Faraday's law expresses this tendency to oppose chan ...
Chapter 23: Electric Potential
... So far, we have learned the potential energy of a charge in an electric field. The expressions, we had depends on the characteristic properties of the field and also to the charge (usually test charge) Now, we will define “electric potential” as the electric potential energy per unit charge. We wi ...
... So far, we have learned the potential energy of a charge in an electric field. The expressions, we had depends on the characteristic properties of the field and also to the charge (usually test charge) Now, we will define “electric potential” as the electric potential energy per unit charge. We wi ...
Electric Fields and Forces
... space near this charge and calculate the effects this charge will have on other charges should they be placed at that point. q1q2 FE k 2 r ...
... space near this charge and calculate the effects this charge will have on other charges should they be placed at that point. q1q2 FE k 2 r ...