Physics 04-Statics, Torque, Rotational Motion
... gyroscope. The torque produced is perpendicular to the angular momentum, thus the direction of the torque is changed, but not its magnitude. The gyroscope precesses around a vertical axis, since the torque is always horizontal and perpendicular to ...
... gyroscope. The torque produced is perpendicular to the angular momentum, thus the direction of the torque is changed, but not its magnitude. The gyroscope precesses around a vertical axis, since the torque is always horizontal and perpendicular to ...
Motion of a charged particle under the action of a magnetic field
... A metal wire of mass m can slide without friction on two parallel, horizontal, conducting rails. The rails are connected by a generator which delivers a constant current i to the circuit. There is a constant, vertical magnetic field, perpendicular to the plane of the rails. If the wire is initially ...
... A metal wire of mass m can slide without friction on two parallel, horizontal, conducting rails. The rails are connected by a generator which delivers a constant current i to the circuit. There is a constant, vertical magnetic field, perpendicular to the plane of the rails. If the wire is initially ...
Monday, Feb. 16, 2004
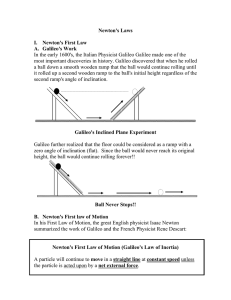
... object. To move faster, ones needs higher force. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion ...
... object. To move faster, ones needs higher force. Galileo’s statement on natural states of matter: Any velocity once imparted to a moving body will be rigidly maintained as long as the external causes of retardation are removed!! Galileo’s statement is formulated by Newton into the 1st law of motion ...
Force and Acceleration
... In this mission, you will start with the block being at rest. Then, by applying forces to it with the joystick, try to get its speed to increase to 2 m/s and then stay at a constant value of 2 m/s afterwards. a. First, predict how you would need to apply force to accomplish this mission. In particul ...
... In this mission, you will start with the block being at rest. Then, by applying forces to it with the joystick, try to get its speed to increase to 2 m/s and then stay at a constant value of 2 m/s afterwards. a. First, predict how you would need to apply force to accomplish this mission. In particul ...
RevfinQans111fa02
... Answer: mg > Ffric Draw the free-body diagram to see this. Also realize that Ffric does NOT equal sN. Ffric is less than or equal sN. It is only equal is the book is about to slip. ...
... Answer: mg > Ffric Draw the free-body diagram to see this. Also realize that Ffric does NOT equal sN. Ffric is less than or equal sN. It is only equal is the book is about to slip. ...
Physics 2 Lecture Notes
... Consider a positively charged ion entering a region where the electric and magnetic fields are uniform and perpendicular to each other. If the particle moves in a straight line, what is its velocity in terms of E and B? ...
... Consider a positively charged ion entering a region where the electric and magnetic fields are uniform and perpendicular to each other. If the particle moves in a straight line, what is its velocity in terms of E and B? ...
333 UNIT 2 - mrdsample
... Example 2: An empty elevator of mass 2700 kg is pulled upward by a cable. The elevator accelerates up at 1.3m/s2. a) Draw a force diagram for the elevator. b) Write the 2nd law force equation with specific forces. c) Determine weight of elevator. ...
... Example 2: An empty elevator of mass 2700 kg is pulled upward by a cable. The elevator accelerates up at 1.3m/s2. a) Draw a force diagram for the elevator. b) Write the 2nd law force equation with specific forces. c) Determine weight of elevator. ...
Unit 3 Objectives: Forces and Laws of Motion
... 6. What is the weight in Newtons of an object whose mass is 40 kg? Fw = mg Fw=40(10)= 400N 7. The gravitational attractive force on the moon is 1/6 that of earth giving objects an acceleration of 1.67 m/s2 (in other words, on the moon g= 1.67 m/s2). What would be the mass of a 150-kg TV set on the m ...
... 6. What is the weight in Newtons of an object whose mass is 40 kg? Fw = mg Fw=40(10)= 400N 7. The gravitational attractive force on the moon is 1/6 that of earth giving objects an acceleration of 1.67 m/s2 (in other words, on the moon g= 1.67 m/s2). What would be the mass of a 150-kg TV set on the m ...
Exam No. 01 (Fall 2013) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... 2. (Schwinger et al., problem 7, chapter 1.) A charge q moves in the vacuum under the influence of uniform fields E and B. Assume that E · B = 0 and v · B = 0. (a) At what velocity does the charge move without acceleration? (b) What is the speed when ε0 E 2 = µ0 H 2 ? 3. A plane wave is incident, in ...
... 2. (Schwinger et al., problem 7, chapter 1.) A charge q moves in the vacuum under the influence of uniform fields E and B. Assume that E · B = 0 and v · B = 0. (a) At what velocity does the charge move without acceleration? (b) What is the speed when ε0 E 2 = µ0 H 2 ? 3. A plane wave is incident, in ...
Extension 3.4: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... A kite is subject to a net force of 0.389 N, northwest. Its acceleration is 2.35 m/s2, northwest. According to Newton’s Second Law (Eq. E3.4.1a), which is a vector relation, the directions of the net force on an object and acceleration of that object must be the same. Luckily, this appears true for ...
... A kite is subject to a net force of 0.389 N, northwest. Its acceleration is 2.35 m/s2, northwest. According to Newton’s Second Law (Eq. E3.4.1a), which is a vector relation, the directions of the net force on an object and acceleration of that object must be the same. Luckily, this appears true for ...
Rotational or Angular Motion
... He has decreased his radius of rotation, so his moment of inertia is decreased. By the law of conservation of angular momentum, a decrease in moment of inertia means an increase in angular ...
... He has decreased his radius of rotation, so his moment of inertia is decreased. By the law of conservation of angular momentum, a decrease in moment of inertia means an increase in angular ...
Chap7Class2
... (a) Determine the work a hiker must do on a 15.0-kg backpack to carry it up a hill of height h = 10.0 m, as shown. Determine also (b) the work done by gravity on the backpack, and (c) the net work done on the backpack. For simplicity, assume the motion is smooth and at constant velocity (i.e., accel ...
... (a) Determine the work a hiker must do on a 15.0-kg backpack to carry it up a hill of height h = 10.0 m, as shown. Determine also (b) the work done by gravity on the backpack, and (c) the net work done on the backpack. For simplicity, assume the motion is smooth and at constant velocity (i.e., accel ...
Simple Harmonic Motion
... The Simple Pendulum • The pendulum shown has a restoring force Fg,x. – A component of the force of gravity – At small angles, Fg,x is proportional to the displacement (), so the pendulum obeys Hooke’s ...
... The Simple Pendulum • The pendulum shown has a restoring force Fg,x. – A component of the force of gravity – At small angles, Fg,x is proportional to the displacement (), so the pendulum obeys Hooke’s ...
Physics 1 Dynamics Lab Activity Investigating Newton`s First and
... showing the direction of motion of the sphere, and the direction of the force. Also show any changes in the motion of the sphere on the diagram. a. Sphere at rest: b. Force in the same direction as the sphere's velocity c. Force in the opposite direction to the sphere's velocity: d. Force at right a ...
... showing the direction of motion of the sphere, and the direction of the force. Also show any changes in the motion of the sphere on the diagram. a. Sphere at rest: b. Force in the same direction as the sphere's velocity c. Force in the opposite direction to the sphere's velocity: d. Force at right a ...
Acceleration - pruettscience
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force & inversely proportional to it’s mass. • F = ma • Force = Mass x Acceleration ...
... Newton’s Second Law • The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force & inversely proportional to it’s mass. • F = ma • Force = Mass x Acceleration ...