Lecture01 - Lcgui.net
... -Questions and Problems: 1 and 2 on page 17 1. Provide definitions for the following measureable flow properties: angular momentum, entropy, thermal conductivity, molecular diffusivity, and surface tension. 2. List the established names for the SI units of force, pressure, energy, and power and thei ...
... -Questions and Problems: 1 and 2 on page 17 1. Provide definitions for the following measureable flow properties: angular momentum, entropy, thermal conductivity, molecular diffusivity, and surface tension. 2. List the established names for the SI units of force, pressure, energy, and power and thei ...
+ T - Purdue Physics
... – An arrow starting at the initial position (the tip of the initial position vector) and ending with the arrowhead at the final position (the tip of the final position vector) – The path of an object does not matter. The displacement d depends d only l on th the starting t ti and d ending di points. ...
... – An arrow starting at the initial position (the tip of the initial position vector) and ending with the arrowhead at the final position (the tip of the final position vector) – The path of an object does not matter. The displacement d depends d only l on th the starting t ti and d ending di points. ...
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
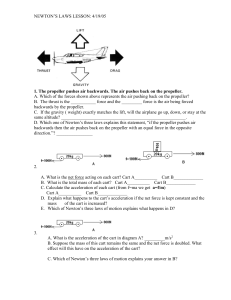
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
Unit 2
... amount of gravity acting on an object - To lift an object on Earth you must over come the gravity pulling on it, you must lift with a force equal to or greater than its weight ...
... amount of gravity acting on an object - To lift an object on Earth you must over come the gravity pulling on it, you must lift with a force equal to or greater than its weight ...
Day 9 Lecture
... First of all note that, depending upon the size of the black hole, an infalling observer may not experience any unpleasant side effects. You may wonder how does Bob head and feet communicate once inside of the horizon. Note that although a nerve signal may not climb any further distance from the sin ...
... First of all note that, depending upon the size of the black hole, an infalling observer may not experience any unpleasant side effects. You may wonder how does Bob head and feet communicate once inside of the horizon. Note that although a nerve signal may not climb any further distance from the sin ...
Work-Energy Principle
... Figure 6: Free body diagram of vehicle falling along curve. The two forces on the vehicle are the normal force, N , and the force due to gravity mg. Figure by MIT OCW. ...
... Figure 6: Free body diagram of vehicle falling along curve. The two forces on the vehicle are the normal force, N , and the force due to gravity mg. Figure by MIT OCW. ...
Connected Particles and Newton`s 3rd Law
... ( provided the forces remain constant ). We can use the equations of motion for constant acceleration to find, for example, the velocity when the time or displacement is given. ...
... ( provided the forces remain constant ). We can use the equations of motion for constant acceleration to find, for example, the velocity when the time or displacement is given. ...
10 Friction File
... Friction is a very common and sometimes troublesome force that is a result of two surfaces in contact with each other. Friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object. If the object is at rest, the force of friction opposing the start of motion is called static friction. If the object is mo ...
... Friction is a very common and sometimes troublesome force that is a result of two surfaces in contact with each other. Friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object. If the object is at rest, the force of friction opposing the start of motion is called static friction. If the object is mo ...
forces and motion notes
... • Two Motions Combine to Cause Orbiting An object is orbiting when it is traveling around another object in space.When a spacecraft orbits Earth, it is moving forward. But the spacecraft is also in free fall toward Earth. • Orbiting and Centripetal Force The unbalanced force that causes objects to m ...
... • Two Motions Combine to Cause Orbiting An object is orbiting when it is traveling around another object in space.When a spacecraft orbits Earth, it is moving forward. But the spacecraft is also in free fall toward Earth. • Orbiting and Centripetal Force The unbalanced force that causes objects to m ...
Doris williams - HCC Learning Web
... In general, friction is the force that slows down the motion of an object. The force of friction is directed along the surface of contact between the object and surface and directed opposite to the direction of motion of object. We deal with: a) Static friction ( fs) This exists when the object is a ...
... In general, friction is the force that slows down the motion of an object. The force of friction is directed along the surface of contact between the object and surface and directed opposite to the direction of motion of object. We deal with: a) Static friction ( fs) This exists when the object is a ...
aguilar (fa6754) – hk7 – opyrchal – (11106)
... is the force of gravity, since the force of tension is always perpendicular to each element of the displacement and hence does no work. Since the force of gravity is a conservative force, the total mechanical energy is constant. Therefore, as the pendulum swings, there is a continuous transfer betwe ...
... is the force of gravity, since the force of tension is always perpendicular to each element of the displacement and hence does no work. Since the force of gravity is a conservative force, the total mechanical energy is constant. Therefore, as the pendulum swings, there is a continuous transfer betwe ...
Chapter 4 Slides
... • To learn to make free-body diagrams Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... • To learn to make free-body diagrams Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
6-6 Conservative Forces and Potential Energy
... convenient level to be the reference level. EXPLORATION 6.6B – Talking about potential energy A 10-N ball is moved by some path from A to B, where B is 2 m lower than A. What is the ball’s initial gravitational potential energy? What is its final gravitational potential energy? What is the change in ...
... convenient level to be the reference level. EXPLORATION 6.6B – Talking about potential energy A 10-N ball is moved by some path from A to B, where B is 2 m lower than A. What is the ball’s initial gravitational potential energy? What is its final gravitational potential energy? What is the change in ...
LAB A7: KINETIC AND STATIC FRICTION
... method involves placing a box on a horizontal ramp and slowly increasing the ramp’s angle of inclination to the horizontal until the box just begins to slide. The largest angle at which the box does not slide is called the critical angle, c. PRELAB a): Following the usual force problem procedure, f ...
... method involves placing a box on a horizontal ramp and slowly increasing the ramp’s angle of inclination to the horizontal until the box just begins to slide. The largest angle at which the box does not slide is called the critical angle, c. PRELAB a): Following the usual force problem procedure, f ...
Notes
... 29. The Earth's gravity exerts no torque on a satellite orbiting the Earth in an elliptical orbit. Compare the motion at the point nearest the Earth (perigee) to the motion at the point farthest from the Earth (apogee). At the point closest to the Earth a. the angular velocity will be greatest altho ...
... 29. The Earth's gravity exerts no torque on a satellite orbiting the Earth in an elliptical orbit. Compare the motion at the point nearest the Earth (perigee) to the motion at the point farthest from the Earth (apogee). At the point closest to the Earth a. the angular velocity will be greatest altho ...