Unit_2_AP_Forces_Review_Problems
... a. Why does the book remain motionless before the force is applied? b. Why does the book move when the hand pushed on it? c. Why does the book eventually come to a stop? d. Under what conditions would the book remain in motion at a constant speed? 2. Why do you lunge forward when your car suddenly c ...
... a. Why does the book remain motionless before the force is applied? b. Why does the book move when the hand pushed on it? c. Why does the book eventually come to a stop? d. Under what conditions would the book remain in motion at a constant speed? 2. Why do you lunge forward when your car suddenly c ...
Notes (fill in)
... The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity is called the __________________________________ ...
... The constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity is called the __________________________________ ...
Chapter 5: Forces in Two DImensions
... You help your mom move a 41kg bookcase to a different place in the living room. If you push with a force of 65N and the bookcase accelerates at 0.12m/s2, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bookcase and the carpet? ...
... You help your mom move a 41kg bookcase to a different place in the living room. If you push with a force of 65N and the bookcase accelerates at 0.12m/s2, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bookcase and the carpet? ...
Physics 2414, Spring 2005 Group Exercise 10, Apr 28, 2005
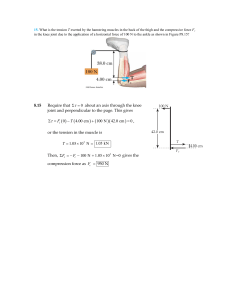
... A ladder of length l = 20 meters weighing mL g = 500 Newtons rests against a wall at a point h = 12 meters above the ground. The center of mass of the ladder is at the center of the ladder. A man weighing mp g = 800 Newtons climbs a distance x = 15 meters up the ladder. The friction on the floor kee ...
... A ladder of length l = 20 meters weighing mL g = 500 Newtons rests against a wall at a point h = 12 meters above the ground. The center of mass of the ladder is at the center of the ladder. A man weighing mp g = 800 Newtons climbs a distance x = 15 meters up the ladder. The friction on the floor kee ...
π π π λ ρ ρ ρ ρ ρ
... 11) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a 6.0-kg object moving to the left at 2.0 m/s. Which statement is correct? a. The total momentum both before and after the collision is 24 kg · m/s. b. The total momentum before the collision is 24 kg · m/s, and the total m ...
... 11) A 3.0-kg object moves to the right at 4.0 m/s. It collides head-on with a 6.0-kg object moving to the left at 2.0 m/s. Which statement is correct? a. The total momentum both before and after the collision is 24 kg · m/s. b. The total momentum before the collision is 24 kg · m/s, and the total m ...
Back
... A 1 g bullet is fired into a 2kg block of wood with a initial velocity of 100m/s sitting on a frictionless surface? What is the final velocity of the bullet and the block of wood? Back ...
... A 1 g bullet is fired into a 2kg block of wood with a initial velocity of 100m/s sitting on a frictionless surface? What is the final velocity of the bullet and the block of wood? Back ...
Unit 3 – Net Force
... a) How much does the suitcase weigh? b) How much is the normal force? c) How much is the friction? ...
... a) How much does the suitcase weigh? b) How much is the normal force? c) How much is the friction? ...