Question Bank Physics Class 12
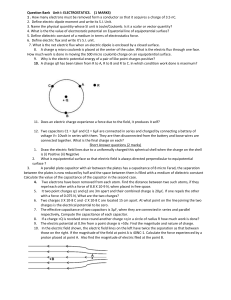
... Q3. What is the effective resistance of ammeter if a shunt resistance S is used across the terminals of the galvanometer of resistance G? Q4. Which physical quantity has the unit Wb/m2? Is it a scalar or a vector quantity? Q5. If magnetic dipole is along the direction of magnetic field. What is the ...
... Q3. What is the effective resistance of ammeter if a shunt resistance S is used across the terminals of the galvanometer of resistance G? Q4. Which physical quantity has the unit Wb/m2? Is it a scalar or a vector quantity? Q5. If magnetic dipole is along the direction of magnetic field. What is the ...
Electric Flux
... c. to curved surfaces d. and finally to closed, rather than open, surfaces. a. With flux associated with the number of field lines crossing the surface, it is straightforward to generalize to the case when E is not perpendicular to the area. Imagine a bull’s eye target. First when arrows are aimed a ...
... c. to curved surfaces d. and finally to closed, rather than open, surfaces. a. With flux associated with the number of field lines crossing the surface, it is straightforward to generalize to the case when E is not perpendicular to the area. Imagine a bull’s eye target. First when arrows are aimed a ...
Space-Charge Polarization
... The dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric material is called polarization vector. ‘ ’ - average dipole moment per molecule and ‘N’ - number of molecules per unit volume polarization vector is given by, Unit: Coulomb / m2 ...
... The dipole moment per unit volume of the dielectric material is called polarization vector. ‘ ’ - average dipole moment per molecule and ‘N’ - number of molecules per unit volume polarization vector is given by, Unit: Coulomb / m2 ...
ENE 429 Antenna and Transmission Lines
... external force to move a charge from point a to point b in an electric field divided by the amount of charge moved. ...
... external force to move a charge from point a to point b in an electric field divided by the amount of charge moved. ...
Thursday, Sept. 8, 2011
... • Since from a far distance, the two charges are very close so that the overall charge gets close to 0!! • This dependence works for the point not on bisector as well ...
... • Since from a far distance, the two charges are very close so that the overall charge gets close to 0!! • This dependence works for the point not on bisector as well ...
A1979HN47900001
... understand the regulatory effects of light on nitrate assimilation.3 The full explanation is currently being developed. "In writing this, it became obvious how dependent I have been on the ...
... understand the regulatory effects of light on nitrate assimilation.3 The full explanation is currently being developed. "In writing this, it became obvious how dependent I have been on the ...
EE 333 Electricity and Magnetism, Fall 2009 Homework #5 solution
... Outside the cable we have Dρ = 0, so Eρ = 0 and Pρ = 0 because of the proportionality between the three quantities. (b) At the interface between the inner conductor and region 1 the polarzation changes discontinuously from Pρ = 0 in the conductor (because there is no electric field in the ρl . We kn ...
... Outside the cable we have Dρ = 0, so Eρ = 0 and Pρ = 0 because of the proportionality between the three quantities. (b) At the interface between the inner conductor and region 1 the polarzation changes discontinuously from Pρ = 0 in the conductor (because there is no electric field in the ρl . We kn ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... bonds between the glucose monomers. Most animals, including humans, also have enzymes that can hydrolyze plant starch, making glucose available as a nutrient for cells. Potato tubers and grains—the fruits of wheat, maize (corn), rice, and other grasses—are the major sources of starch in the human d ...
... bonds between the glucose monomers. Most animals, including humans, also have enzymes that can hydrolyze plant starch, making glucose available as a nutrient for cells. Potato tubers and grains—the fruits of wheat, maize (corn), rice, and other grasses—are the major sources of starch in the human d ...
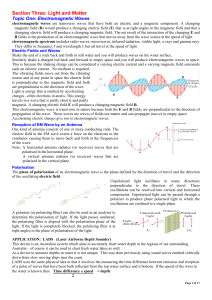
Section Three: Light and Matter
... magnetic field (B) would produce a changing electric field (E) that is at right angles to the magnetic field and that a changing electric field will produce a changing magnetic field. The net result of the interaction of the changing E and B fields is the production of an electromagnetic wave that m ...
... magnetic field (B) would produce a changing electric field (E) that is at right angles to the magnetic field and that a changing electric field will produce a changing magnetic field. The net result of the interaction of the changing E and B fields is the production of an electromagnetic wave that m ...
Document
... This expression is valid for spherical isotropic Brownian motion of a dipole in an Onsager cavity. To obtain the molecular DCF it is necessary to average over distribution of orientations at time t, for a given initial orientation and then to average over an equilibrium distribution of initial orien ...
... This expression is valid for spherical isotropic Brownian motion of a dipole in an Onsager cavity. To obtain the molecular DCF it is necessary to average over distribution of orientations at time t, for a given initial orientation and then to average over an equilibrium distribution of initial orien ...
Chapter 7
... • Deoxy sugars are monosaccharides with one or more hydroxyl groups replaced by hydrogens • 2-Deoxy-D-ribose is a constituent of DNA • Rhamnose is a component of ouabain, a toxic “cardiac glycoside” • Fucose is a component of some cell walls ...
... • Deoxy sugars are monosaccharides with one or more hydroxyl groups replaced by hydrogens • 2-Deoxy-D-ribose is a constituent of DNA • Rhamnose is a component of ouabain, a toxic “cardiac glycoside” • Fucose is a component of some cell walls ...
Circular dichroism

Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light. Left-hand circular (LHC) and right-hand circular (RHC) polarized light represent two possible spin angular momentum states for a photon, and so circular dichroism is also referred to as dichroism for spin angular momentum. This phenomenon was discovered by Jean-Baptiste Biot, Augustin Fresnel, and Aimé Cotton in the first half of the 19th century. It is exhibited in the absorption bands of optically active chiral molecules. CD spectroscopy has a wide range of applications in many different fields. Most notably, UV CD is used to investigate the secondary structure of proteins. UV/Vis CD is used to investigate charge-transfer transitions. Near-infrared CD is used to investigate geometric and electronic structure by probing metal d→d transitions. Vibrational circular dichroism, which uses light from the infrared energy region, is used for structural studies of small organic molecules, and most recently proteins and DNA.