Flexure Mounts For High Resolution Optical Elements
... Less hysteresis than rolling or sliding contacts More robust to adverse environment effects such as extreme temperatures, vacuum, and abrasive dust Needs very little maintenance if any ...
... Less hysteresis than rolling or sliding contacts More robust to adverse environment effects such as extreme temperatures, vacuum, and abrasive dust Needs very little maintenance if any ...
The Microscope in a Computer: Image Synthesis from Three
... in which η0 = (µ0 /ǫ0 )1/2 is the wave impedance of free space. Although alternative terminologies do exist, we will use the term light intensity or simply intensity for the radiated power per unit area. The light intensity is a direct measure of the signal collected by recording media that convert ...
... in which η0 = (µ0 /ǫ0 )1/2 is the wave impedance of free space. Although alternative terminologies do exist, we will use the term light intensity or simply intensity for the radiated power per unit area. The light intensity is a direct measure of the signal collected by recording media that convert ...
Image transmission through a stable paraxial cavity
... free-propagation of a field changes its transverse distribution, but in some planes, such as conjugate planes, or Fourier plane, one get simple transformations of the image. On the other hand, transmission through cavity has a drastic effect on the transverse distribution of the field, as one must t ...
... free-propagation of a field changes its transverse distribution, but in some planes, such as conjugate planes, or Fourier plane, one get simple transformations of the image. On the other hand, transmission through cavity has a drastic effect on the transverse distribution of the field, as one must t ...
UNIVERSIDAD DE MURCIA ABERRACIONES EN LENTES OFTÁLMICAS DE POTENCIA
... llega finalmente al sensor HS, formado por una matriz de microlentes (distancia focal 40 mm y apertura 0.6 mm) y una cámara CCD. Para medir solo las lentes, se sustituye el ojo por un espejo que dirige el haz de luz hacia la superficie posterior de la lente. Todas las medidas se realizan replicando ...
... llega finalmente al sensor HS, formado por una matriz de microlentes (distancia focal 40 mm y apertura 0.6 mm) y una cámara CCD. Para medir solo las lentes, se sustituye el ojo por un espejo que dirige el haz de luz hacia la superficie posterior de la lente. Todas las medidas se realizan replicando ...
pdf
... viewed with a wave aberration corresponding to a single Zernike mode. During the second interval, the stimulus was viewed with a wave aberration corresponding to a standard aberration. The standard aberration was created by combining all 18 Zernike modes from the second through fifth order, each hav ...
... viewed with a wave aberration corresponding to a single Zernike mode. During the second interval, the stimulus was viewed with a wave aberration corresponding to a standard aberration. The standard aberration was created by combining all 18 Zernike modes from the second through fifth order, each hav ...
Fourier-domain holography in photorefractive quantum-well films
... images inside living tissue.9 However, the current generation of PRQW devices has fabrication-related defects that limit the sensitivity and dynamic range of photorefractive holography because of scattered background. The dynamic range 共without any spatial filtering兲 was reported to be 45 dB for the ...
... images inside living tissue.9 However, the current generation of PRQW devices has fabrication-related defects that limit the sensitivity and dynamic range of photorefractive holography because of scattered background. The dynamic range 共without any spatial filtering兲 was reported to be 45 dB for the ...
File
... distance of only 8.2 mm 8.0 mm 0.2 mm to bring the object into focus. In general, camera lenses don’t need to ...
... distance of only 8.2 mm 8.0 mm 0.2 mm to bring the object into focus. In general, camera lenses don’t need to ...
Gradient Index Optics at DARPA - Institute for Defense Analyses
... Defense Analyses (IDA) to assemble a summary of work on gradient index optics completed under funding from the Agency. The purpose was to archive the efforts, motivation, and accomplishments that the Agency supported and to provide a reference for any future programs that explore this new area of op ...
... Defense Analyses (IDA) to assemble a summary of work on gradient index optics completed under funding from the Agency. The purpose was to archive the efforts, motivation, and accomplishments that the Agency supported and to provide a reference for any future programs that explore this new area of op ...
