Ch. 12 Notes - leavellphysicalscience
... **Net force is not zero with action reaction forces. b/c action and reaction forces do not act on the same object (swimmer in water) Only when equal and opposite forces act on the same object do they result in a net force of 0. ...
... **Net force is not zero with action reaction forces. b/c action and reaction forces do not act on the same object (swimmer in water) Only when equal and opposite forces act on the same object do they result in a net force of 0. ...
Scalar and Vector Fields - METU | Department of Mechanical
... Scalar and Vector Fields Scalar: A geometrical or physical quantity that can completely be characterized by a single number. • For example: length of a bar, mass of an object, electrical resistivity of a metal, viscosity of a fluid, temperature of an object, pressure at a point, etc. Vector: A physi ...
... Scalar and Vector Fields Scalar: A geometrical or physical quantity that can completely be characterized by a single number. • For example: length of a bar, mass of an object, electrical resistivity of a metal, viscosity of a fluid, temperature of an object, pressure at a point, etc. Vector: A physi ...
momentum
... Impulse Newton’s second law of motion, F = ma, can be rewritten by using the definition of acceleration as the change in velocity divided by the time needed to make that change. It can be represented by the following equation ...
... Impulse Newton’s second law of motion, F = ma, can be rewritten by using the definition of acceleration as the change in velocity divided by the time needed to make that change. It can be represented by the following equation ...
Slides
... The wrench is hung freely from two different pivots The intersection of the lines indicates the center of gravity A rigid object can be balanced by a single force equal in magnitude to its weight as long as the force is acting upward through the object’s center of gravity ...
... The wrench is hung freely from two different pivots The intersection of the lines indicates the center of gravity A rigid object can be balanced by a single force equal in magnitude to its weight as long as the force is acting upward through the object’s center of gravity ...
Lecture13
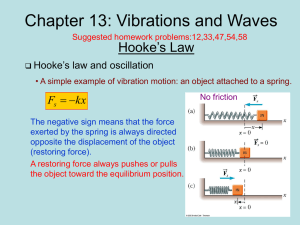
... Frequency is how many complete rotations/cycles a simple harmonic oscillation or uniform circular motion makes per unit time. ...
... Frequency is how many complete rotations/cycles a simple harmonic oscillation or uniform circular motion makes per unit time. ...
Chapter 4-4
... • Weight is the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on an object. • Weight = Fg • Fg = mass x gravity ...
... • Weight is the magnitude of the force of gravity acting on an object. • Weight = Fg • Fg = mass x gravity ...
WORK AND ENERGY
... Make a data table just for you! Record you weight in lbs and Newtons. (1 lb= 4.45 N) Calculate the distance you will travel (25 steps, each step .16 m) record With the help of a partner, time yourself walking, running and jumping UP the stairs- record Calculate the Work done for each trial (W = F x ...
... Make a data table just for you! Record you weight in lbs and Newtons. (1 lb= 4.45 N) Calculate the distance you will travel (25 steps, each step .16 m) record With the help of a partner, time yourself walking, running and jumping UP the stairs- record Calculate the Work done for each trial (W = F x ...
4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... of Motion Newton’s first law is called the law of inertia: In the absence of an unbalanced applied force (Fnet = 0), a body at rest remains at rest, and a body already in motion remains in motion with a constant velocity (constant speed and direction). The bottom line: There is NO ACCELERATION in th ...
... of Motion Newton’s first law is called the law of inertia: In the absence of an unbalanced applied force (Fnet = 0), a body at rest remains at rest, and a body already in motion remains in motion with a constant velocity (constant speed and direction). The bottom line: There is NO ACCELERATION in th ...
Current_Classes_files/HW Chpt 9 Lin Momentm
... an angle of 30° from the x-axis and object B has a mass of 1.9 kg and has a velocity v B of 6.2 m/s at an angle of 72° from the x-axis. What is the total momentum of the system? 32) A 0.250-kg rubber ball is dropped from a height of 2.00 m. It hits the floor and rebounds to a height of 1.80 m. What ...
... an angle of 30° from the x-axis and object B has a mass of 1.9 kg and has a velocity v B of 6.2 m/s at an angle of 72° from the x-axis. What is the total momentum of the system? 32) A 0.250-kg rubber ball is dropped from a height of 2.00 m. It hits the floor and rebounds to a height of 1.80 m. What ...
Modified True/False
... Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. 1. The normal force force ...
... Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the sentence or statement true. 1. The normal force force ...
The Science of Spaceflight - FMA Live!
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion says that force equals mass times acceleration. Force is a push or pull. Mass is the substance that makes up an object, and acceleration is a change in motion. How hard do you have to push or pull on something to make it move? It depends on the mass of the object. Demon ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion says that force equals mass times acceleration. Force is a push or pull. Mass is the substance that makes up an object, and acceleration is a change in motion. How hard do you have to push or pull on something to make it move? It depends on the mass of the object. Demon ...