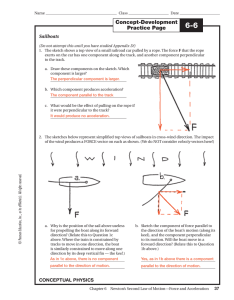
Chapter 8
... 3. As Halley’s Comet orbits the sun, its distance from the sun changes dramatically, from 8.8 × 1010 m to 5.2 × 1012 m. If the comet’s speed at closest approach is 5.4 × 104 m/s, what is its speed when it is farthest from the sun if angular momentum is conserved? ...
... 3. As Halley’s Comet orbits the sun, its distance from the sun changes dramatically, from 8.8 × 1010 m to 5.2 × 1012 m. If the comet’s speed at closest approach is 5.4 × 104 m/s, what is its speed when it is farthest from the sun if angular momentum is conserved? ...
Describing Motion - Science
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
... First we need to define the word FORCE: • The cause of motion (what causes objects to move) • Two types of forces – Pushes – Pulls ...
332 Unit 7 Momentum student handout
... b) Find the % of kinetic energy lost during the collision. ...
... b) Find the % of kinetic energy lost during the collision. ...
sessnn9
... transmitting sounds, the atoms of solids conveying temperature or the electrons in antennas. We are now going to study some of the properties of such periodic oscillations, often called Harmonic Motions. The frequency A simple oscillating system consists of a particle moving repeatedly back and fort ...
... transmitting sounds, the atoms of solids conveying temperature or the electrons in antennas. We are now going to study some of the properties of such periodic oscillations, often called Harmonic Motions. The frequency A simple oscillating system consists of a particle moving repeatedly back and fort ...
Force and Motion
... combined forces Forces in the same direction combine by addition Forces in Opposite directions combine by subtraction ...
... combined forces Forces in the same direction combine by addition Forces in Opposite directions combine by subtraction ...
Physics 513 Topic List/Study Checksheet This should function more
... - Horizontal projectile motion and projectiles fired at an angle on level ground - Uniform Circular Motion – centripetal force, direction of velocity, net force and acceleration - Definition of period - Vertical Circular motion* - At the top and bottom of a circle, vmin and vmax - Newton’s Law of Un ...
... - Horizontal projectile motion and projectiles fired at an angle on level ground - Uniform Circular Motion – centripetal force, direction of velocity, net force and acceleration - Definition of period - Vertical Circular motion* - At the top and bottom of a circle, vmin and vmax - Newton’s Law of Un ...
Force and Acceleration
... air to provide friction. • The ratio of moon-weight to mass for each object is the same, and they both accelerate ...
... air to provide friction. • The ratio of moon-weight to mass for each object is the same, and they both accelerate ...
POP4e: Ch. 1 Problems
... 4 (8.4) A particle of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point A and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure. Determine the particle’s speed at points B and C and the net work done by the gravitational force as the particle moves from A to C. ...
... 4 (8.4) A particle of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point A and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure. Determine the particle’s speed at points B and C and the net work done by the gravitational force as the particle moves from A to C. ...
Recitation 1
... for the maximum vector acceleration, so the direction did matter. (d) The period of our particle is T = 1/f = 2/3 s. t = 1.00 s = 1.5T . That means it travels 0 → A → −A → A → 0, for a grand total of d = A + 2A + 2A + A = 6A = 12.0 cm. Problem 12.12. A 1.00 kg glider attached to a spring with a forc ...
... for the maximum vector acceleration, so the direction did matter. (d) The period of our particle is T = 1/f = 2/3 s. t = 1.00 s = 1.5T . That means it travels 0 → A → −A → A → 0, for a grand total of d = A + 2A + 2A + A = 6A = 12.0 cm. Problem 12.12. A 1.00 kg glider attached to a spring with a forc ...
Chapter 6
... The object is called the SYSTEM. The world around the object that exerts forces on it is called the ENVIRONMENT. Forces have both magnitude and direction and are therefore _____________. ...
... The object is called the SYSTEM. The world around the object that exerts forces on it is called the ENVIRONMENT. Forces have both magnitude and direction and are therefore _____________. ...