Comparison of LSST and DECam Wavefront Recovery
... The optical system is based on a modified Paul-Baker 3-mirror telescope design having an 8.4m primary, 3.4m secondary, and 5.0m tertiary feeding a three-element refractive camera system producing a flat 9.6 square degree field-of-view with an effective clear aperture of ∼6.5m. LSST will use an activ ...
... The optical system is based on a modified Paul-Baker 3-mirror telescope design having an 8.4m primary, 3.4m secondary, and 5.0m tertiary feeding a three-element refractive camera system producing a flat 9.6 square degree field-of-view with an effective clear aperture of ∼6.5m. LSST will use an activ ...
labs for the photon/photon2 experiment kit
... the film darkens immediately, try a shorter exposure. If the image is too light, use a longer exposure. Conclusions/Observations: Describe the image you created- was it sharp or blurred? Compare your photograph to one taken by a regular (lens) camera. Applications/Explorations: 1. Photographs taken ...
... the film darkens immediately, try a shorter exposure. If the image is too light, use a longer exposure. Conclusions/Observations: Describe the image you created- was it sharp or blurred? Compare your photograph to one taken by a regular (lens) camera. Applications/Explorations: 1. Photographs taken ...
Methods and Applications of Optical Holography
... employing binary mask to record two-dimensional [43, 44] and three-dimensional objects [45, 46] viewed in coherent light. The CGH is based on numerical computation of virtual wavefront therefore requires substantial computing resources. For improved security the Electron Beam Lithography is used for ...
... employing binary mask to record two-dimensional [43, 44] and three-dimensional objects [45, 46] viewed in coherent light. The CGH is based on numerical computation of virtual wavefront therefore requires substantial computing resources. For improved security the Electron Beam Lithography is used for ...
Non-iterative phase hologram computation for low
... applications such as optical tweezers, beam shaping, optical information processing, optical data storage, optical communications, adaptive optics, wave-front correction and holographic displays [4–8]. CGHs are also used in holographic image projection (HIP), which has been receiving increasing inte ...
... applications such as optical tweezers, beam shaping, optical information processing, optical data storage, optical communications, adaptive optics, wave-front correction and holographic displays [4–8]. CGHs are also used in holographic image projection (HIP), which has been receiving increasing inte ...
Design, fabrication and testing of microlens arrays for sensors and
... Figure 9(a) shows an interferogram of a resist lens (Ø ≈ 150 µm, NA ≈ 0.15) tested in a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Figure 9(b) shows the modulation transfer function (MTF) calculated from the wave aberrations. Diffraction-limited performance is observed for the lens shown in figure 9(a). 4.2.4. Co ...
... Figure 9(a) shows an interferogram of a resist lens (Ø ≈ 150 µm, NA ≈ 0.15) tested in a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. Figure 9(b) shows the modulation transfer function (MTF) calculated from the wave aberrations. Diffraction-limited performance is observed for the lens shown in figure 9(a). 4.2.4. Co ...
5377 17paper
... be designed so that it is most sensitive to particular aberration types and order. Rather than spatially, it is convenient to examine this object structure in the frequency domain. The idea is to find the optimum linear combination of features that samples the entire pupil. As an example, Figure 2(a ...
... be designed so that it is most sensitive to particular aberration types and order. Rather than spatially, it is convenient to examine this object structure in the frequency domain. The idea is to find the optimum linear combination of features that samples the entire pupil. As an example, Figure 2(a ...
Performance of extended depth of field systems and
... system as generally as possible, in order to address all of these methods. The considered optical system is a stop combined to a phase function and an amplitude function. This model could represent a lens, as well as a more complex assembly. Note that this model could be considered as the best case, ...
... system as generally as possible, in order to address all of these methods. The considered optical system is a stop combined to a phase function and an amplitude function. This model could represent a lens, as well as a more complex assembly. Note that this model could be considered as the best case, ...
Chapter 18 - Handbook of Optics
... was developed by Wynne (1965, 1974) for the region of the spectrum extending from 365 to 1014 nm. It is used to extend the field of a parabolic mirror. Versions for a Ritchey-Chretien primary also exist. The corrector is able to correct spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, and field curvature wh ...
... was developed by Wynne (1965, 1974) for the region of the spectrum extending from 365 to 1014 nm. It is used to extend the field of a parabolic mirror. Versions for a Ritchey-Chretien primary also exist. The corrector is able to correct spherical aberration, coma, astigmatism, and field curvature wh ...
