moment of a force
... In these diagrams, the magnitude of the moment is the same, but they are in opposite senses. An anticlockwise moment is generally regarded as positive and a clockwise one as negative. In most situations you have two or more forces, each with its own turning effect. You can combine these to give an o ...
... In these diagrams, the magnitude of the moment is the same, but they are in opposite senses. An anticlockwise moment is generally regarded as positive and a clockwise one as negative. In most situations you have two or more forces, each with its own turning effect. You can combine these to give an o ...
Chapter 2: Statics of Particles
... - replacing multiple forces acting on a particle with a single equivalent or resultant force, - relations between forces acting on a particle that is in a state of equilibrium. • The focus on particles does not imply a restriction to miniscule bodies. Rather, the study is restricted to analyses in w ...
... - replacing multiple forces acting on a particle with a single equivalent or resultant force, - relations between forces acting on a particle that is in a state of equilibrium. • The focus on particles does not imply a restriction to miniscule bodies. Rather, the study is restricted to analyses in w ...
Three-Body Problem
... This equilateral triangle solution was discovered by Lagrange. Fig.3 shows the orbits for elliptical motion. ...
... This equilateral triangle solution was discovered by Lagrange. Fig.3 shows the orbits for elliptical motion. ...
Homework #9 Extra credit
... and the rim of the liquid surface is a function of angular velocity , fluid density , gravitational acceleration g, and radius R. Use the method of repeating variables to find a relationship between the parameters. (b) Consider now a transient process where the container was originally at rest and ...
... and the rim of the liquid surface is a function of angular velocity , fluid density , gravitational acceleration g, and radius R. Use the method of repeating variables to find a relationship between the parameters. (b) Consider now a transient process where the container was originally at rest and ...
Chapter 12.1
... When an elevator you are riding in accelerates downward, you may feel lighter for a short time. If you were standing on a scale during the downward acceleration, the scale would show that you weighed less than usual. Your mass would not have changed, nor would the pull of gravity. What would cause t ...
... When an elevator you are riding in accelerates downward, you may feel lighter for a short time. If you were standing on a scale during the downward acceleration, the scale would show that you weighed less than usual. Your mass would not have changed, nor would the pull of gravity. What would cause t ...
Tejas Engineers Academy
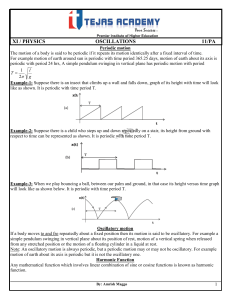
... 22. The motion of a particle executing SHM is described by the displacement function: x(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) If the initial (t=0) position of the particle is 1 cm and its initial velocity is ω cm/s, what are its amplitude and initial phase angle? The angular frequency of the particle is π s-1. If inst ...
... 22. The motion of a particle executing SHM is described by the displacement function: x(t) = A cos(ωt + φ) If the initial (t=0) position of the particle is 1 cm and its initial velocity is ω cm/s, what are its amplitude and initial phase angle? The angular frequency of the particle is π s-1. If inst ...
Chapter 12 Test Study Guide: Simple Machines WORK A force
... Much of the work done on rusty machines is lost due to friction. POWER The rate at which work is done is called power. Power is measured in units called watts. EFFICIENCY An ideal machine would have an efficiency of 100 percent. SIMPLE MACHINES The wedge, screw, and lever are all examples of simple ...
... Much of the work done on rusty machines is lost due to friction. POWER The rate at which work is done is called power. Power is measured in units called watts. EFFICIENCY An ideal machine would have an efficiency of 100 percent. SIMPLE MACHINES The wedge, screw, and lever are all examples of simple ...
printer-friendly sample test questions
... 4. About how long will it take for Sam to travel 5 km at a speed of 4 m/s? A. 2 hours B. 1 hour C. 30 minutes D. 20 minutes 2nd Item Specification: Explain how balanced and unbalanced forces are related to the motion of an object. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 ...
... 4. About how long will it take for Sam to travel 5 km at a speed of 4 m/s? A. 2 hours B. 1 hour C. 30 minutes D. 20 minutes 2nd Item Specification: Explain how balanced and unbalanced forces are related to the motion of an object. Depth Of Knowledge Level 1 ...
Chapter 4 - Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion w./ QuickCheck
... What do forces do? - They cause an object to move, accelerate An object pulled with a constant force experiences a constant acceleration (both pointing in the same direction) Acceleration is directly proportional to the force (F ∝a) Acceleration is inversely proportional to an object’s mass (a ∝ 1/m ...
... What do forces do? - They cause an object to move, accelerate An object pulled with a constant force experiences a constant acceleration (both pointing in the same direction) Acceleration is directly proportional to the force (F ∝a) Acceleration is inversely proportional to an object’s mass (a ∝ 1/m ...
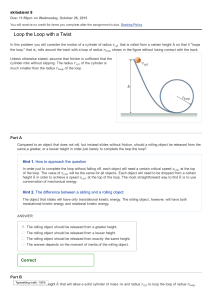
Loop the Loop with a Twist
... ProblemSolving Strategy: Rotational dynamics for rigid bodies IDENTIFY the relevant concepts: In some cases you may be able to use an energy approach. However, if the target variable is a force, a torque, an acceleration, an angular acceleration, or an elapsed time, using Στz = I αz is almost alw ...
... ProblemSolving Strategy: Rotational dynamics for rigid bodies IDENTIFY the relevant concepts: In some cases you may be able to use an energy approach. However, if the target variable is a force, a torque, an acceleration, an angular acceleration, or an elapsed time, using Στz = I αz is almost alw ...
phy_outline_ch04
... motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or the change in the object’s velocity) is zero. ...
... motion continues in motion with constant velocity (that is, constant speed in a straight line) unless the object experiences a net external force. • In other words, when the net external force on an object is zero, the object’s acceleration (or the change in the object’s velocity) is zero. ...
HW 3 - Seattle Central College
... The positively charged rod slightly polarizes the molecules in the paper. The negative charges in the paper are slightly attracted to the part of the paper closest to the rod, while the positive charges in the paper are slightly repelled from the part of the paper closest to the rod. Since the oppos ...
... The positively charged rod slightly polarizes the molecules in the paper. The negative charges in the paper are slightly attracted to the part of the paper closest to the rod, while the positive charges in the paper are slightly repelled from the part of the paper closest to the rod. Since the oppos ...
Section 2 What Is a Force?
... Forces acting on an object can be combined and may cause changes in motion. ...
... Forces acting on an object can be combined and may cause changes in motion. ...