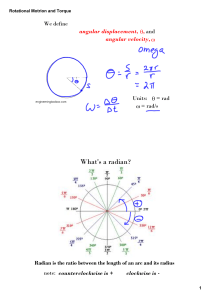
Example 2
... •Neglect air resistance •Consider motion only after release and before it hits •Analyze the vertical and horizontal components separately (Galileo) •No acceleration in the horizontal, so velocity is constant •Acceleration in the vertical is – 9.8 m/s2 due to gravity and thus velocity is not constant ...
... •Neglect air resistance •Consider motion only after release and before it hits •Analyze the vertical and horizontal components separately (Galileo) •No acceleration in the horizontal, so velocity is constant •Acceleration in the vertical is – 9.8 m/s2 due to gravity and thus velocity is not constant ...
Slide 1
... than wider. A 3N pull is exerted in the upper left corner to the left and a 4N pull is exerted in the lower right corner in the downward direction. What is the magnitude of the force exerted from the person in the upper right corner at what angle relative to the top side of the sheet? Explain all an ...
... than wider. A 3N pull is exerted in the upper left corner to the left and a 4N pull is exerted in the lower right corner in the downward direction. What is the magnitude of the force exerted from the person in the upper right corner at what angle relative to the top side of the sheet? Explain all an ...
IGCSE-12-Forces&Shape
... ___________ or change shape. newtons (N) with a newtonmeter. Force is measured in _______ ...
... ___________ or change shape. newtons (N) with a newtonmeter. Force is measured in _______ ...
Appendix A Glossary
... Internal (sometimes cross-sectional) stress resultants - when a slender body (bar, beam, shaft, strut, truss) is cut by a plane and separated into two parts, the crosssectional resultants could be imagined occurring at the centroid of the cut-face (section) of one part such that the resultants repre ...
... Internal (sometimes cross-sectional) stress resultants - when a slender body (bar, beam, shaft, strut, truss) is cut by a plane and separated into two parts, the crosssectional resultants could be imagined occurring at the centroid of the cut-face (section) of one part such that the resultants repre ...
Make Up Lab: Newtonian Gravity
... him on the head, but it is true that Newton was able to figure out why the apple fell, as well as why the planets stay in their orbits. The idea of an action-at-a-distance force (as opposed to a contact force) was a significant scientific advancement. In most situations Newton’s Law of Gravitation ( ...
... him on the head, but it is true that Newton was able to figure out why the apple fell, as well as why the planets stay in their orbits. The idea of an action-at-a-distance force (as opposed to a contact force) was a significant scientific advancement. In most situations Newton’s Law of Gravitation ( ...
WD013-013.17_DU Engineering of Extreme
... Need for differentials and/or steering linkages = Steering = Driven ...
... Need for differentials and/or steering linkages = Steering = Driven ...
5, 6, 10, 13, 14, 18, 23 / 5, 7, 16, 23, 31, 34, 39, 43, 45
... internal. These pulling forces, therefore, do not create a net external torque, and the angular momentum of the system is conserved. In other words, it remains constant. We will use the conservation of angular momentum to obtain a relationship between the initial and final angular speeds. Then, we w ...
... internal. These pulling forces, therefore, do not create a net external torque, and the angular momentum of the system is conserved. In other words, it remains constant. We will use the conservation of angular momentum to obtain a relationship between the initial and final angular speeds. Then, we w ...
chapter 5 - Portal UniMAP
... When a rigid body is subjected to a system of forces and couple moments, it is often simpler to study the external effects on the body by replacing the system by an equivalent single resultant force acting at a specified point O and a resultant couple moment. Referring to the Figure (c)i, Since poin ...
... When a rigid body is subjected to a system of forces and couple moments, it is often simpler to study the external effects on the body by replacing the system by an equivalent single resultant force acting at a specified point O and a resultant couple moment. Referring to the Figure (c)i, Since poin ...
Momentum and Impulse MC practice problems
... 59. If one knows only the constant resultant force acting on an object and the time during which this force acts, one can determine the (A) change in momentum of the object (B) change in velocity of the object (C) change in kinetic energy of the object (D) mass of the object (E) acceleration of the ...
... 59. If one knows only the constant resultant force acting on an object and the time during which this force acts, one can determine the (A) change in momentum of the object (B) change in velocity of the object (C) change in kinetic energy of the object (D) mass of the object (E) acceleration of the ...
Practice test Midterm 2-1_Chapter 7
... The rigid body shown rotates about an axis through its center of mass and perpendicular to the paper. If M = 2.0 kg and L = 80 cm, what is the kinetic energy of this object when its angular speed about this axis is equal to 5.0 rad/s? Neglect the mass of the connecting rod and treat the masses as pa ...
... The rigid body shown rotates about an axis through its center of mass and perpendicular to the paper. If M = 2.0 kg and L = 80 cm, what is the kinetic energy of this object when its angular speed about this axis is equal to 5.0 rad/s? Neglect the mass of the connecting rod and treat the masses as pa ...