Resolving the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict in Head Mounted
... help with this issue in future designs. In Section 3, we describe the various methods and metrics that have been proposed or applied to evaluate the effectiveness of existing solutions. Finally, in Section 4, we identify potential areas within the solution space that have yet to be explored or can b ...
... help with this issue in future designs. In Section 3, we describe the various methods and metrics that have been proposed or applied to evaluate the effectiveness of existing solutions. Finally, in Section 4, we identify potential areas within the solution space that have yet to be explored or can b ...
What Brown saw, and you can too
... (by B. C.) of imaging by a 1mm diameter spherical (ball) lens, whose magnification is close to that of Brown’s lens. Section VI, Theory, is meant for advanced physics undergraduates or graduate students and their teachers. It consists of seven theoretical appendices, tutorials on classical physics. ...
... (by B. C.) of imaging by a 1mm diameter spherical (ball) lens, whose magnification is close to that of Brown’s lens. Section VI, Theory, is meant for advanced physics undergraduates or graduate students and their teachers. It consists of seven theoretical appendices, tutorials on classical physics. ...
introductory practical physics ii - National Open University of Nigeria
... your protractor, measure an angle PQN equals 10 and draw line PQ. This line PQ is an incident ray and angle PQN is an angle of incidence (i). Now insert two erect pins at point P and Q respectively. The pins inserted on these points should be straight and view the two pins from side DC of the glass ...
... your protractor, measure an angle PQN equals 10 and draw line PQ. This line PQ is an incident ray and angle PQN is an angle of incidence (i). Now insert two erect pins at point P and Q respectively. The pins inserted on these points should be straight and view the two pins from side DC of the glass ...
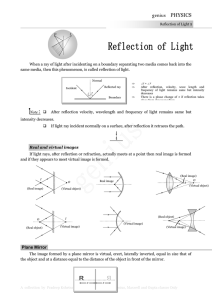
genius PHYSICS
... (iii) A man of height h requires a mirror of length at least equal to h/2, to see his own complete image. (iv) To see complete wall behind himself a person requires a plane mirror of at least one third the height of wall. It should be noted that person is standing in the middle of the room. ...
... (iii) A man of height h requires a mirror of length at least equal to h/2, to see his own complete image. (iv) To see complete wall behind himself a person requires a plane mirror of at least one third the height of wall. It should be noted that person is standing in the middle of the room. ...
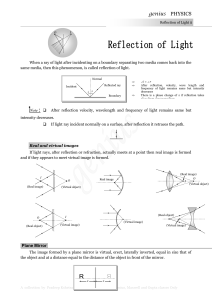
Colours of opaque object - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... (iii) A man of height h requires a mirror of length at least equal to h/2, to see his own complete image. (iv) To see complete wall behind himself a person requires a plane mirror of at least one third the height of wall. It should be noted that person is standing in the middle of the room. ...
... (iii) A man of height h requires a mirror of length at least equal to h/2, to see his own complete image. (iv) To see complete wall behind himself a person requires a plane mirror of at least one third the height of wall. It should be noted that person is standing in the middle of the room. ...
Light-Scattering Study of the Normal Human Eye
... acoustic modes of materials. The expansions and contractions created in the material by propagating acoustic waves result in spatial and temporal modulations of the material density. The resulting time-dependent changes in the electromagnetic characteristics, such as the refractive index of the mate ...
... acoustic modes of materials. The expansions and contractions created in the material by propagating acoustic waves result in spatial and temporal modulations of the material density. The resulting time-dependent changes in the electromagnetic characteristics, such as the refractive index of the mate ...
1 Fundamental Optics www.cvimellesgriot.com
... are made to determine critical parameters such as magnification, focal length(s), clear aperture (diameter), and object and image position. These paraxial calculations are covered in the next section of this chapter. Second, actual components are chosen based on these paraxial values, and their actu ...
... are made to determine critical parameters such as magnification, focal length(s), clear aperture (diameter), and object and image position. These paraxial calculations are covered in the next section of this chapter. Second, actual components are chosen based on these paraxial values, and their actu ...