Chapter 4
... Strong nuclear force – attractive force that binds quarks to form protons & neutrons (strongest force) Electromagnetic force – binding atoms and molecules to each other Weak nuclear force – binding force between protons and neutrons Gravity- attractive force between masses (weakest of all types of f ...
... Strong nuclear force – attractive force that binds quarks to form protons & neutrons (strongest force) Electromagnetic force – binding atoms and molecules to each other Weak nuclear force – binding force between protons and neutrons Gravity- attractive force between masses (weakest of all types of f ...
Speed and Acceleration
... A skydiver accelerates from 20 m/s to 40 m/s in 2 seconds. What is the skydiver’s average acceleration? ...
... A skydiver accelerates from 20 m/s to 40 m/s in 2 seconds. What is the skydiver’s average acceleration? ...
Document
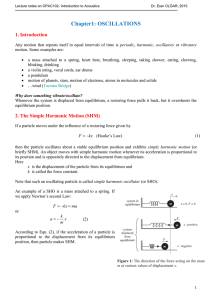
... stopped and jerked backwards when it is started.) - mass of a body is a measure of its inertia which shows reluctance in changing its state of rest or motion. Mass under such consideration is called inertial mass. c) Newton’s second law It states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is prop ...
... stopped and jerked backwards when it is started.) - mass of a body is a measure of its inertia which shows reluctance in changing its state of rest or motion. Mass under such consideration is called inertial mass. c) Newton’s second law It states that the rate of change of momentum of a body is prop ...
3rd Six Weeks Review
... b) slow down c) change direction a) It increases the force that we apply to a task. b) example: we pull down on a pulley and this makes the object easier to lift (uses less effort on our part) we apply. Rather than pulling up, we pull down. This makes it easier to lift an object. b) examples: A pull ...
... b) slow down c) change direction a) It increases the force that we apply to a task. b) example: we pull down on a pulley and this makes the object easier to lift (uses less effort on our part) we apply. Rather than pulling up, we pull down. This makes it easier to lift an object. b) examples: A pull ...
Newton`s Second Law - Dallastown Area School District Moodle
... the gates. To do this, enter an “=”sign in the formula window. Enter the formula to the right of this sign, and press enter when finished. To enter the contents of cell A3, for instance, you may either click on cell A3 or type “A3.” Either way, “A3” will appear in the formula window. For example, to ...
... the gates. To do this, enter an “=”sign in the formula window. Enter the formula to the right of this sign, and press enter when finished. To enter the contents of cell A3, for instance, you may either click on cell A3 or type “A3.” Either way, “A3” will appear in the formula window. For example, to ...
University Physics AI No. 4 The Gravitational Force and the
... and Neptune) possess nearly circular surrounding rings, perhaps composed of material that failed to form a satellite. dM m x In addition, many galaxies contain ring-like structures. θ R Consider a homogeneous ring of mass M and radius R. (a) x Find an expression for the gravitational force exerted b ...
... and Neptune) possess nearly circular surrounding rings, perhaps composed of material that failed to form a satellite. dM m x In addition, many galaxies contain ring-like structures. θ R Consider a homogeneous ring of mass M and radius R. (a) x Find an expression for the gravitational force exerted b ...
Dynamics Introduction to Forces Fundamental Forces
... Inertia: Inertia is the natural tendency of an object to remain in its current state of motion. The amount of an object’s inertia is directly related to its mass. Mass: The quantity of matter an object contains. (A.K.A. The amount of stuff in an object) Gravitational influence: the property of matte ...
... Inertia: Inertia is the natural tendency of an object to remain in its current state of motion. The amount of an object’s inertia is directly related to its mass. Mass: The quantity of matter an object contains. (A.K.A. The amount of stuff in an object) Gravitational influence: the property of matte ...
Motion, Force, Gravity, Projectile Motion and Friction NYS Standards
... 5.1a The motion of an object is always judged with respect to some other object or point. The idea of absolute motion or rest is misleading. 5.1b The motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and speed. 5.1c An objects motion is the result of the combined effect of a ...
... 5.1a The motion of an object is always judged with respect to some other object or point. The idea of absolute motion or rest is misleading. 5.1b The motion of an object can be described by its position, direction of motion, and speed. 5.1c An objects motion is the result of the combined effect of a ...
L14_RigidBody
... Center of Mass Object’s “position” is the position of its center of mass Integration of differential mass times position in object Approximate by summing over representational particles in object ...
... Center of Mass Object’s “position” is the position of its center of mass Integration of differential mass times position in object Approximate by summing over representational particles in object ...