Chapter 11 Science Notes
... • Speed- how fast an object’s position changes over time. To calculate speed: Speed=distance ÷ time ...
... • Speed- how fast an object’s position changes over time. To calculate speed: Speed=distance ÷ time ...
More on energy plus gravitation
... Newton figured out the 1/r2 dependence, assuming that the celestial objects and the Earth were point particles. By inventing integral calculus he could prove that for a mass m2, outside a spherical mass m1, the force of gravity was as if all of the mass m1 was at the center of the sphere. Therefore ...
... Newton figured out the 1/r2 dependence, assuming that the celestial objects and the Earth were point particles. By inventing integral calculus he could prove that for a mass m2, outside a spherical mass m1, the force of gravity was as if all of the mass m1 was at the center of the sphere. Therefore ...
Force and Motion - mrhsluniewskiscience
... the book to the right, the book moves towards right. The symbol F is a vector and represents the size and direction of a force, while F represents only the magnitude. ...
... the book to the right, the book moves towards right. The symbol F is a vector and represents the size and direction of a force, while F represents only the magnitude. ...
2004_11_03ImpulseMomentum
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
ch15
... Example, pendulum: In Fig. a, a meter stick swings about a pivot point at one end, at distance h from the stick’s center of mass. (a) What is the period of oscillation T? KEY IDEA: The stick is not a simple pendulum because its mass is not concentrated in a bob at the end opposite the pivot point—s ...
... Example, pendulum: In Fig. a, a meter stick swings about a pivot point at one end, at distance h from the stick’s center of mass. (a) What is the period of oscillation T? KEY IDEA: The stick is not a simple pendulum because its mass is not concentrated in a bob at the end opposite the pivot point—s ...
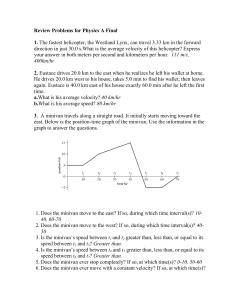
Review for Final - Lewis-Palmer School District 38
... 48. Although it cannot sustain its top speed for more than 8.65 s, the cheetah can run a distance of 274 m during that time. If a cheetah with a mass of 50.0 kg is moving north at its top speed, what is its momentum? 1583.8 kgm/s 49. A net force of 10.0 N to the right pushes a 3.0 kg book across a t ...
... 48. Although it cannot sustain its top speed for more than 8.65 s, the cheetah can run a distance of 274 m during that time. If a cheetah with a mass of 50.0 kg is moving north at its top speed, what is its momentum? 1583.8 kgm/s 49. A net force of 10.0 N to the right pushes a 3.0 kg book across a t ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued ...
... Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued ...
Newton`s Third Law - K
... will go”. Be careful about this! It is not accurate. What the person means to say is that, “The more force you add the greater the rate at which the object speeds up.” Force is related to acceleration. Zero net force is related to constant velocity! ...
... will go”. Be careful about this! It is not accurate. What the person means to say is that, “The more force you add the greater the rate at which the object speeds up.” Force is related to acceleration. Zero net force is related to constant velocity! ...
CIRCULAR MOTION, ORBITS, AND GRAVITY
... from above the north pole. A point on the earth’s equator would have a positive angular velocity as seen from this position. Assess: Angular velocity is positive for counterclockwise rotations. ...
... from above the north pole. A point on the earth’s equator would have a positive angular velocity as seen from this position. Assess: Angular velocity is positive for counterclockwise rotations. ...
Ch 5 Newton`s 2nd Law
... µ = the coefficient of sliding friction (has no units) 1. Ben is walking through the school cafeteria but does not realize that the person in front of him has just spilled his glass of chocolate milk. As Ben, who weighs 420 N, steps in the milk, the coefficient of sliding friction between Ben and th ...
... µ = the coefficient of sliding friction (has no units) 1. Ben is walking through the school cafeteria but does not realize that the person in front of him has just spilled his glass of chocolate milk. As Ben, who weighs 420 N, steps in the milk, the coefficient of sliding friction between Ben and th ...