THE EARTH`S MAGNETIC FIELD
... • The Earth’s magnetic field can be mapped by means of isomagnetic charts. These are explained on the next page. • Secular variations are slow changes in the Earth’s magnetic field with time. For example magnetic north drifts gradually over the years. • Polarity reversals: There is very strong evide ...
... • The Earth’s magnetic field can be mapped by means of isomagnetic charts. These are explained on the next page. • Secular variations are slow changes in the Earth’s magnetic field with time. For example magnetic north drifts gradually over the years. • Polarity reversals: There is very strong evide ...
Voltage-tunable ferromagnetism in semimagnetic quantum dots with
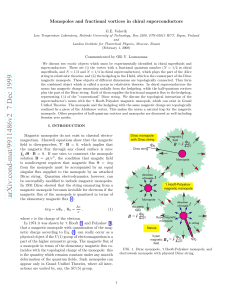
... material systems.4 This ability to externally control the properties of magnetic crystals with means other than the external magnetic field may have important device applications. An important feature of modern nanotechnology is the ability to shape semiconductor crystals, designing their quantum pr ...
... material systems.4 This ability to externally control the properties of magnetic crystals with means other than the external magnetic field may have important device applications. An important feature of modern nanotechnology is the ability to shape semiconductor crystals, designing their quantum pr ...
ch15 lecture-1-2-S06
... Each particle experiences the same electric force and the same acceleration. (b) The electric force on the proton is greater in magnitude than the force on the electron but in the opposite direction. (c) The electric force on the proton is equal in magnitude to the force on the electron, but in the ...
... Each particle experiences the same electric force and the same acceleration. (b) The electric force on the proton is greater in magnitude than the force on the electron but in the opposite direction. (c) The electric force on the proton is equal in magnitude to the force on the electron, but in the ...
Plasma environment of magnetized asteroids
... To sum up the basic idea of these boundary conditions, the electromagnetic field quantities as well as the moments of the particle distribution function are fixed on constant, timeindependent values in the inner region. Of course, the divergence of the magnetic field vanishes at the grid points insi ...
... To sum up the basic idea of these boundary conditions, the electromagnetic field quantities as well as the moments of the particle distribution function are fixed on constant, timeindependent values in the inner region. Of course, the divergence of the magnetic field vanishes at the grid points insi ...
The watt-balance operation: magnetic force and induced electric
... the geometric factor BL, we obtain the equation mgu = UI, which virtually relates mechanical and electrical powers and allows m to be determined in terms of electrical quantities and, hence, of the Planck constant. A number of subtleties have been dismissed in the previous analysis. Firstly, the Lor ...
... the geometric factor BL, we obtain the equation mgu = UI, which virtually relates mechanical and electrical powers and allows m to be determined in terms of electrical quantities and, hence, of the Planck constant. A number of subtleties have been dismissed in the previous analysis. Firstly, the Lor ...
Pdf
... X, momentum P! via potential v (x,X). At the same time the heavier particle experiences an external potential V(X). The two-particle Hamiltonian consequently has the form P2 p2 ...
... X, momentum P! via potential v (x,X). At the same time the heavier particle experiences an external potential V(X). The two-particle Hamiltonian consequently has the form P2 p2 ...
... bound charges. In class we discussed the physical interpretation of bound charges. The displacement of the charges in the material caused by the polarization will only result in a net charge near the surface of the material or near areas where the polarization is not constant, i.e. has a non-zero di ...
Resonant ionization of shallow donors in electric field Linköping University Post Print
... 3.1 MV/m [cf. figure 1(a)], which will be argued to correspond to the anti-crossings at 2.45 and 3.25 MV/m observed in [4], despite of the disagreement in the critical-field values. Let us regard first the dependence of the energy of the ground state on the electric field [figure 1(a)]. This depend ...
... 3.1 MV/m [cf. figure 1(a)], which will be argued to correspond to the anti-crossings at 2.45 and 3.25 MV/m observed in [4], despite of the disagreement in the critical-field values. Let us regard first the dependence of the energy of the ground state on the electric field [figure 1(a)]. This depend ...