Learning Standard # 1
... Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Distinguish the difference between Velocity and acceleration. Graphically represent and interpret distance - time, velocity – time, and acceleration and time. Understand that gravity causes objects to accelerate towards earth’s center. Solve acceler ...
... Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Distinguish the difference between Velocity and acceleration. Graphically represent and interpret distance - time, velocity – time, and acceleration and time. Understand that gravity causes objects to accelerate towards earth’s center. Solve acceler ...
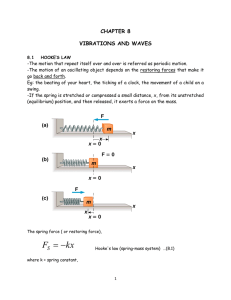
f F = mg X
... Three objects are connected by strings that pass over massless and frictionless pulleys. The objects move and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the middle object and the surface of the table is 0.100 (the other two being suspended by strings). (a) What is the acceleration of the three obje ...
... Three objects are connected by strings that pass over massless and frictionless pulleys. The objects move and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the middle object and the surface of the table is 0.100 (the other two being suspended by strings). (a) What is the acceleration of the three obje ...
physics EM curriculm A
... Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Distinguish the difference between Velocity and acceleration. Graphically represent and interpret distance - time, velocity – time, and acceleration and time. Understand that gravity causes objects to accelerate towards earth’s center. Solve acceler ...
... Explain the difference between speed and velocity. Distinguish the difference between Velocity and acceleration. Graphically represent and interpret distance - time, velocity – time, and acceleration and time. Understand that gravity causes objects to accelerate towards earth’s center. Solve acceler ...
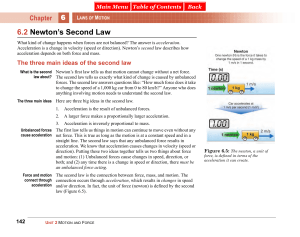
6.2 Newton`s Second Law
... Reviewing the Newton One newton is the force needed to change the speed of one kilogram by 1 m/s in one second. This means that: 1 N = 1 kg-m/s2 Or you can say one newton equals one kilogram-meter per second squared. ...
... Reviewing the Newton One newton is the force needed to change the speed of one kilogram by 1 m/s in one second. This means that: 1 N = 1 kg-m/s2 Or you can say one newton equals one kilogram-meter per second squared. ...
The Nature of Force
... engine exerts a force of 650 N [forward]. The air resistance acting on Kendre and the bike is 230 N [backward]. The friction between the tires and the road is 110 N [backward]. The normal force exerted by the road is 1820 N [up]. a) Draw a free-body diagram for the system that includes Kendre and he ...
... engine exerts a force of 650 N [forward]. The air resistance acting on Kendre and the bike is 230 N [backward]. The friction between the tires and the road is 110 N [backward]. The normal force exerted by the road is 1820 N [up]. a) Draw a free-body diagram for the system that includes Kendre and he ...
Chapter 7 Rotational Motion 7.1 Angular Quantities Homework # 51
... 03. A 0.875-kg solid ball is tied to a string and rotated in a circle of radius 0.925 m. A force of air resistance of 0.0245 N acts as the ball rotates. a.) What is the moment of inertia of the ball? b.) What torque must be applied to the ball to keep it rotating at a constant angular velocity? 04. ...
... 03. A 0.875-kg solid ball is tied to a string and rotated in a circle of radius 0.925 m. A force of air resistance of 0.0245 N acts as the ball rotates. a.) What is the moment of inertia of the ball? b.) What torque must be applied to the ball to keep it rotating at a constant angular velocity? 04. ...
AP Physics Daily Problem #30
... A 4wd all terrain vehicle of mass 500kg approaches a 45 degree hill at 10m/s. The tires of the vehicle have a k of 0.70. The vehicle’s powerful engine spins its wheels in a forward direction at all times. Determine the acceleration of the vehicle after it starts up the slope ...
... A 4wd all terrain vehicle of mass 500kg approaches a 45 degree hill at 10m/s. The tires of the vehicle have a k of 0.70. The vehicle’s powerful engine spins its wheels in a forward direction at all times. Determine the acceleration of the vehicle after it starts up the slope ...
Slides
... speed v. If the same force acts for the same time on a different mass 2M, what would be the final speed of the bigger mass? ...
... speed v. If the same force acts for the same time on a different mass 2M, what would be the final speed of the bigger mass? ...
15.4 outline phy sci
... you apply the force, the force you apply ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. If you were using this lever to lif ...
... you apply the force, the force you apply ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. If you were using this lever to lif ...
Name of Model
... a. Draw a force diagram for Tarzan. Be sure to break angled forces into components and indicate which forces are equal with equality marks. ...
... a. Draw a force diagram for Tarzan. Be sure to break angled forces into components and indicate which forces are equal with equality marks. ...
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... forces are balanced. The first law - sometimes referred to as the "law of inertia" states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to ...
... forces are balanced. The first law - sometimes referred to as the "law of inertia" states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to ...
TAKS Physics Review (Objective 5)
... When one tuning fork is sounded, the second tuning fork is energized by the specific frequencies emitted by the first, and begins to vibrate and sound as well! ...
... When one tuning fork is sounded, the second tuning fork is energized by the specific frequencies emitted by the first, and begins to vibrate and sound as well! ...
Force and Motion
... Mass and weight are two different quantities Weight is equal to the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the object ...
... Mass and weight are two different quantities Weight is equal to the magnitude of the gravitational force exerted on the object ...
Unit 8 force - Kowenscience.com
... Friction The force that opposes the motion of an object, It is a force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. Friction acts in the direction opposite to motion. and is the force that brings an object to rest Without friction or other unbalanced forces, an object will ...
... Friction The force that opposes the motion of an object, It is a force that two surfaces exert on each other when they rub against each other. Friction acts in the direction opposite to motion. and is the force that brings an object to rest Without friction or other unbalanced forces, an object will ...
Single Point of Contact Manipulation of Unknown Objects
... – Caveat: assume we take observations frequently enough that the forces applied to the object remain about constant. We can stop looking when bad stuff (impact) happens. – So we need to predict the acceleration based on state and force applied. – In general, we can’t get an explicit answer to this q ...
... – Caveat: assume we take observations frequently enough that the forces applied to the object remain about constant. We can stop looking when bad stuff (impact) happens. – So we need to predict the acceleration based on state and force applied. – In general, we can’t get an explicit answer to this q ...
Newton`s 2 nd Law of Motion
... object will remain at rest or in motion with constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force. An external force is a force applied to the object from some other object. force from an impact, gravity, air resistance, etc. ...
... object will remain at rest or in motion with constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force. An external force is a force applied to the object from some other object. force from an impact, gravity, air resistance, etc. ...